Output Logs in Docker Compose

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Published: 3/5/2024
The short answer
In Docker Compose, to output the logs of all the containers related to all the services defined in your compose.yaml file at once, you can use the docker compose logs command without arguments:
$ docker compose logs
For example, considering the following compose.yaml file:
version: '3'
services:
website:
build: .
ports:
- "3000:3000"
api:
build: .
ports:
- "3001:3001"
This command will output all the logs of both the website and api services:
$ docker compose logs
website-1 | [INFO] Starting website server …
api-1 | [INFO] Starting api server …
website-1 | [INFO] New client login attempt
api-1 | [ERROR] Credentials not found
Viewing the logs of a specific service
To output the logs of one or more specific services, you can use the docker compose logs command as follows:
$ docker compose logs <service_name …>
Where service_name … is a list of service names separated by a space character.
For example, this command will only output the logs of the containers related to the api service:
$ docker compose logs api
api-1 | [INFO] Starting api server …
api-1 | [ERROR] Credentials not found
You can learn more about container logs by reading our article on how to monitor the logs of single containers in Docker.
Customizing the logs output
To output the logs of containers without including the name of their related services, which helps making the output cleaner and easier to parse, you can use the --no-log-prefix flag:
$ docker compose logs --no-log-prefix [<service_name> …]
For example, this command will only output the logs generated by the containers without the names of the related services:
$ docker compose logs --no-log-prefix
[INFO] Starting website server …
[INFO] Starting api server …
[INFO] New client login attempt
[ERROR] Credentials not found
Including the logs timestamp in the output
To output the logs of containers including the timestamp at which they were generated, you can use the -t flag (short for --timestamps ):
$ docker compose logs -t [<service_name> …]
For example, this command will include the timestamp of every single log line:
$ docker compose logs -t
website-1 | 2024-02-23T13:40:41.928346630Z [INFO] Starting website server …
api-1 | 2024-02-23T13:41:32.628446430Z [INFO] Starting api server …
website-1 | 2024-02-23T14:12:20.928346630Z [INFO] New client login attempt
api-1 | 2024-02-23T14:13:30.928346630Z [ERROR] Credentials not found
Displaying service logs in real-time
To monitor the logs of the containers related to one or more services in real-time, you can use the docker compose logs command with the -f flag (short for --follow) :
$ docker compose logs -f [<service_name …>]
Note that this command will not only output the new logs generated by the containers in real-time, but also the previous ones. You can learn more about filtering these logs in the following sections.
Easily retrieve this command using Warp’s AI Command Suggestions
If you’re using Warp as your terminal, you can easily retrieve this command using the Warp AI Command Suggestions feature:
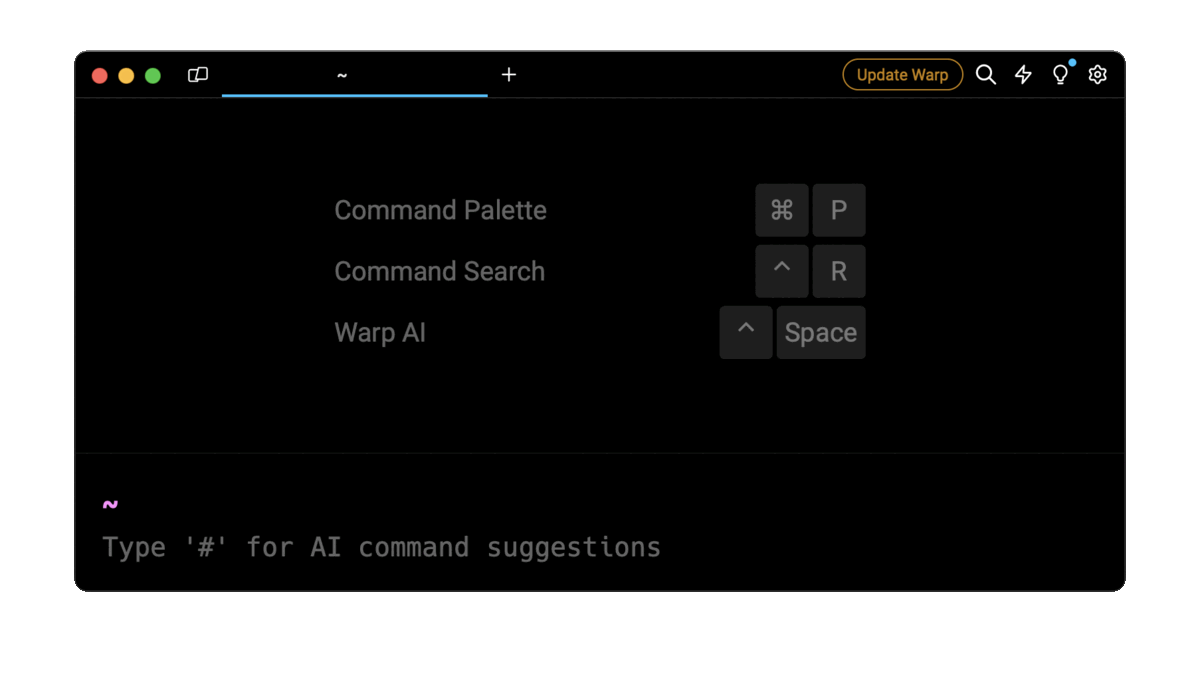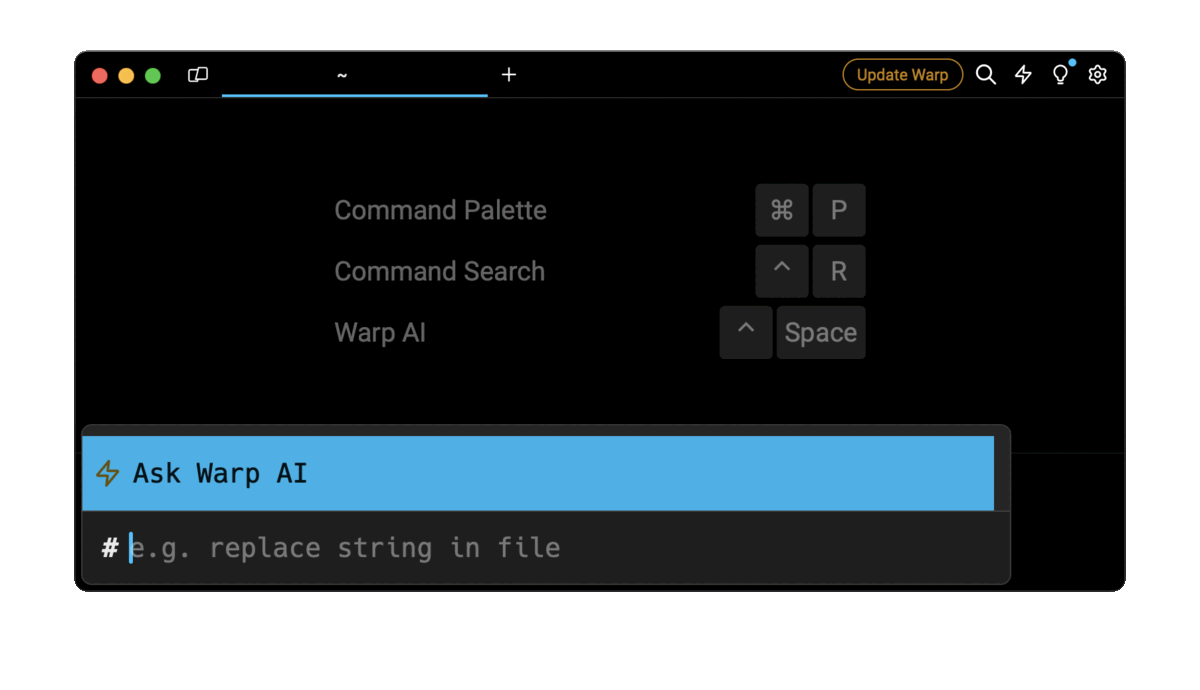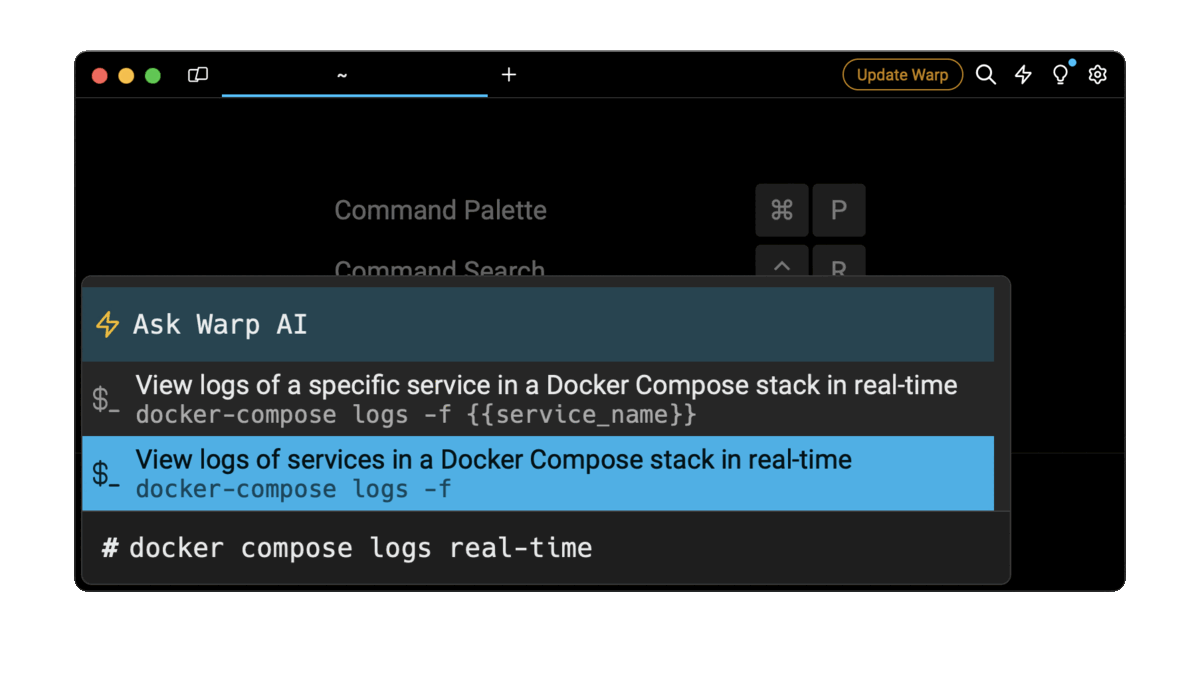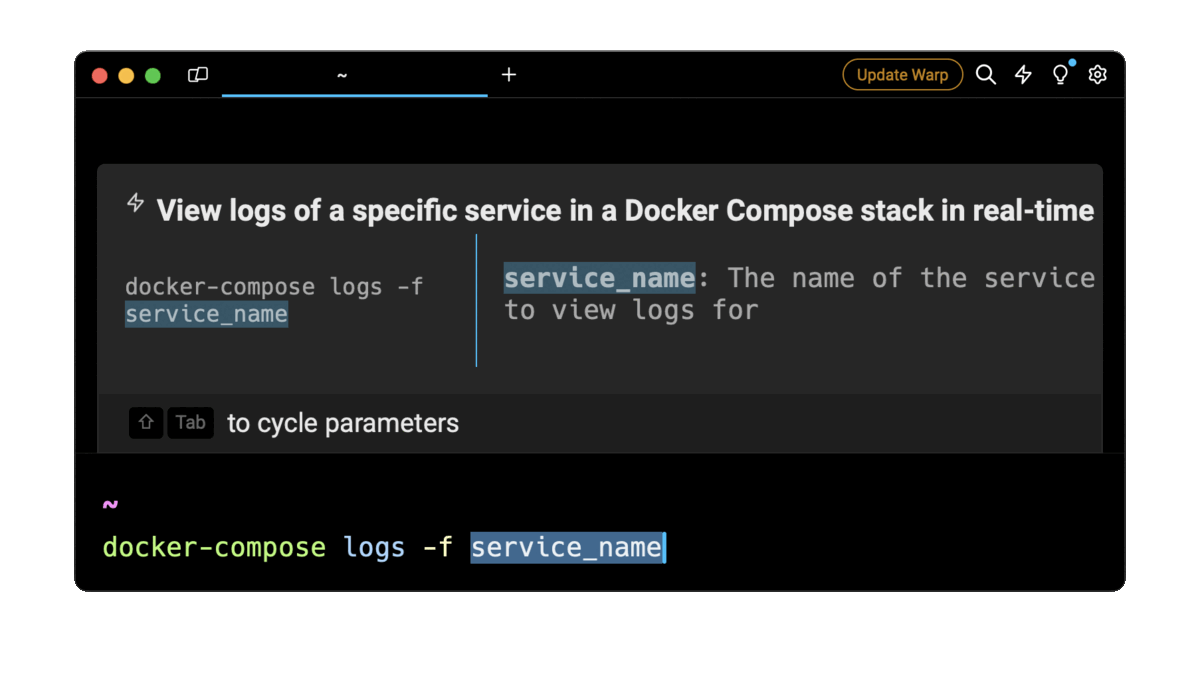
For example, entering docker compose logs real-time in the AI Command Suggestions will prompt a docker command that can then quickly be inserted into your shell by doing CMD+ENTER .
Filtering container logs
In Docker Compose, container logs can be filtered in several ways.
Outputting the last N logs
To show the latest log entries, you can use the -n flag (short for --tail ) followed by the number of logs to display:
$ docker compose logs -n <number> [<service_name …>]
For example, the following command shows the latest 80 logs of the containers related to the api service:
$ docker compose logs -n 80 api
Filtering logs by date and time
To filter container logs based on timeframes, you can either use the --since flag to fetch the logs that occurred after a specific time:
$ docker compose logs --since <time> [<service_name …>]
Or you can use the --until flag to fetch the logs that occurred before a specific time:
$ docker compose logs --until <time> [<service_name …>]
Where time is either:
- A timestamp expressed in the following format: YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS.NNNNNNZ .
- A relative duration expressed in the following format: <number>[h|m|s] where h , m , s stand for hours, minutes, and seconds.
For example, this command will output all the logs generated in the last hour:
$ docker compose logs --since="1h"
And this command will output all the logs generated until January 2nd, 2024:
$ docker compose logs --until="2024-01-02"
Filtering logs based on patterns using the grep command
To filter container logs based on specific keywords or patterns, you can pipe the output of the docker compose logs command into the grep command as follows:
$ docker compose logs [<service_name …>] | grep '<pattern>'
For instance, this command will output all the logs of the containers related to the api service containing the ERROR keyword:
$ docker compose logs api | grep 'ERROR'
api-1 | [ERROR] Credentials not found
You can learn more filtering methods by reading our article on how to filter the output of commands with grep and awk.
Written by

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Filed Under
Related Articles
Override the Container Entrypoint With docker run
Learn how to override and customize the entrypoint of a Docker container using the docker run command.
The Dockerfile ARG Instruction
Learn how to define and set build-time variables for Docker images using the ARG instruction and the --build-arg flag.

Start a Docker Container
Learn how to start a new Docker container from an image in both the foreground and the background using the docker-run command.

Stop All Docker Containers
How to gracefully shutdown running containers and forcefully kill unresponsive containers with signals in Docker using the docker-stop and docker-kill commands.

Use An .env File In Docker
Learn how to write and use .env files in Docker to populate the environment of containers on startup.
Run SSH In Docker
Learn how to launch and connect to a containerized SSH server in Docker using password-based authentication and SSH keys.

Launch MySQL Using Docker Compose
Learn how to launch a MySQL container in Docker Compose.
Execute in a Docker Container
Learn how to execute one or multiple commands in a Docker container using the docker exec command.

Expose Docker Container Ports
Learn how to publish and expose Docker container ports using the docker run command and Dockerfiles.
Restart Containers In Docker Compose
Learn how to restart and rebuild one or more containers in Docker Compose.

Rename A Docker Image
Learn how to rename Docker images locally and remotely using the docker tag command.
Understand healthcheck in Docker Compose
Learn how to check if a service is healthy in Docker Compose using the healthcheck property.

