The short answer
To remove (delete) all locally installed Docker images from your machine, you can use a combination of the docker rmi and the docker images commands as follows:
Here, the docker images command is used to show the list of all locally installed images. The -a flag (short for --all ) is used to list all images, including the intermediate images that are hidden by default. The -q flag (short for --quiet) is used to only show the image ID.
The docker rmi command, on the other hand, is used to delete one or more specific images.
Here is an example of what this command may look like right before being executed by the shell:
Note that if one or more containers are still using any of the images you are trying to delete, Docker will output an error message saying that the image is in use and cannot be deleted. In this case, you will need to stop and remove those containers first before you can delete all images (see section below).
Easily retrieve this command using Warp’s AI Command Search
If you’re using Warp as your terminal, you can easily retrieve this command using the Warp AI Command Search feature:
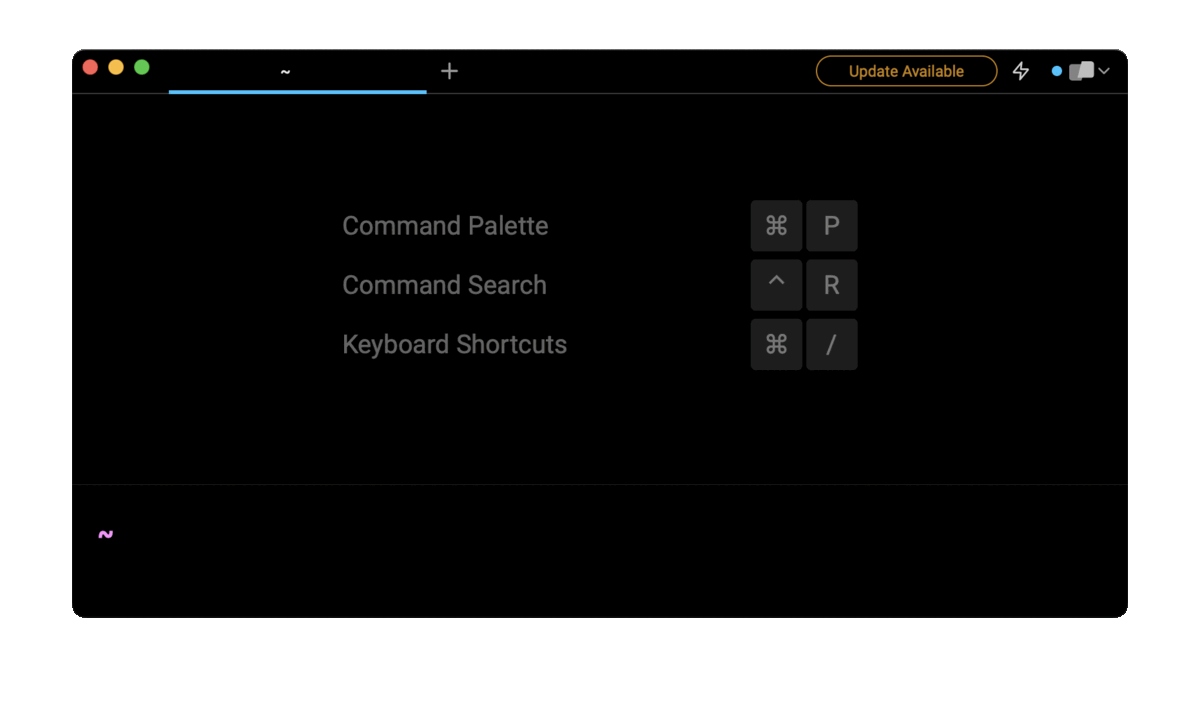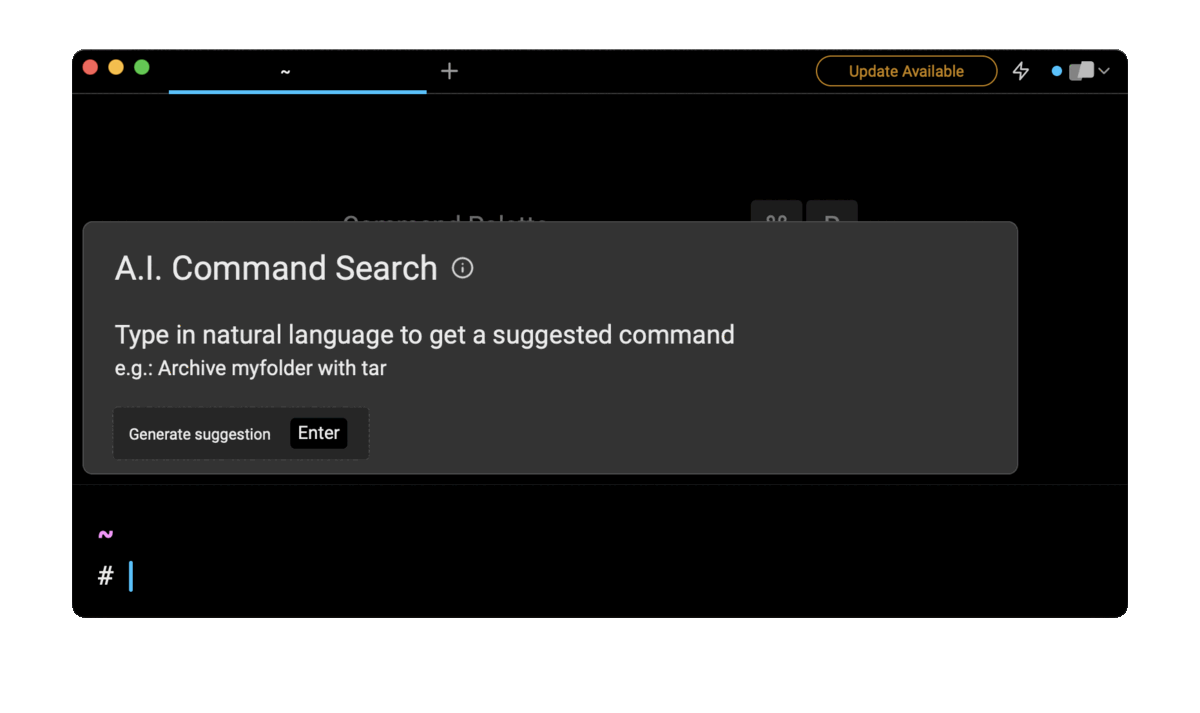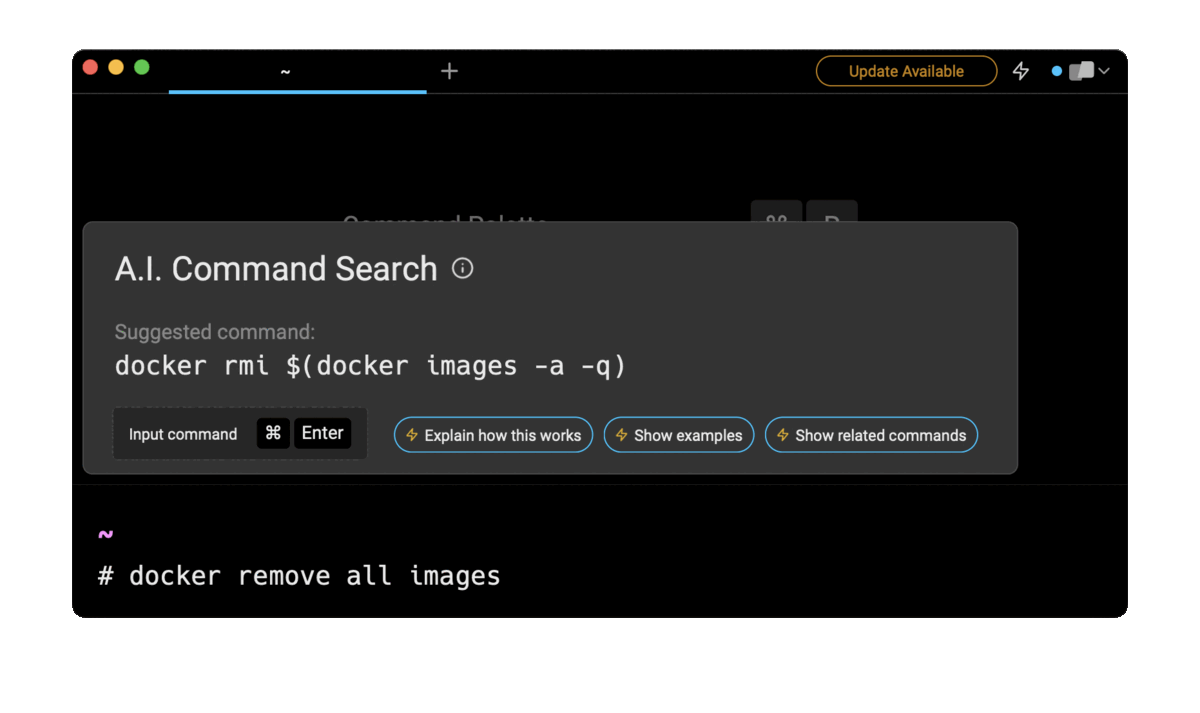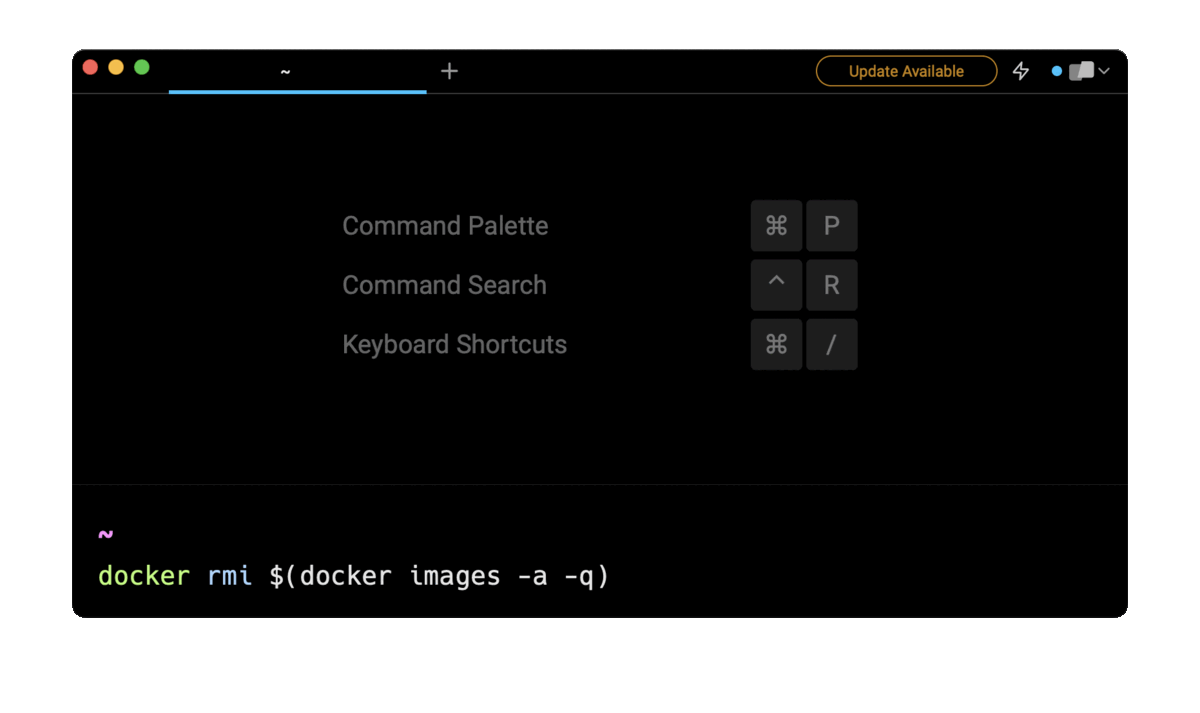
Entering docker remove all images in the AI Command Search will prompt a docker command that can then quickly be inserted into your shell by doing CMD+ENTER .
Remove unused images only
To delete all dangling images, which means images that have neither a repository nor a name tag, you can use the following docker command:
To delete all unused images (i.e. not referenced by any container) including dangling ones, you can use the -a flag (short for --all ) as follows:
Remove all images and containers at once
To remove all images and containers on your local machine, you must first stop any currently running container using a combination of the docker stop command and the docker ps command:
Where docker stop will stop running containers and docker ps -q will list the ID of all running containers.
Once all containers are stopped, you can remove them using the docker rm command:
Where the -a flag of the docker ps command is used to list all containers including stopped ones. See our post on removing stopped Docker containers for more details.
Finally, you can remove all locally installed images using the docker rmi command:
The difference between docker rmi and docker image prune
While both commands are used to deal with the removal of Docker images, they have different functionalities.
The docker rmi command is used to delete one or more specific Docker images based on their name or identifier.
The docker image prune command, on the other hand, is used to clean up all unused Docker images including dangling ones.
Written by

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Filed Under
Related Articles
Override the Container Entrypoint With docker run
Learn how to override and customize the entrypoint of a Docker container using the docker run command.
The Dockerfile ARG Instruction
Learn how to define and set build-time variables for Docker images using the ARG instruction and the --build-arg flag.

Start a Docker Container
Learn how to start a new Docker container from an image in both the foreground and the background using the docker-run command.

Stop All Docker Containers
How to gracefully shutdown running containers and forcefully kill unresponsive containers with signals in Docker using the docker-stop and docker-kill commands.

Use An .env File In Docker
Learn how to write and use .env files in Docker to populate the environment of containers on startup.
Run SSH In Docker
Learn how to launch and connect to a containerized SSH server in Docker using password-based authentication and SSH keys.

Launch MySQL Using Docker Compose
Learn how to launch a MySQL container in Docker Compose.
Execute in a Docker Container
Learn how to execute one or multiple commands in a Docker container using the docker exec command.

Expose Docker Container Ports
Learn how to publish and expose Docker container ports using the docker run command and Dockerfiles.
Restart Containers In Docker Compose
Learn how to restart and rebuild one or more containers in Docker Compose.

Output Logs in Docker Compose
Learn how to output, monitor, customize and filter the logs of the containers related to one or more services in Docker Compose

Rename A Docker Image
Learn how to rename Docker images locally and remotely using the docker tag command.