The short answer
To start an interactive Bash shell in a Docker container, you can use the docker exec command that allows developers to execute commands in running containers.
$ docker exec -it <container> bash
Where container is either the name or the identifier of a Docker container that can be obtained using the docker ps command.
Use Warp's Workflows feature to easily recall the syntax
If you’re using Warp as your terminal and you need to quickly retrieve this command, you can use Warp's Workflows feature by pressing CTRL-SHIFT-R, typing start bash docker, then pressing ENTER to use the suggested command:
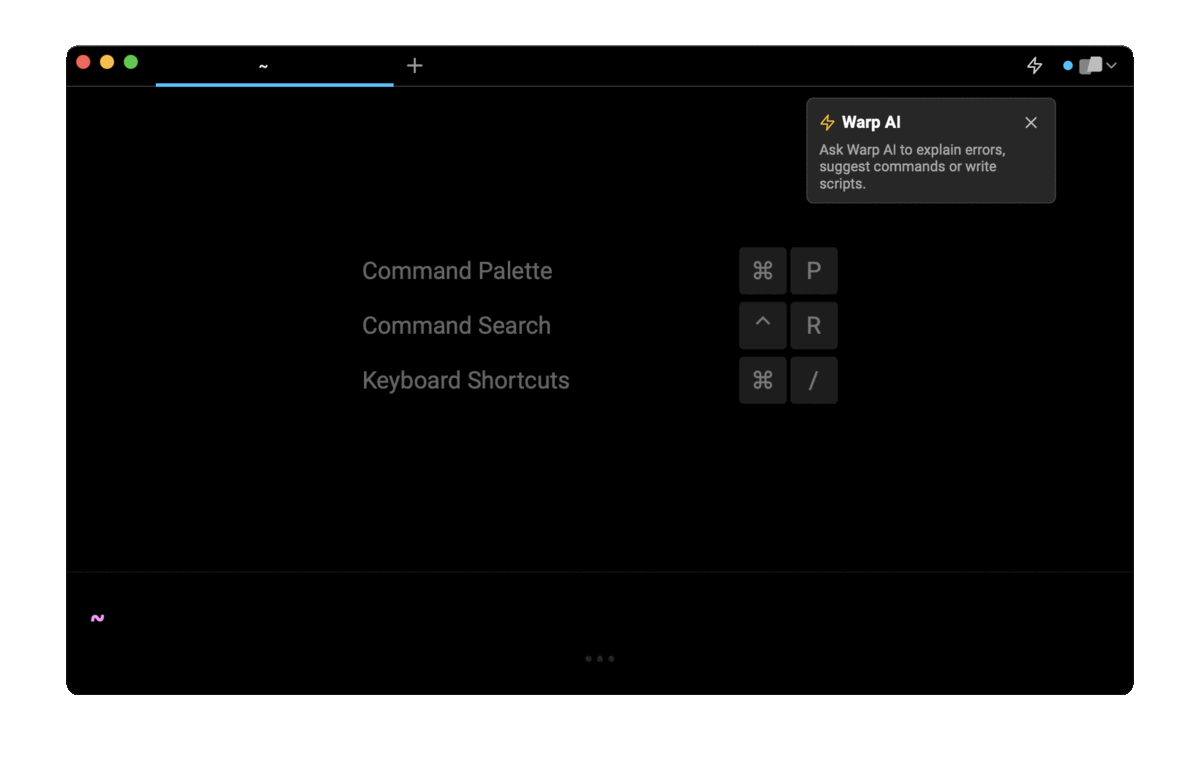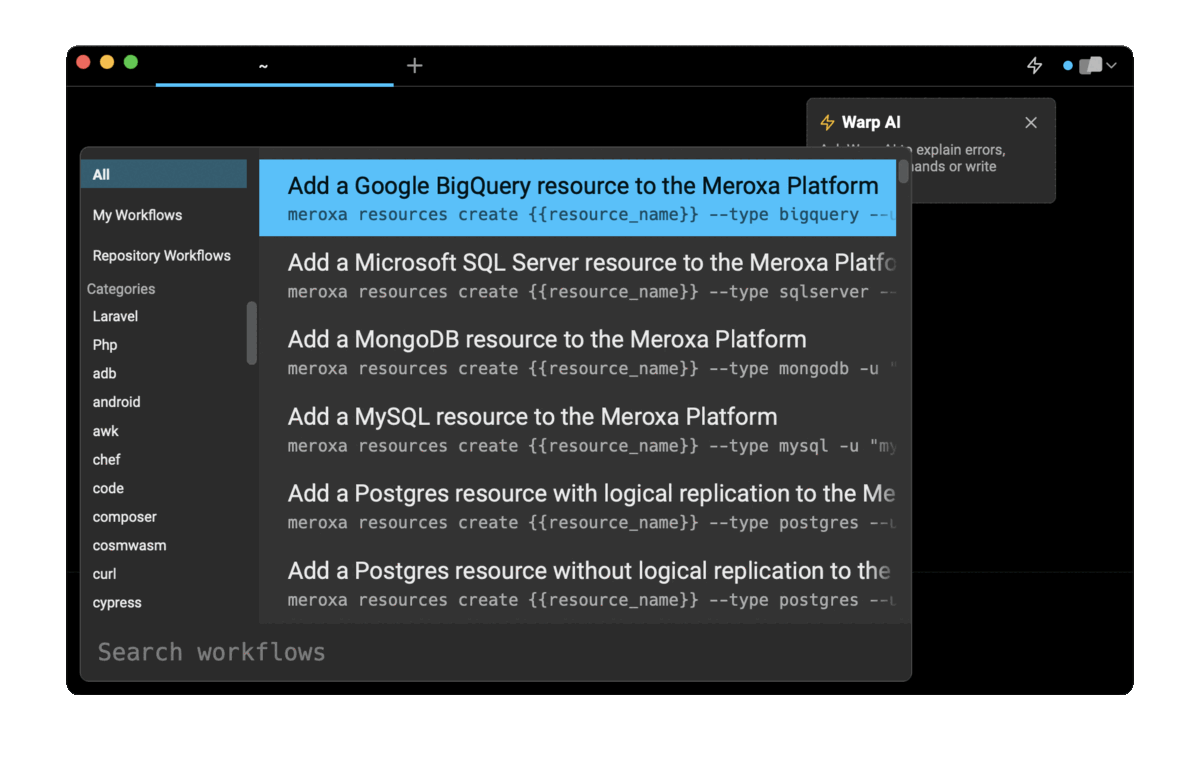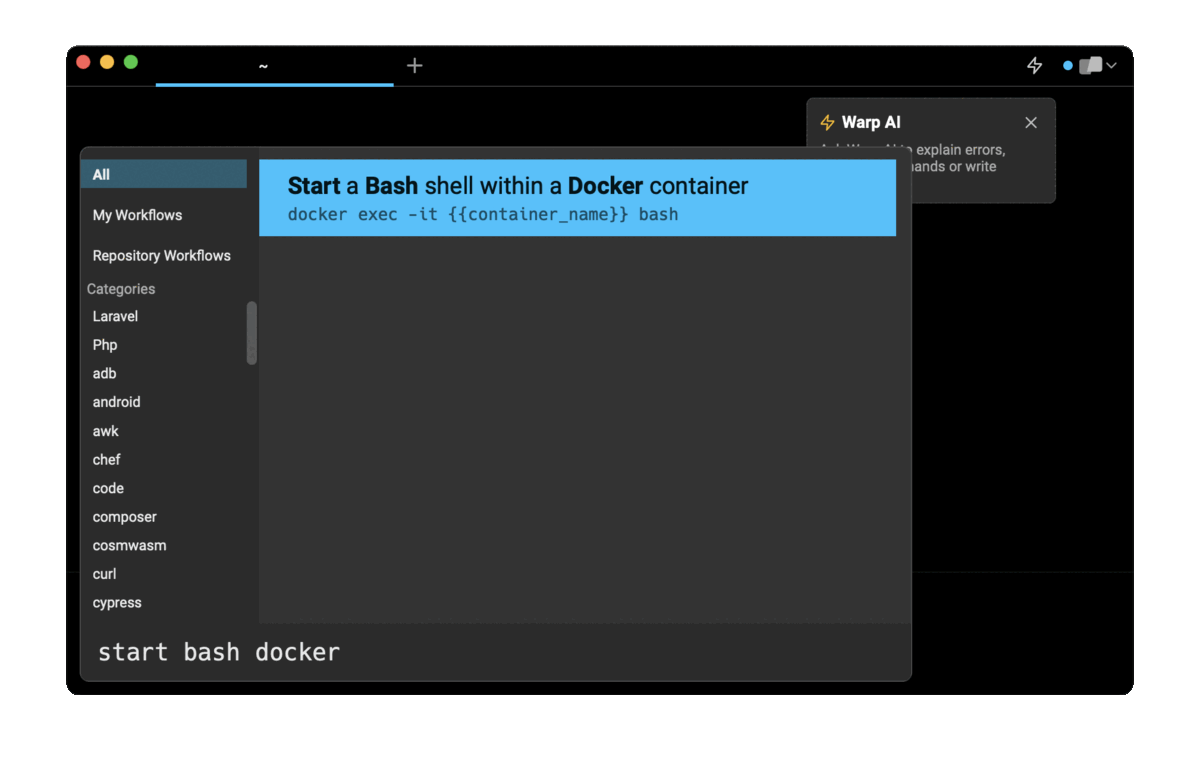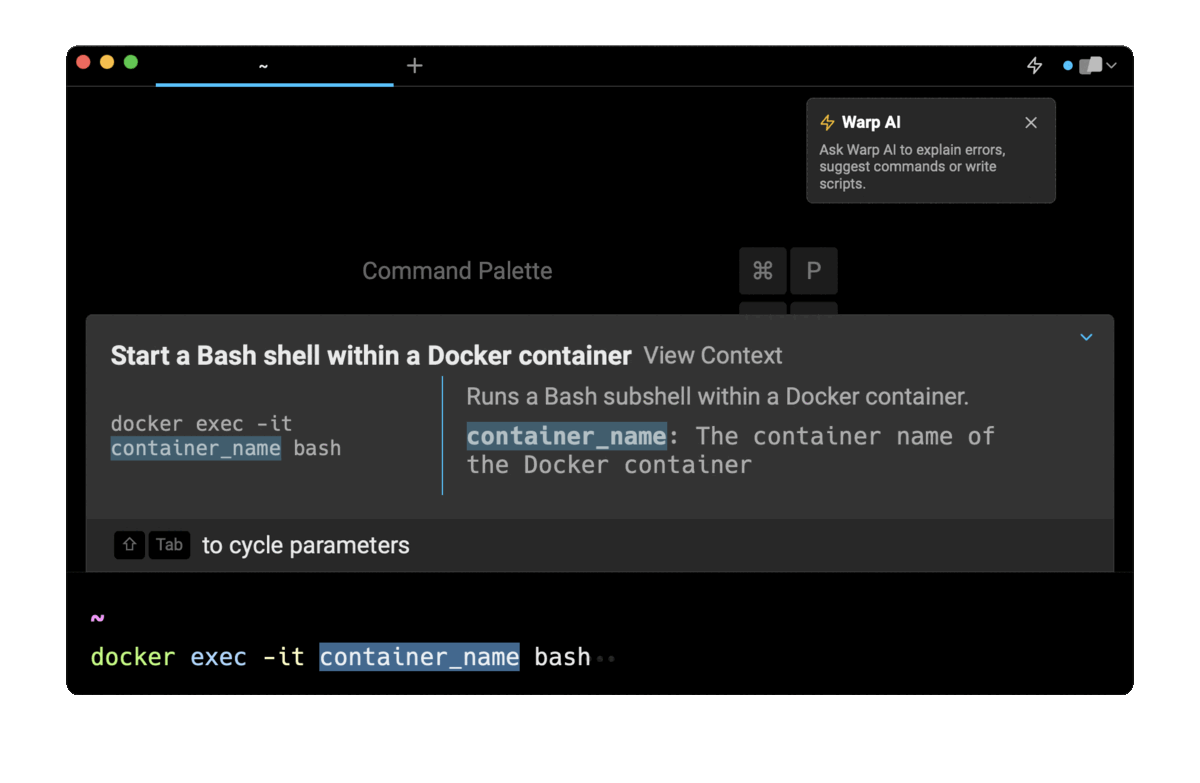
Running a Bash shell on container startup
To start a Docker container with an interactive Bash shell, you can combine the -i flag (short for interactive) and the -t flag (short for TTY) of the docker run command, which instructs Docker to allocate a pseudo-TTY connected to the container’s standard input (i.e. stdin).
$ docker run -it <image> bash
Where image is the name of the image you want to start a container from.
Running sh and other shells
Most images usually come pre-packaged with several shell binaries such as sh, csh, etc. To start a Docker container with an interactive shell other than Bash, simply replace the command argument by the shell you want to use when running the docker run command.
$ docker run -it <image> /bin/sh
Overriding the entrypoint
Some Docker images may include an ENTRYPOINT instruction that specifies which command to run when the container is started.
For example, if the Docker image has the following ENTRYPOINT:
ENTRYPOINT ['node', 'app.js']
Then, by default, the container will start by running the node app.js command.
To override this entry point and start the container with a Bash shell instead of the default command, you can use the --entrypoint flag as follows:
$ docker run --entrypoint /bin/bash -it <image>
Running a single command in a container with Bash
It may happen that you need to run a single command in a running Docker container. Instead of starting an interactive shell session, you can use the -c flag (short for command) of the bash utility which will execute the specified command.
$ docker exec <container> /bin/bash -c '<command>'
Where:
- container is either the name or the identifier of a container.
- command is the command you want to run in the container.
For example, to restart a running service:
$ docker exec ab4fb7dd8ffa /bin/bash -c 'service ssh restart'
If you want to learn how to execute entire scripts instead of single commands, you can read our other article on how to run a shell script using a Dockerfile.
Running Bash as a container
If you want to run the Bash shell as a standalone container to test new features of more recent versions or test shell scripts against different Bash versions to ensure compatibility, you can use the official bash image available on Docker hub.
$ docker run -it bash
Written by

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Filed Under
Related Articles
Bash If Statement
Learn how to use the if statement in Bash to compare multiple values and expressions.

Bash While Loop
Learn how to use and control the while loop in Bash to repeat instructions, and read from the standard input, files, arrays, and more.
POST JSON Data With Curl
How to send valid HTTP POST requests with JSON data payloads using the curl command and how to avoid common syntax pitfalls. Also, how to solve the HTTP 405 error code.

Use Cookies With cURL
Learn how to store and send cookies using files, hard-coded values, environment variables with cURL.
Loop Through Files in Directory in Bash
Learn how to iterate over files in a directory linearly and recursively using Bash and Python.

How To Use sudo su
A quick overview of using sudo su

Generate, Sign, and View a CSR With OpenSSL
Learn how to generate, self-sign, and verify certificate signing requests with `openssl`.

How to use sudo rm -rf safely
We'll help you understand its components

How to run chmod recursively
Using -R is probably not what you want

Curl Post Request
Use cURL to send data to a server

Reading User Input
Via command line arguments and prompting users for input

Bash Aliases
Create an alias for common commands

