The short answer
In Unix-like operating systems such as Linux and macOS, to copy a file into a specific directory, you can use the cp command as follows:
$ cp <source> <destination>
Where:
- source is the path to the file you want to copy.
- destination is the path to the directory you want to copy the file into.
For example, this command will copy the local file named index.js into the local directory named test:
$ cp index.js test
Easily retrieve this command using the Warp’s AI Command Suggestions
If you’re using Warp as your terminal, you can easily retrieve this command using the Warp AI Command Suggestions feature:
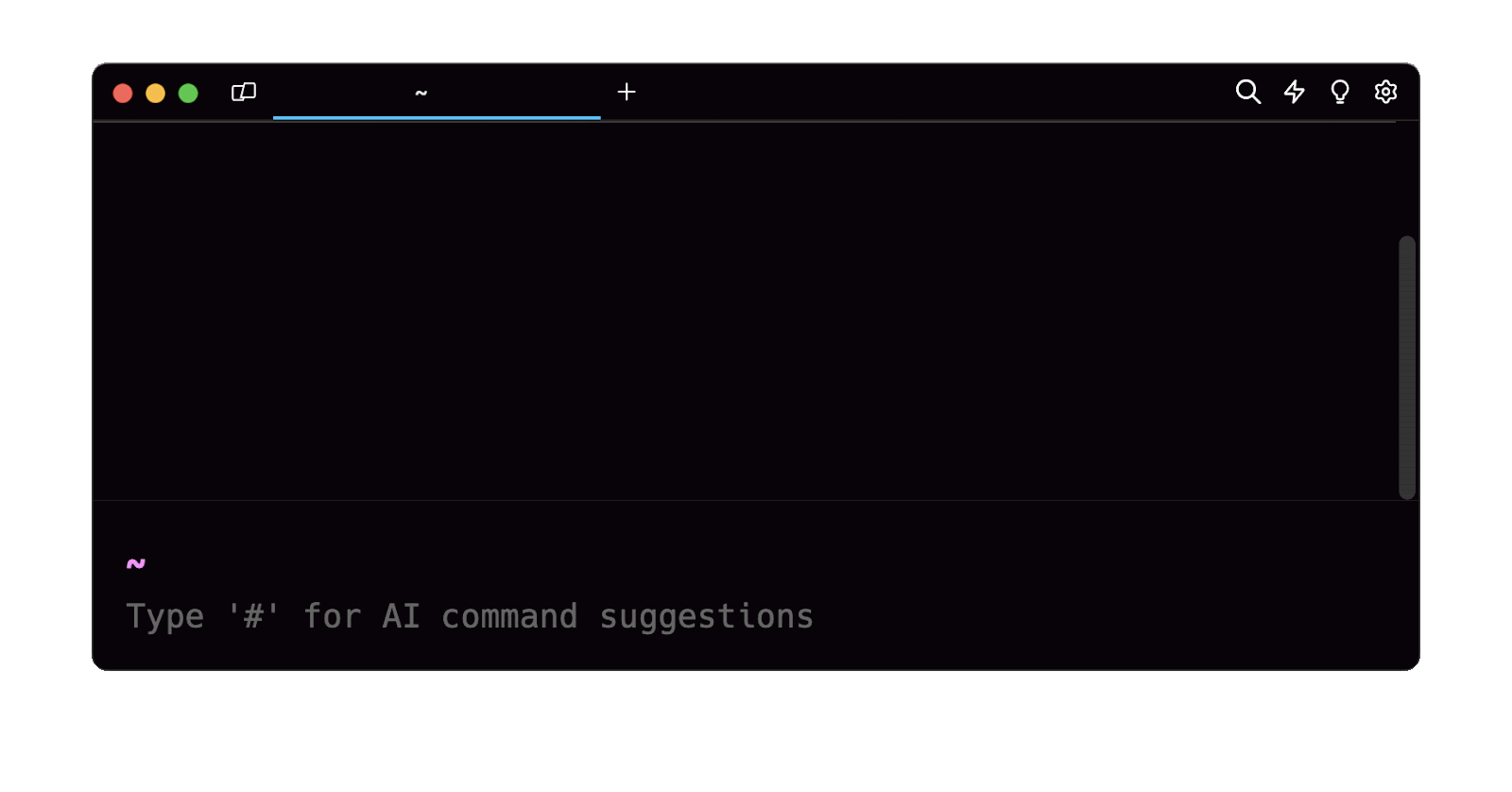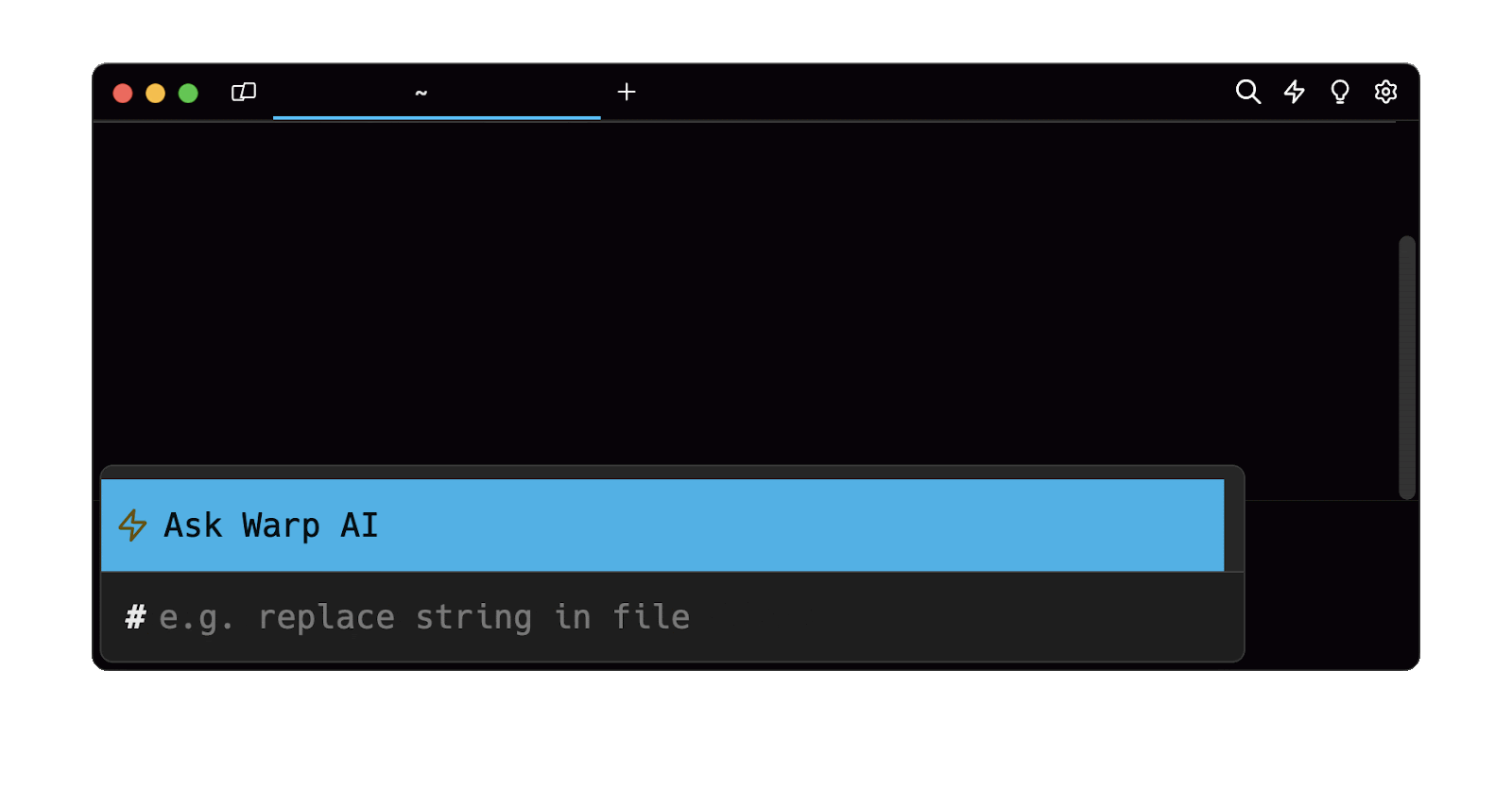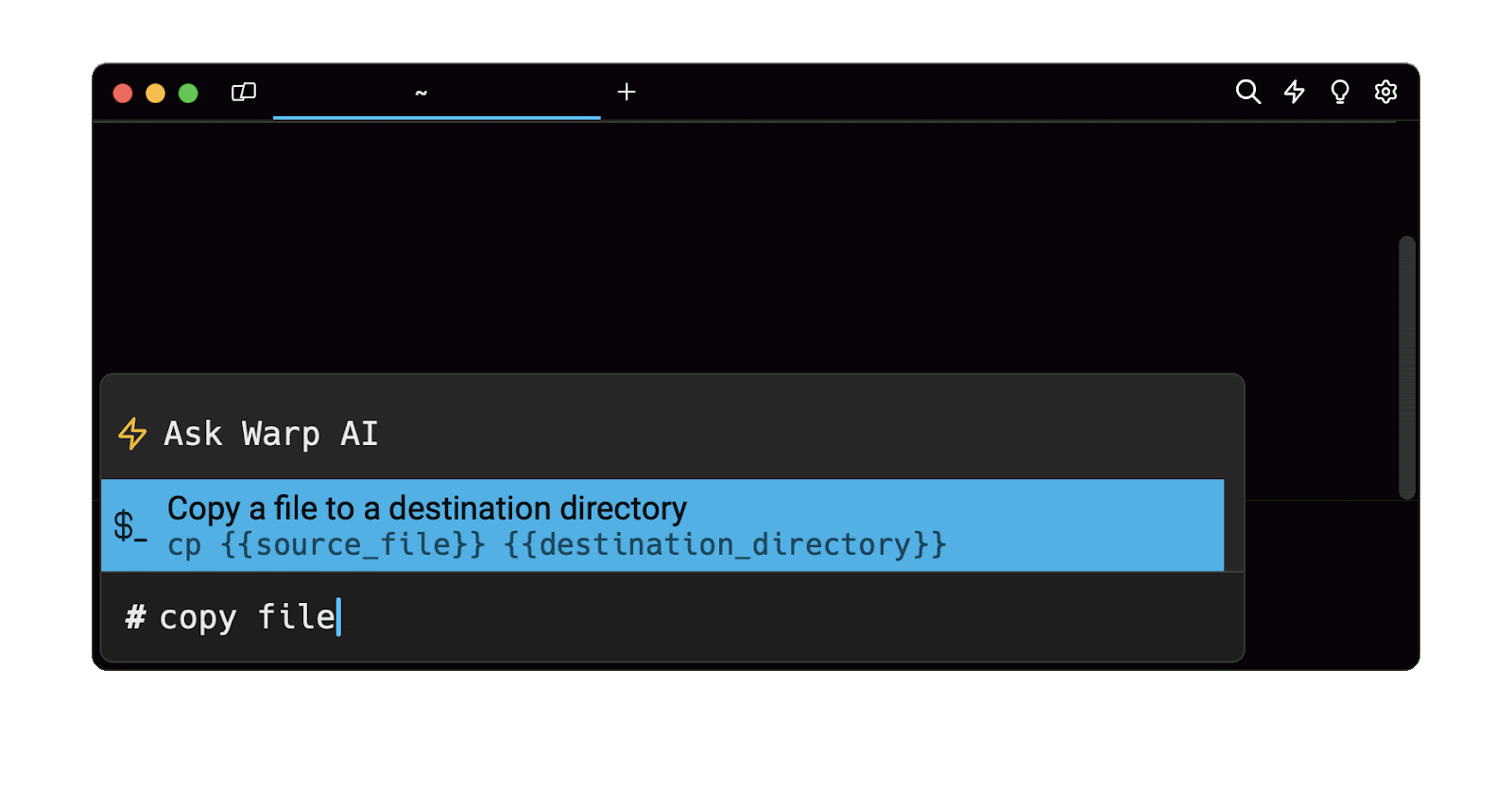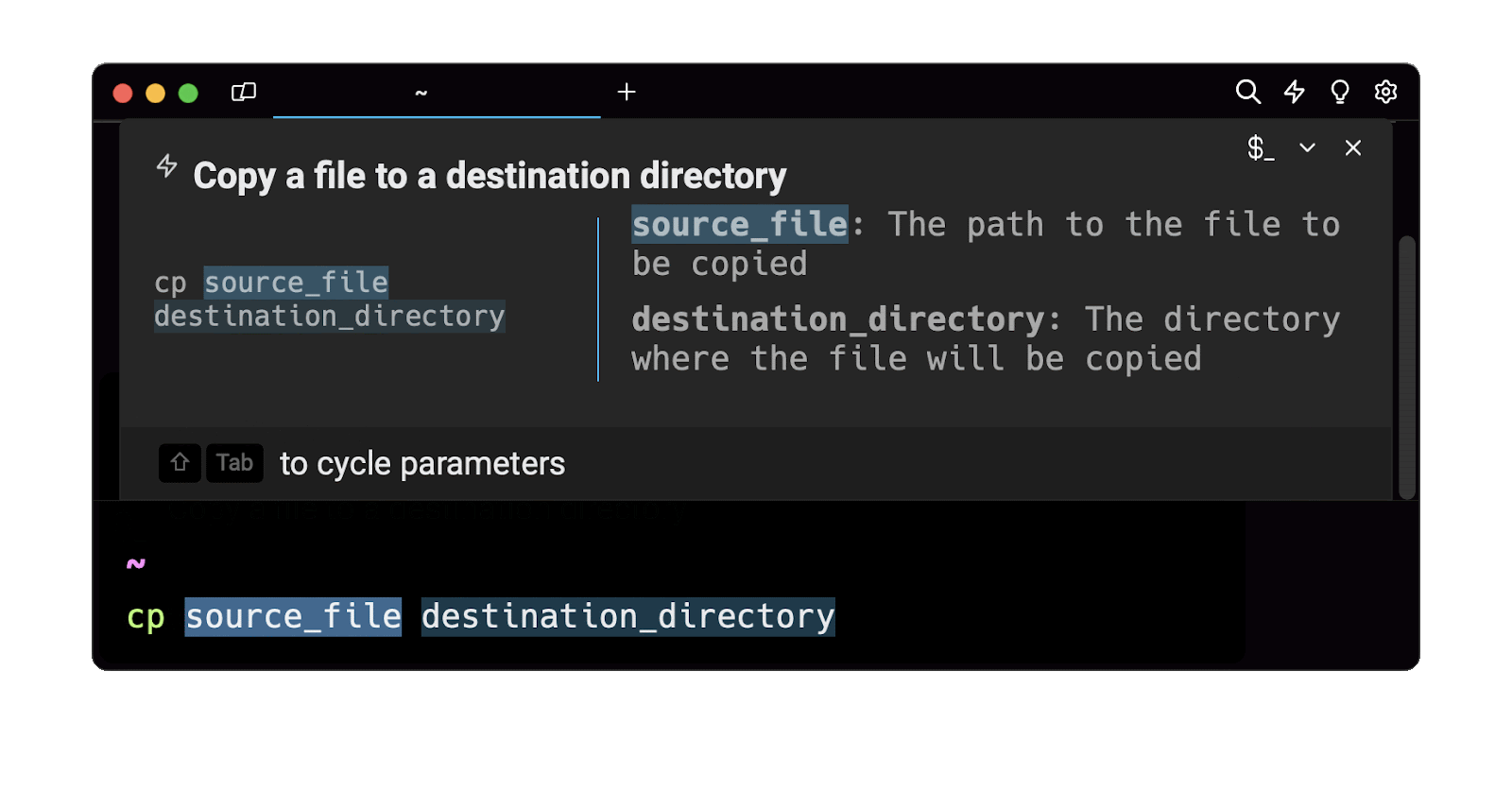
Entering copy file into the AI Command Suggestions will prompt a cp command that can then be quickly inserted into your shell by doing CMD+ENTER.
Copying files into a root directory
To copy files into a directory located outside of your home directory, you will need to gain elevated privileges (i.e., root access) using the sudo command (short for “superuser do") as follows:
$ sudo cp <source> <destination>
Note that when executing this command, you will be prompted to enter your password.
Copying multiple files at once
To copy one or more files at once into another directory, you can use the cp command with the following syntax:
$ cp <source ...> <destination>
Where:
- source ... is a list of paths to the files you want to copy.
- destination is the path to the directory you want to copy the files into.
For example, this command will copy the files named index.js, package.json, and package-lock.json into the directory named website located in the parent directory:
$ cp index.js package.json package-lock.json ../website
Note that you can also use the -v flag (short for *verbose*) to display the list of files that were successfully copied into the destination directory as follows:
$ cp -v <source ...> <destination>
Copying multiple files based on patterns
Additionally, you can use wildcards characters (e.g., *, ?) to copy multiple files based on patterns.
For example, this command will copy all the files with a .csv file extension located in the ~/Downloads directory into the ~/data directory:
$ cp ~/Download/*.csv ~/data
You can learn more about copying files recursively by reading our other article on how to copy a directory in Linux.
Copying and renaming a file
To copy a file into a specific directory under a different name, you can use the cp command as follows:
$ cp <source> <destination>/<filename>
Where:
- <filename> is the new name of the file you want to copy
For example, the following command will copy the file called auth.dev.py into the directory called authenticationand rename it to auth.py:
$ cp auth.dev.py authentication/auth.py
Preventing the overwriting of existing files
By default, the cp command will overwrite the files with the same name as the source files located in the destination directory.
Copying files in interactive mode
To be prompted for confirmation every time a file overlaps with an existing one, you can use the cp command with the -i flag (short for --interactive) as follows:
$ cp -i <source> <destination>
When prompted with this question, you can either type y (short for yes) to confirm the overwriting of the file, or n (short for no) to skip it, and press ENTER to confirm your choice:
cp: overwrite 'file'?
Note that, by default, pressing ENTER directly will be considered as a no for safety reasons.
Silently skipping overlapping files
To silently skip the copy of overlapping files without being prompted, you can use the cp command with the -n flag (short for --no-clobber) as follows:
$ cp -n <source> <destination>
Preserving attributes while copying files
By default, the cp command doesn't preserve file attributes such as permissions or timestamps.
To preserve the file permissions, ownership, and timestamps, you can use the cp command with the -p flag as follows:
$ cp -p <source> <destination>
Alternatively, you can selectively preserve specific attributes using the --preserve flag as follows:
$ cp --preserve=<attributes> <source> <destination>
Where:
- attributes is a comma-separated list of attributes.
For example, this command will copy the script.sh file into the scripts directory while preserving the permissions and ownership:
$ cp --preserve=mode,ownership script.sh scripts
Copying a file to multiple directories at once
To copy the same file into multiple directories at once, you can use a Bash script as follows:
#!/bin/bash
# Define the file to copy
source_file="<source_file>"
# List of destination directories
destination_directories=("<dir1>" ... "<dirN>")
# Loop through each destination directory
for dir in "${destination_directories[@]}"
do
# Copy the file to the current destination directory
cp "$source_file" "$dir"
done
Where:
- "<source_file>" is the path to the file you want to copy (e.g., "package.json").
- "<dir1>" ... "<dirN>" is the list of paths to the directories you want to copy the file into (e.g., "
/projects/app" "/projects/website").
You can then give execution permission to the script using the chmod command as follows:
$ chmod +x copy_to_multiple_dir.sh
Finally, you can run the script using the following command:
$ ./copy_to_multiple_dir.sh
You can learn more about setting file permissions by reading our other article on how to use the chmod command in Linux.
Copying the content of a file to the clipboard
To copy the content of a file to the clipboard, you can use the xclip command as follows:
$ xclip -selection clipboard < <source>
Where:
- -selection clipboard is used to specify that the copied content should be stored in the clipboard.
For example, this command will copy the content of the file named usernames.txt into the clipboard:
$ xclip -selection clipboard < data/users/usernames.txt
Copying files from and to a USB drive
To copy files from or to a USB drive, you will have to first mount the drive (if not automatically done) to an existing directory using the mount command:
$ sudo mount /dev/<drive> /mnt/<mount>
Where:
- drive is the name of the USB drive, usually located in the /dev directory.
- mount is the name of the directory the drive will be mounted to, usually located in the /mnt or /media directory.
Then copy the desired file(s) from the drive into the file system of the host (or vice versa):
$ sudo cp /mnt/<mountpoint>/<source> <destination>
And finally, unmount the USB drive using the umount command:
$ sudo umount /mnt/<mountpoint>
For example, these commands will mount the USB drive named sdb1 to the local directory named usb, copy the files located in the scripts directory, and unmount the drive:
$ sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/usb
$ sudo cp /mnt/usb/scripts/* ~/scripts/.
$ sudo umount /dev/sdb1
Copying files over the SSH protocol
To copy a file over SSH from your local machine to a remote server, you can use the scp command as follows:
$ scp <source> <ssh_username>@<ssh_server_ip>:<destination>
Where:
- ssh_username is the username used to authenticate to the remote server.
- ssh_server_ip is the IP address of the remote server
You can learn more about copying files over SSH by reading our other article on [how to copy a file from remote to local using scp] (https://www.warp.dev/terminus/scp-from-remote-to-local).
Copying a file with a symlink
To copy a file with symlink, there are few options you can use to treat them.
To keep their properties as symlink, you would use the following options:
- -P or --preserve=links which preserves the symbolic link by copying them as link. This further maintains the properties of the symbolic link
To dereference symbolic links and copy the files they point to, you can use the option:
- -L or --dereference which instructs the cp command to follow the symbolic link and copy the actual files they reference.
Written by
Durojaye Olusegun
Filed Under
Related Articles
List Open Ports in Linux
Learn how to output the list of open TCP and UDP ports in Linux, as well as their IP addresses and ports using the netstat command.

Count Files in Linux
Learn how to count files and folders contained in directories and subdirectories in Linux using the ls, find, and wc commands.

How to Check the Size of Folders in Linux
Learn how to output the size of directories and subdirectories in a human-readable format in Linux and macOS using the du command.

Linux Chmod Command
Understand how to use chmod to change the permissions of files and directories. See examples with various chmod options.

POST JSON Data With Curl
How to send valid HTTP POST requests with JSON data payloads using the curl command and how to avoid common syntax pitfalls. Also, how to solve the HTTP 405 error code.

Format Command Output In Linux
Learn how to filter and format the content of files and the output of commands in Linux using the awk command.
Create Groups In Linux
Learn how to manually and automatically create and list groups in Linux.
Switch Users In Linux
Learn how to switch between users, log in as another user, and execute commands as another user in Linux.
Remover Users in Linux
Learn how to remove local and remote user accounts and associated groups and files in Linux using the userdel and deluser commands.
Delete Files In Linux
Learn how to selectively delete files in Linux based on patterns and properties using the rm command.
Find Files In Linux
Learn how to find and filter files in Linux by owner, size, date, type and content using the find command.
Create Files In Linux
Learn how to create regular files in Linux using command line interface commands like touch, echo, cat, printf, and in-terminal text editors like Vim.
