Restart Containers In Docker Compose

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Published: 3/14/2024
The short answer
In Docker Compose, to restart all the containers related to all the services defined in the compose.yaml file of your project at once, you must first navigate to the directory containing that configuration file, then use the docker compose restart command:
$ docker compose restart
Note that this command will not rebuild the containers or pull updated images; it will only stop and restart the existing containers.
You can learn more about restarting individual containers by reading our article on how to restart single containers in Docker.
Restarting the containers of one or more services
To restart the containers associated with one or more specific services, you can use the following command:
$ docker compose restart <service_name …>
Where service_name … is a list of service names separated by a space character.
For example, this command will restart the containers of the website and api services:
$ docker compose restart website api
Restarting containers with a timeout
By default, when executing the docker compose restart command, all the containers associated with the specified services are immediately killed by Compose before being restarted.
To allow these containers to stop gracefully, you can specify a restart delay, called a timeout, expressed in seconds using the -t flag (short for --timeout):
$ docker compose restart -t <seconds> [<service_name …>]
Note that if the containers don't stop within the specified timeout, Compose will forcefully terminate them.
For example, the following command will give 90 seconds to the api service to perform its cleanup tasks and gracefully exit before being restarted by Compose:
$ docker compose restart -t 90 api
Easily retrieve these commands using Wrap’s AI Command Suggestions
If you’re using Wrap as your terminal, you can easily retrieve these commands using the Wrap AI Command Suggestions feature:
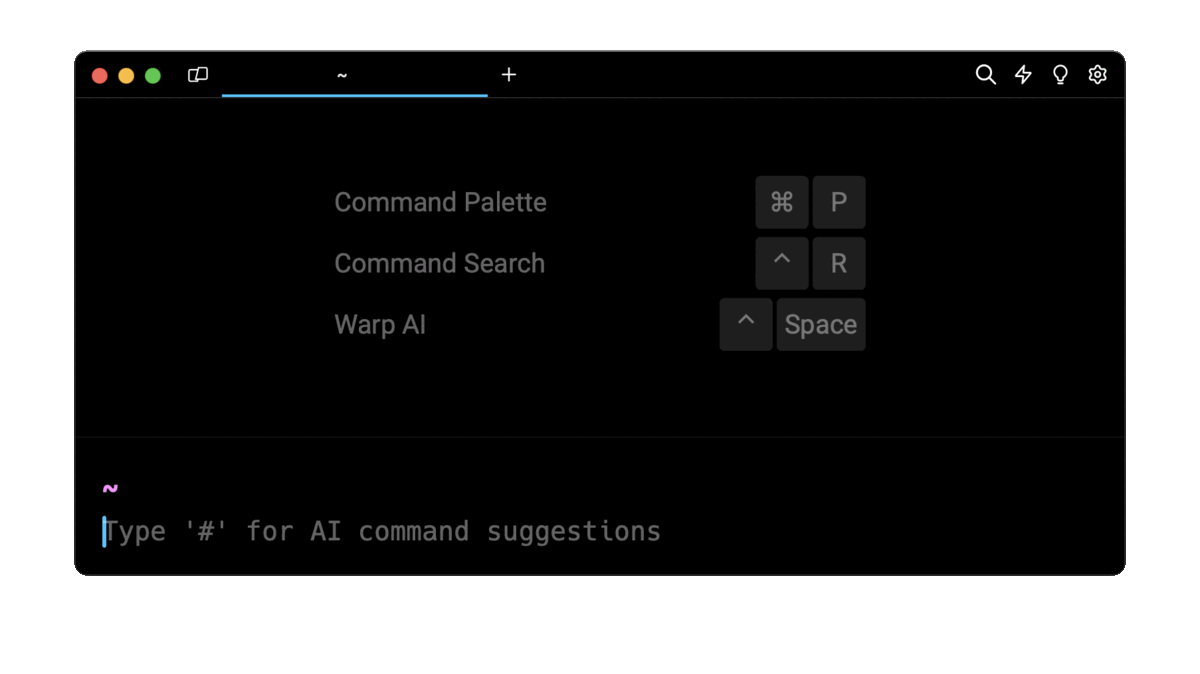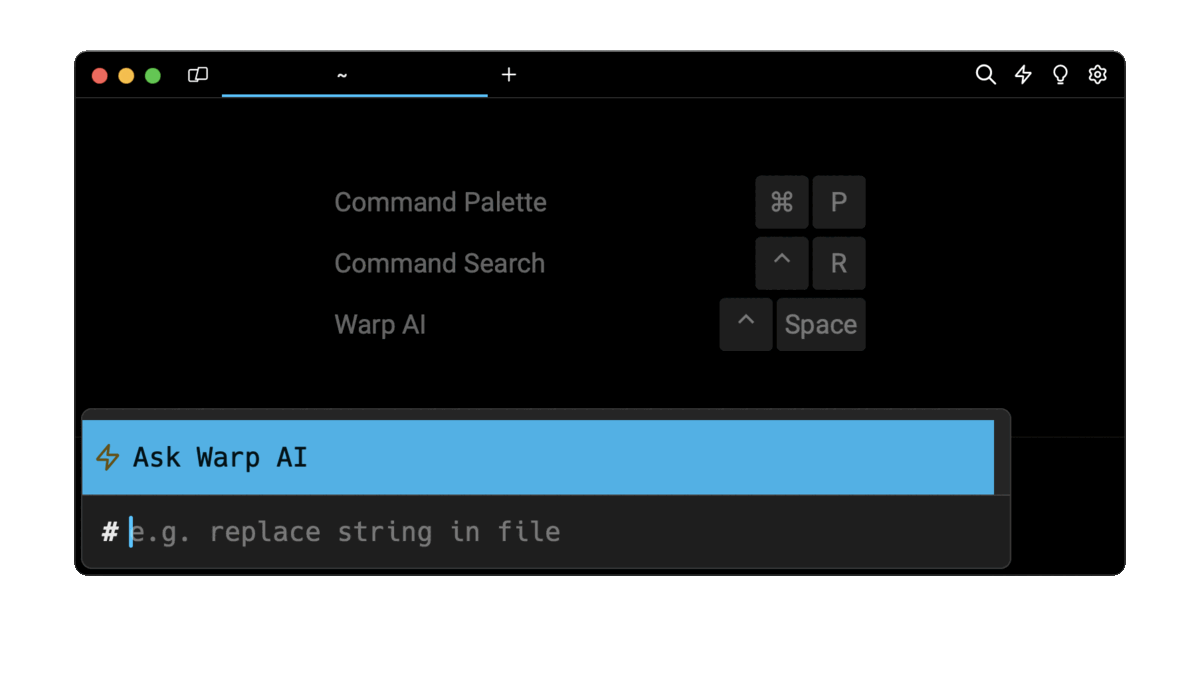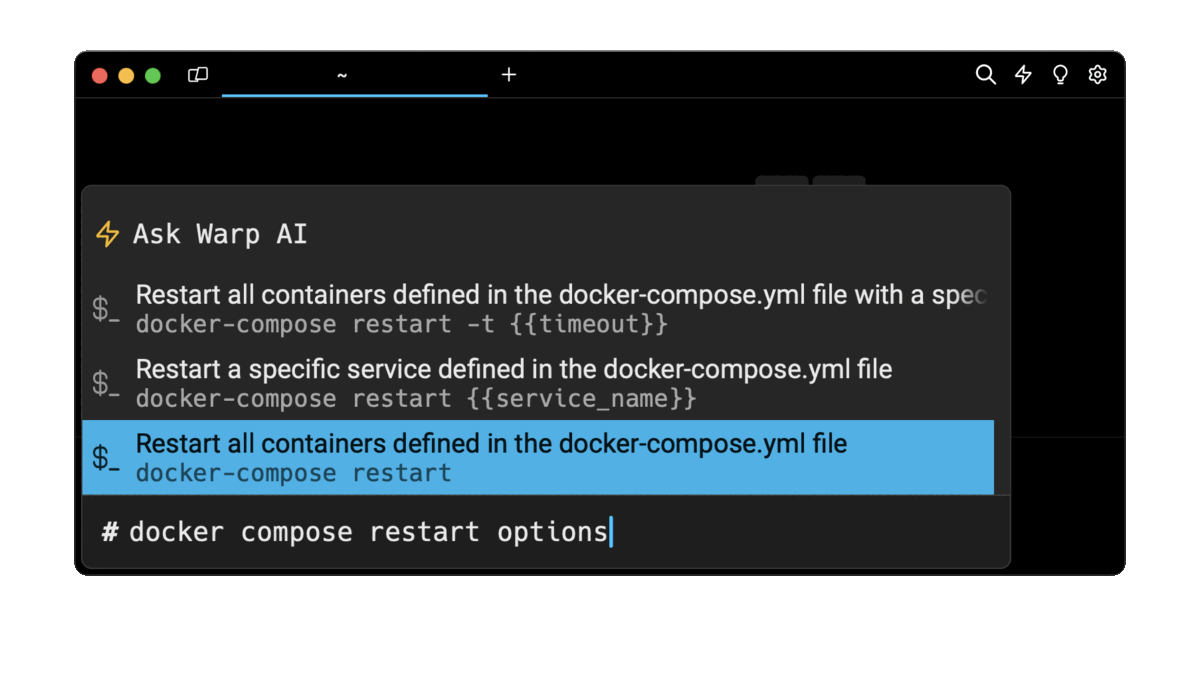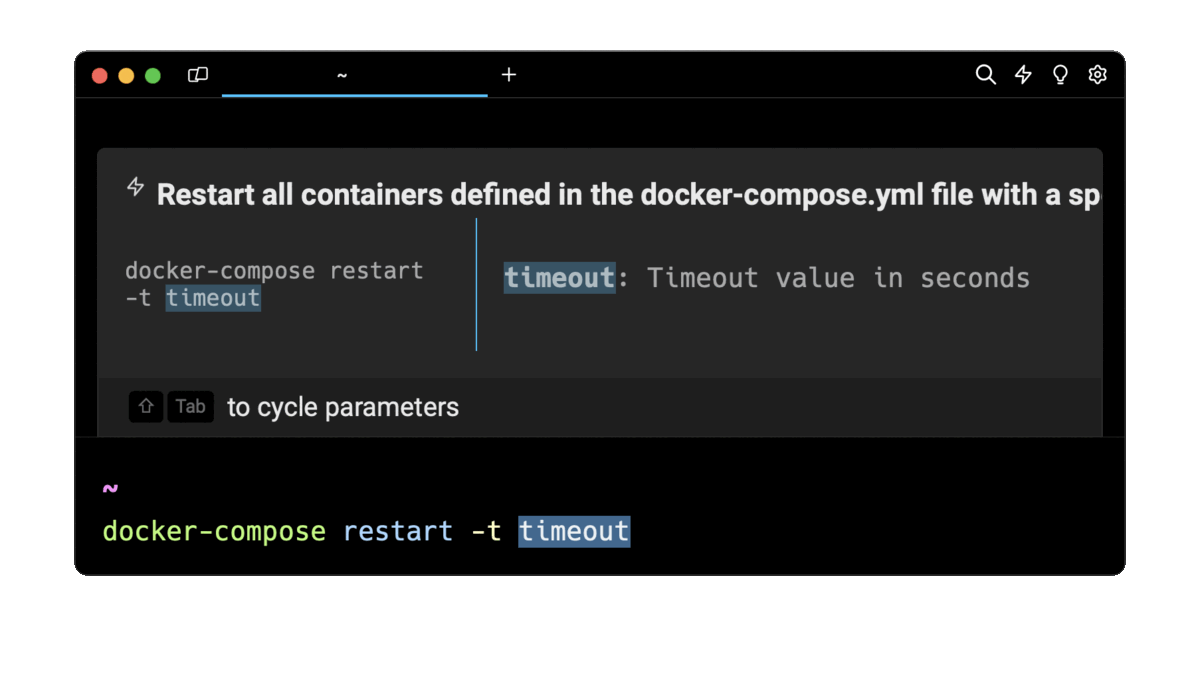
Entering docker compose restart options in the AI Command Suggestion will prompt a list of docker commands that can then quickly be inserted into your shell by pressing CMD + ENTER.
Rebuilding containers on configuration or image change
To automatically stop, remove, and rebuild all the containers associated with all the services defined in the compose.yaml file whose configuration or image have changed, you can use the docker compose up command:
$ docker compose up
Alternatively, if you only want to rebuild the containers associated with specific services, you can use the following syntax instead:
$ docker compose up <service_name …>
Where service_name … is a list of service names separated by a space character.
Rebuilding containers without dependencies
By default, when rebuilding a service that depends on other services, the dependent services will also be automatically rebuilt by Compose.
To prevent this behavior and rebuild the desired services only, you can use the docker compose up command with the --no-deps flag as follows:
$ docker compose up --no-deps <service_name …>
You can learn more about service dependencies by reading our article on understanding the depends_on property in Docker Compose.
Rebuilding containers forcefully
To rebuild the containers associated with specific services regardless of a configuration or image change, you can use the docker compose up command with the --force-recreate flag as follows:
$ docker compose up --force-recreate <service_name …>
Defining the restart policy of containers
In Docker Compose, you can use restart policies to define how your containers should behave in case of termination or failure.
These policies are defined through the restart property and take one of the following values:
- no: The default restart policy. It does not restart the container under any circumstances.
- always: The policy always restarts the container until its removal.
- on-failure: The policy restarts the container if the exit code indicates an error.
- unless-stopped: The policy restarts the container irrespective of the exit code but stops restarting when the service is stopped or removed.
services:
<service_name>:
image: <image_name>
restart: <policy>
For example, the following configuration will try to restart the container of the api service for a maximum of 3 times on failure:
services:
api:
build: ./api
restart: on-failure:3
You can learn more about restart policies for single containers by reading our article on how to restart a Docker container.
Restarting unhealthy services using a health check
In Docker Compose, the healthcheck property allows you to define a test command to periodically check the health of a container. It is often combined with the restart property to define under which condition a service should restart whenever it becomes unhealthy.
services:
<service_name>:
image: <image_name>
healthcheck:
test: <command>
For example, the following configuration checks whether the container of the webserver service is healthy by sending an HTTP request to the nginx server located at the localhost address:
services:
webserver:
image: nginx
healthcheck:
test: "curl -f http://localhost"
You can learn more about health check by reading our article on understanding the healthcheck property in Docker Compose.
Written by

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Filed Under
Related Articles
Override the Container Entrypoint With docker run
Learn how to override and customize the entrypoint of a Docker container using the docker run command.
The Dockerfile ARG Instruction
Learn how to define and set build-time variables for Docker images using the ARG instruction and the --build-arg flag.

Start a Docker Container
Learn how to start a new Docker container from an image in both the foreground and the background using the docker-run command.

Stop All Docker Containers
How to gracefully shutdown running containers and forcefully kill unresponsive containers with signals in Docker using the docker-stop and docker-kill commands.

Use An .env File In Docker
Learn how to write and use .env files in Docker to populate the environment of containers on startup.
Run SSH In Docker
Learn how to launch and connect to a containerized SSH server in Docker using password-based authentication and SSH keys.

Launch MySQL Using Docker Compose
Learn how to launch a MySQL container in Docker Compose.
Execute in a Docker Container
Learn how to execute one or multiple commands in a Docker container using the docker exec command.

Expose Docker Container Ports
Learn how to publish and expose Docker container ports using the docker run command and Dockerfiles.
Output Logs in Docker Compose
Learn how to output, monitor, customize and filter the logs of the containers related to one or more services in Docker Compose

Rename A Docker Image
Learn how to rename Docker images locally and remotely using the docker tag command.
Understand healthcheck in Docker Compose
Learn how to check if a service is healthy in Docker Compose using the healthcheck property.

