In Docker, a network is a communication mechanism that allows isolated containers to communicate with each other as well as external services located on the same host or distant machines.
The short answer
The base command for managing Docker networks is the docker network command, which enables developers to create, inspect, connect, disconnect, and remove networks:
$ docker network <subcommand>
Where subcommand includes create , inspect , connect , and so on.
retrieve these commands using Wrap’s AI Command Suggestions
If you’re using Warp as your terminal, you can easily retrieve these commands using the Warp AI Command Suggestions feature:
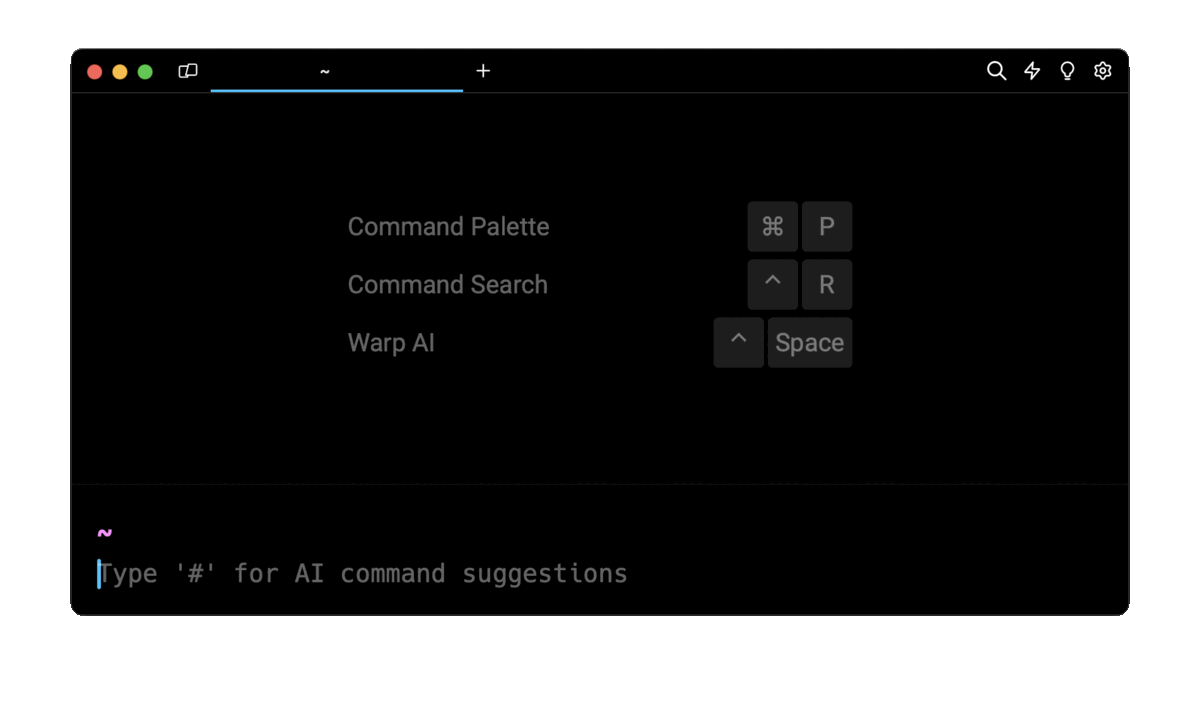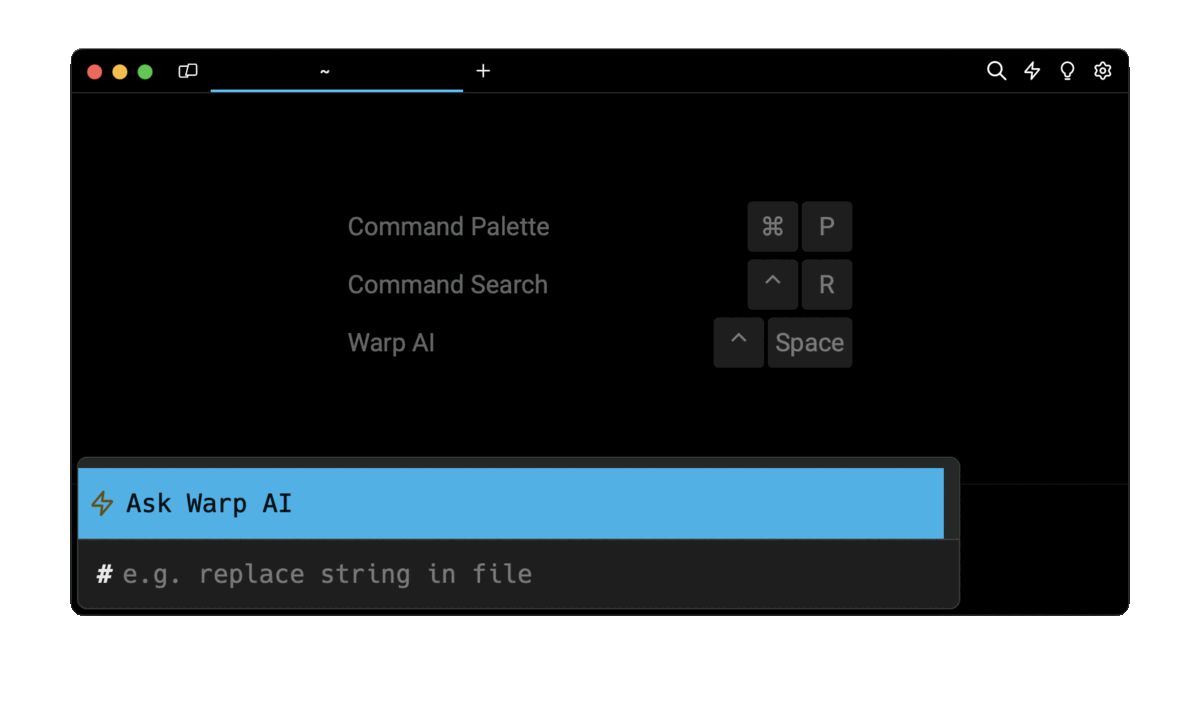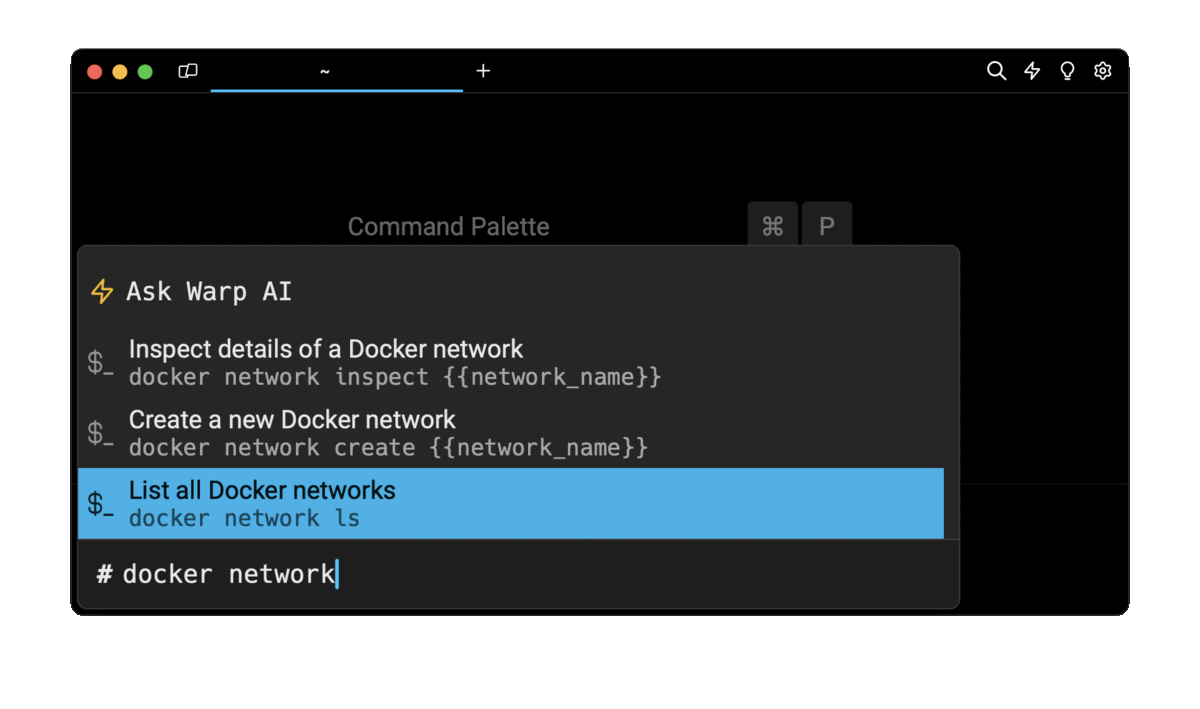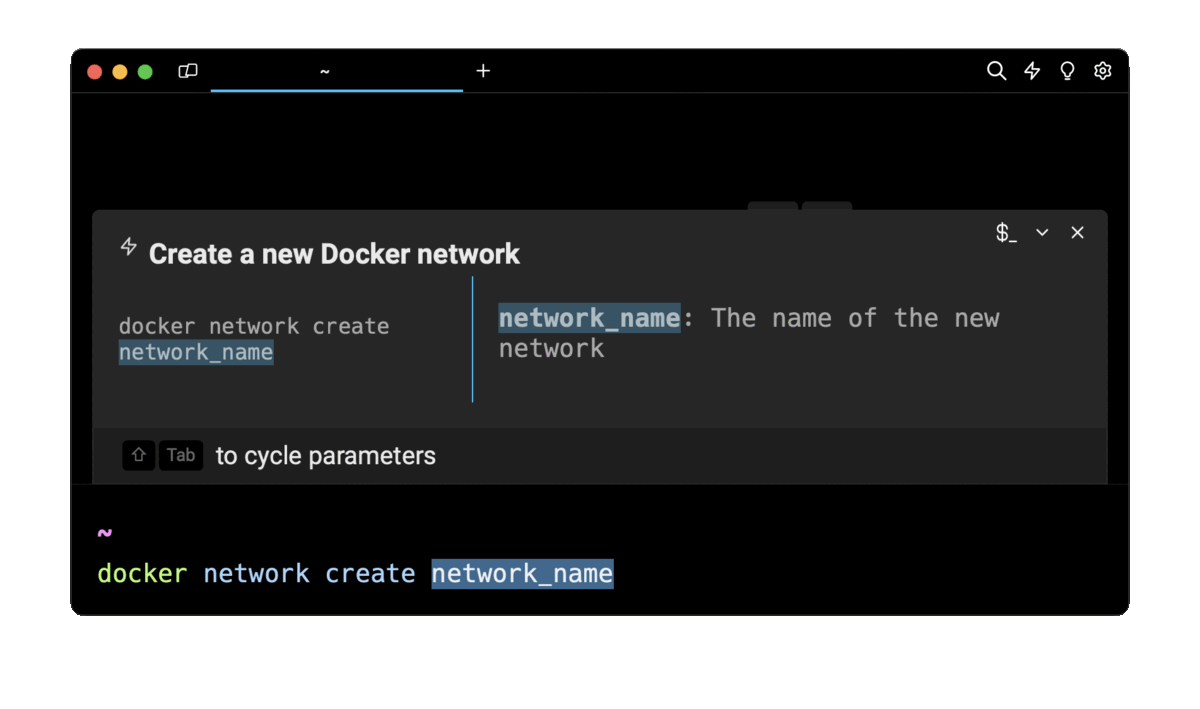
Entering docker network in the AI Command Suggestion will prompt a list of docker commands that can then quickly be inserted into your shell by pressing CMD+ENTER .
Creating a new network
To create a new Docker network, you can use the docker network create command as follows:
$ docker network create <network_name>
For example, this command will create a new network named my_network :
$ docker network create my_network
Specifying a network driver
In Docker, a network driver is a component responsible for determining how containers on a Docker host connect and communicate with each other and with external networks.
Docker supports multiple network drivers, each designed to meet specific use cases:
- The default bridge driver enables communication between containers on the same host. Only the containers connected to the same bridge network can communicate, but they are isolated from containers on different bridge networks.
- The host driver removes network isolation between the container and the Docker host. Containers share the host's network namespace. This driver can provide better network performance as it skips the additional encapsulation used in other drivers.
- The overlay driver is used in Docker swarm mode for multi-host networking. It facilitates communication between containers running on different nodes in a swarm.
- The macvlan driver allows containers to have their own MAC addresses, giving them a physical presence on the network.
- The ipvlan driver enables containers to have their own MAC address but share the same IP address as the underlying host or other containers.
- The none driver disables all networking for a container, which is useful when a container doesn’t need network access.
To create a new Docker network with a specific driver instead of the default bridge driver, you can use the docker network create command with the -d flag (short for --driver ):
$ docker network create -d <driver_type> <network_name>
Note that, if the -d flag is not specified, the network driver will default to bridge.
For example, this command will create a new network named my_new_bridge using the host driver:
$ docker network create -d host my_new_bridge
Listing existing networks
To get the list of existing Docker networks, you can use the docker network ls command:
$ docker network ls
For example:
$ docker network ls
NETWORK ID NAME DRIVER SCOPE
d4fe037a03e3 bridge bridge local
Getting detailed information about networks
To get detailed information about a Docker network, such as its name, ID, driver type, IP address, associated containers, and more, you can use the docker network inspect command:
$ docker network inspect <network_name>
For example, this command will return the detailed information of the network named my_network :
$ docker network inspect my_network
Adding containers to a network
To connect a running container to an existing network and enable it to communicate and exchange data with the other containers connected to the same network, you can use the docker network connect command as follows:
$ docker network connect <network_name> <container_id>
Note that, by default, Docker automatically assigns an IP address to the container from the subnet of the specified network.
For example, this command connects the container identified by the ID 7783cbb0deaa to the network named my_network :
$ docker network connect my_network 7783cbb0deaa
Alternatively, you can launch a new container and connect it to a network at the same time using the docker run command combined with the --network flag as follows:
$ docker run -it --network my_network busybox:latest
Disconnecting a container from a network
To disconnect a container from a network, you can use the docker network disconnect command as follows:
$ docker network disconnect <network_name> <container_id>
For example:
$ docker network disconnect my_network 7783cbb0deaa
Removing networks
To remove an existing Docker network, you can use the docker network rm command as follows:
$ docker network rm <network_name>
Note that, if containers are connected to the network you are trying to remove, Docker will prompt you for confirmation before disconnecting these containers and removing the network.
For example:
$ docker network rm my_network
Pruning networks
To free up disk space and resources, you can remove all unused networks that are not connected to any containers (i.e. pruning) using the docker network prune command:
$ docker network prune
Running containers in isolation
The none network driver is used to create containers without any networking capabilities, which means that they won’t be able to communicate with the external world or with other containers.
This network mode is mostly useful for containers that are used solely for data storage, batch processing jobs, or debugging.
To create a container without any networking capabilities, you can use the --network flag as follows:
$ docker run -it --network none alpine:latest
Written by
Nitish Singh
Filed Under
Related Articles
Override the Container Entrypoint With docker run
Learn how to override and customize the entrypoint of a Docker container using the docker run command.
The Dockerfile ARG Instruction
Learn how to define and set build-time variables for Docker images using the ARG instruction and the --build-arg flag.

Start a Docker Container
Learn how to start a new Docker container from an image in both the foreground and the background using the docker-run command.

Stop All Docker Containers
How to gracefully shutdown running containers and forcefully kill unresponsive containers with signals in Docker using the docker-stop and docker-kill commands.

Use An .env File In Docker
Learn how to write and use .env files in Docker to populate the environment of containers on startup.
Run SSH In Docker
Learn how to launch and connect to a containerized SSH server in Docker using password-based authentication and SSH keys.

Launch MySQL Using Docker Compose
Learn how to launch a MySQL container in Docker Compose.
Execute in a Docker Container
Learn how to execute one or multiple commands in a Docker container using the docker exec command.

Expose Docker Container Ports
Learn how to publish and expose Docker container ports using the docker run command and Dockerfiles.
Restart Containers In Docker Compose
Learn how to restart and rebuild one or more containers in Docker Compose.

Output Logs in Docker Compose
Learn how to output, monitor, customize and filter the logs of the containers related to one or more services in Docker Compose

Rename A Docker Image
Learn how to rename Docker images locally and remotely using the docker tag command.
