Copy File From Remote To Local Using Scp

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Published: 1/31/2024
The short answer
To copy and download a file from a remote server to your local machine, you can use the scp (secure copy) in the following way:
$ scp <user>@<host>:<source> <destination>
Where:
- user is your username on the remote server.
- host is the IP address or the hostname of the remote server.
- source is the path of the file you want to copy on the remote server.
- destination is the destination path of the file you want to copy on your local machine.
When executing this command, you will be prompted to enter the password of the specified user account on the remote server.
For example, the following command will attempt to copy the index.js file located in the /home/john/app directory on the remote server to your home directory on your local machine using the johndoe account.
$ scp [email protected]:/home/johndoe/app/index.js ~/index.js
Remind yourself of the syntax using AI Command Search
If you’re using Warp as your terminal, you can easily retrieve this command using the Warp AI Command Search feature:
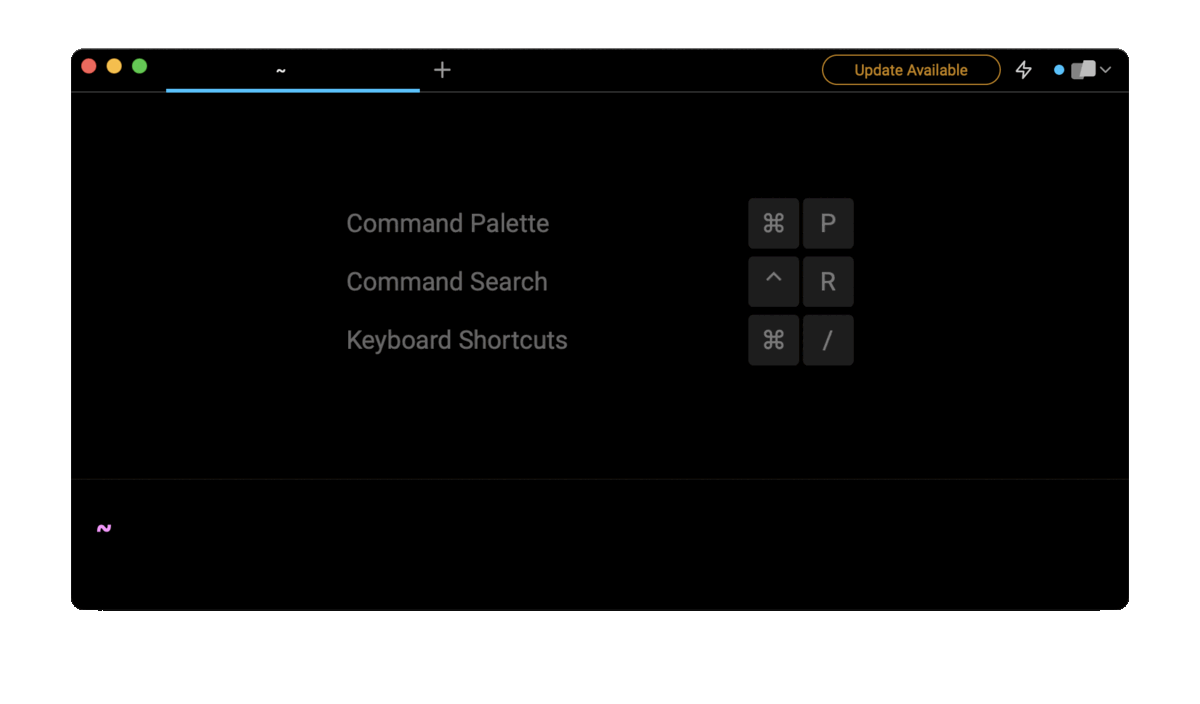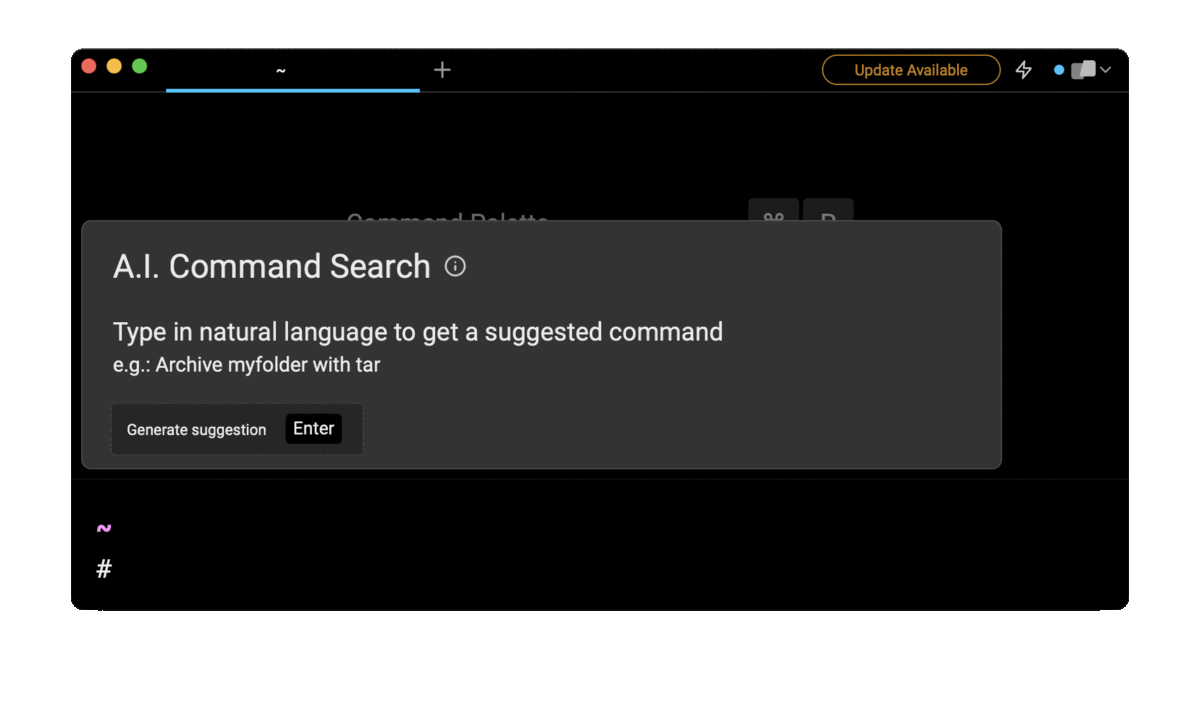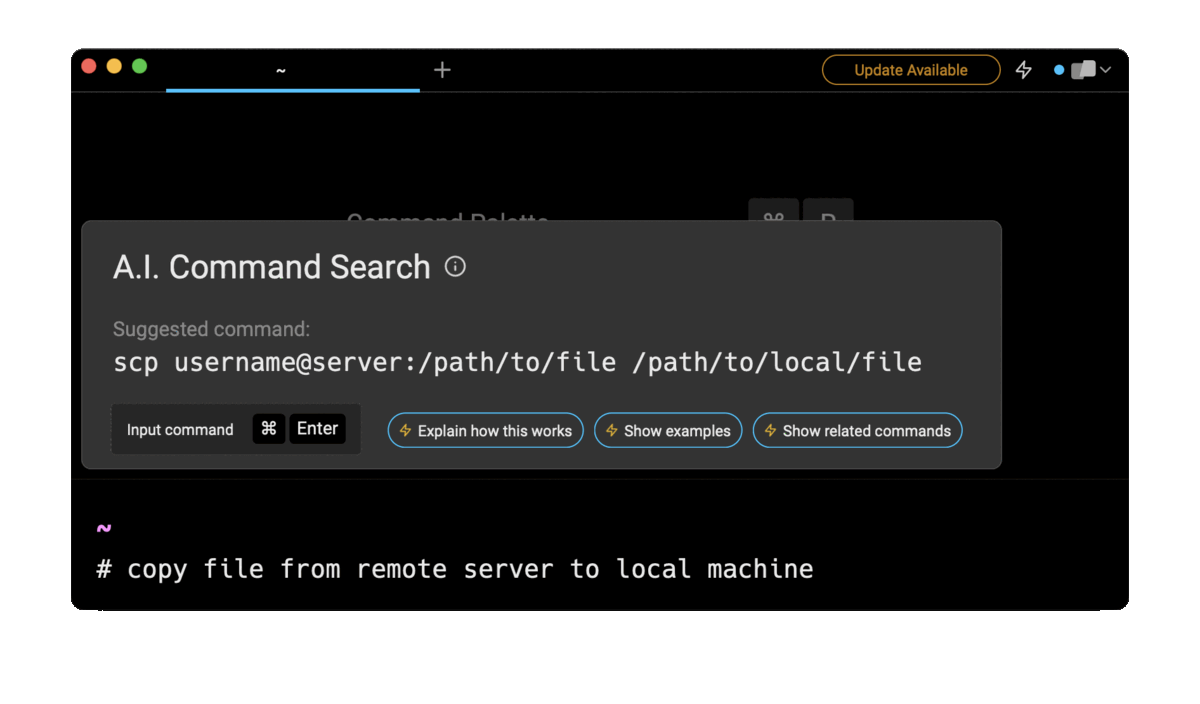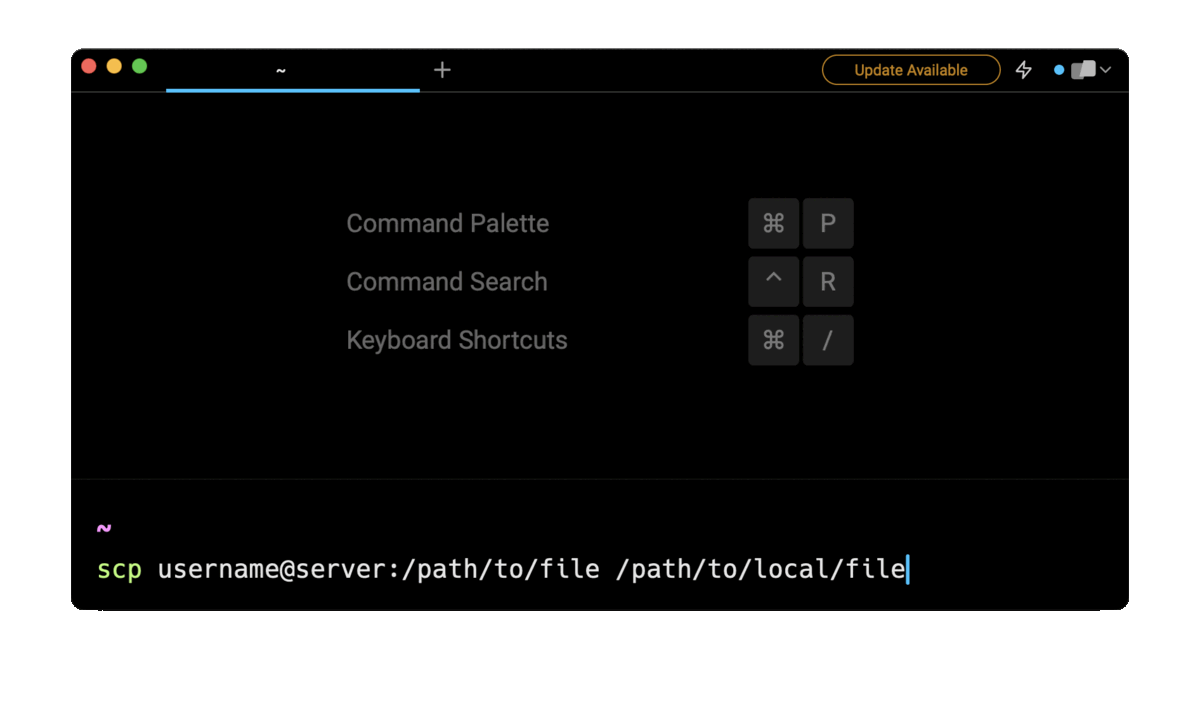
Entering copy file from remote server to local machine in the AI Command Search will suggest you the correct scp command, which you can then quickly insert into your shell by doing CMD+ENTER.
scp multiple files at once
To copy multiple files located in the same directory on the remote server at once, you can either use a wildcard pattern:
$ scp <user>@<host>:/path/to/directory/* /path/to/local/directory
Or a brace expansion:
$ scp <user>@<host>:/path/to/directory/{file_1,file_2}
/path/to/local/directory
scp an entire folder from remote to local
To copy an entire folder and all of its content including subdirectories, you can use the -r flag (short for recursive):
$ scp -r <user>@<host>:/path/to/directory /path/to/local/directory
Note that when using this command, the source directory will be copied from the remote server within the specified destination directory on the local machine.
For example:
$ scp -r [email protected]:/home/johndoe/app ~/Projects
$ ls ~/Projects
app
scp to your local machine while being connected to a remote machine via ssh
Although it is unusual, the scp command can be used to copy files from a remote server to the local machine whilst being connected to the remote server.
To do so, you must first connect to the remote server using the ssh command:
$ ssh <user>@<host>
Where:
- user is your username on the remote server.
- host is the IP address or the hostname of the remote server.
Which will prompt you to enter the password of the specified user account on the remote server.
Once connected, you can use the following syntax:
$ scp /path/to/file ${SSH_CLIENT%% *}:/path/to/local/file
Where:
- ${SSH_CLIENT%% *} will be replaced by the IP address of the client connected to the remote server (i.e. your machine) using a parameter substitution symbolized by the ${} expression.
Note that for this to work, you will need to run an SSH server on your local machine and set up an SSH account in order to allow remote connections.
Written by

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Filed Under
Related Articles
List Open Ports in Linux
Learn how to output the list of open TCP and UDP ports in Linux, as well as their IP addresses and ports using the netstat command.

Count Files in Linux
Learn how to count files and folders contained in directories and subdirectories in Linux using the ls, find, and wc commands.

How to Check the Size of Folders in Linux
Learn how to output the size of directories and subdirectories in a human-readable format in Linux and macOS using the du command.

Linux Chmod Command
Understand how to use chmod to change the permissions of files and directories. See examples with various chmod options.

POST JSON Data With Curl
How to send valid HTTP POST requests with JSON data payloads using the curl command and how to avoid common syntax pitfalls. Also, how to solve the HTTP 405 error code.

Format Command Output In Linux
Learn how to filter and format the content of files and the output of commands in Linux using the awk command.
Create Groups In Linux
Learn how to manually and automatically create and list groups in Linux.
Switch Users In Linux
Learn how to switch between users, log in as another user, and execute commands as another user in Linux.
Remover Users in Linux
Learn how to remove local and remote user accounts and associated groups and files in Linux using the userdel and deluser commands.
Delete Files In Linux
Learn how to selectively delete files in Linux based on patterns and properties using the rm command.
Find Files In Linux
Learn how to find and filter files in Linux by owner, size, date, type and content using the find command.
Copy Files In Linux
Learn how to safely and recursively copy one or more files locally and remotely in Linux using the cp and scp command.
