Removing Directories in Linux

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Published: 1/31/2024
On Linux and Unix-like operating systems, including Ubuntu and MacOS, directories can be removed and deleted using either the rm or rmdir bash commands.
The short answer
To remove an entire directory or folder, including the files and subdirectories it contains, you can use the rm command with the -r flag (short for recursive):
$ rm -r directory
Remind yourself of the syntax using AI Command Search
If you’re using Warp as your terminal, you can easily retrieve this command using the Warp AI Command Search feature:
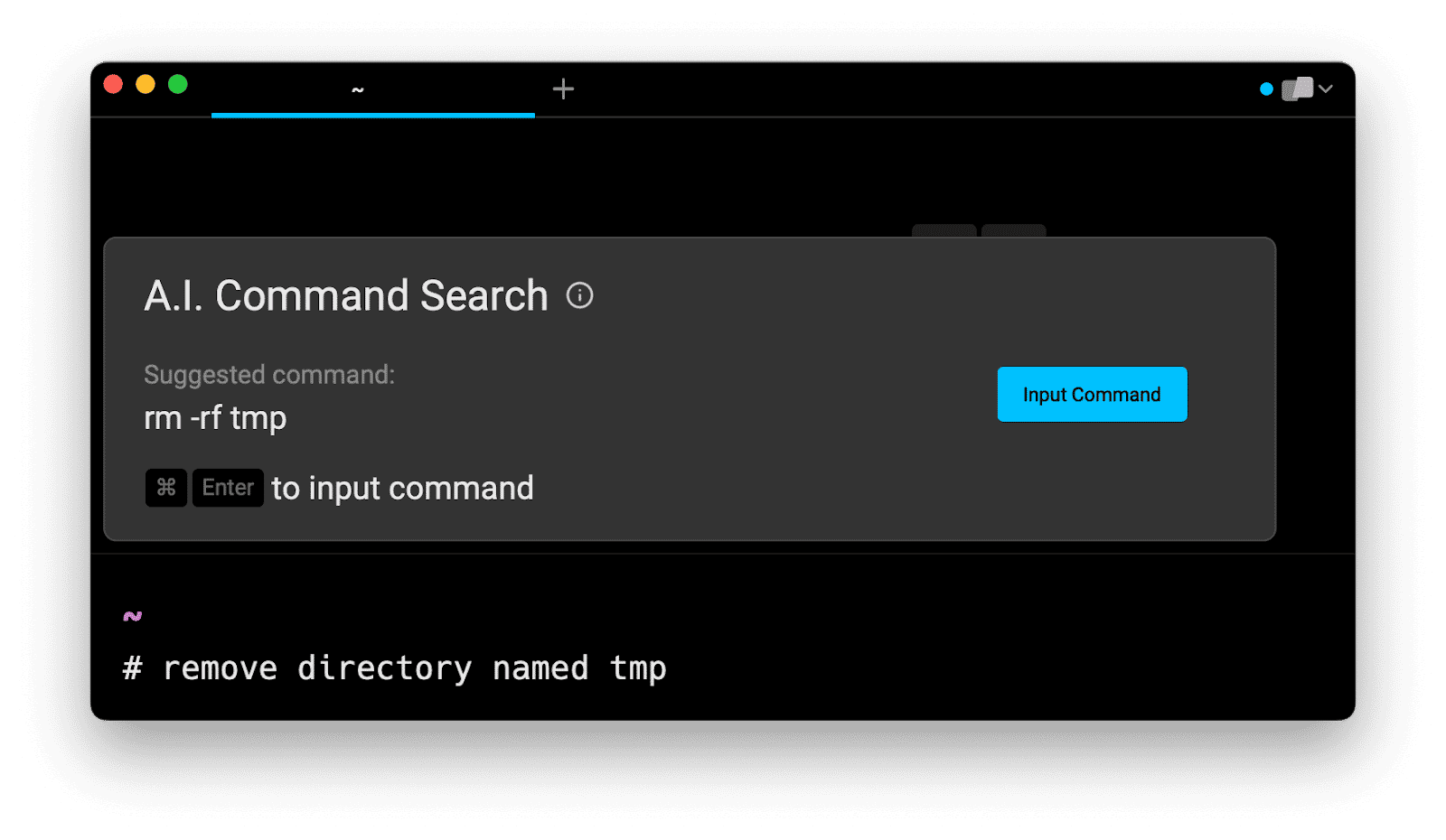
Entering remove directory in the AI Command Search prompt results in rm -rf directory, which you can then quickly insert into your shell by doing CMD+ENTER.
Forcing the removal of directories with rm -f
When trying to remove a read-only directory (write permission not set), the rm command will produce the following error message:
$ rm -r tmp
rm: cannot remove 'tmp': Permission denied
To bypass this behavior, you can either change its permissions using the chmod command, or you can use the -f flag (short for force) in combination with the -r flag, which will remove it without prompting you for confirmation.
$ rm -rf directory
Note that in case the directory belongs to another user, you'll have to use the sudo command to gain elevated privileges in order to remove it.
$ sudo rm -rf directory
Also note that this command is potentially harmful to the operating system and must be used with extreme caution. As a rule of thumb, never use this command on directories that begin with a slash (/) or that include wildcards (*) in their path.
Safely removing directories with rm
Unlike when removing files and directories using the graphical interface, the rm command doesn't move the selected entries into the trash, but immediately and irreversibly erases them from the disk.
Removing directories in interactive mode
One option for safely removing directories, is to use the -i flag (short for interactive), which will prompt you for confirmation before attempting to remove any of them:
$ rm -ri directory
You can then either press y to confirm or n to skip, followed by ENTER.
Testing a wildcard pattern with ls
Another option for safely removing directories when using wildcards is to first test your pattern using the ls command, which will display the list of matched entries:
$ ls -R dir_*
Once you are certain of your selection, you can then replace ls with rm to actually remove them:
$ rm -R dir_*
Note that when using rm, the -r flag and the -R flag will have the same effect.
Removing empty directories with rm and rmdir
To remove empty directories only, you can use the rm command with the -d flag (short for directory):
$ rm -d directory
Or use the rmdir command, which is specifically designed for that purpose:
$ rmdir directory
The advantage of using rmdir, though, is that it allows you to recursively remove empty directories using the -p flag:
$ rmdir -p dir/subdir/
Written by

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Filed Under
Related Articles
List Open Ports in Linux
Learn how to output the list of open TCP and UDP ports in Linux, as well as their IP addresses and ports using the netstat command.

Count Files in Linux
Learn how to count files and folders contained in directories and subdirectories in Linux using the ls, find, and wc commands.

How to Check the Size of Folders in Linux
Learn how to output the size of directories and subdirectories in a human-readable format in Linux and macOS using the du command.

Linux Chmod Command
Understand how to use chmod to change the permissions of files and directories. See examples with various chmod options.

POST JSON Data With Curl
How to send valid HTTP POST requests with JSON data payloads using the curl command and how to avoid common syntax pitfalls. Also, how to solve the HTTP 405 error code.

Format Command Output In Linux
Learn how to filter and format the content of files and the output of commands in Linux using the awk command.
Create Groups In Linux
Learn how to manually and automatically create and list groups in Linux.
Switch Users In Linux
Learn how to switch between users, log in as another user, and execute commands as another user in Linux.
Remover Users in Linux
Learn how to remove local and remote user accounts and associated groups and files in Linux using the userdel and deluser commands.
Delete Files In Linux
Learn how to selectively delete files in Linux based on patterns and properties using the rm command.
Find Files In Linux
Learn how to find and filter files in Linux by owner, size, date, type and content using the find command.
Copy Files In Linux
Learn how to safely and recursively copy one or more files locally and remotely in Linux using the cp and scp command.
