Copy File To Docker Container

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Published: 8/3/2023
The short answer
The docker cp command allows you to copy files and directories from your local machine to a running container.
$ docker cp src_path container:dest_path
Where:
- src_path is the path on your local machine of the file you want to copy.
- container is the name or the ID of the container you want to copy files to.
- dest_path is the path in the container of the directory you want to copy files to.
To get the name or ID of the container you want to copy files to, you can use the docker ps command, which will output the list of all the running containers.
Use Warp's Workflows feature to easily recall the syntax
If you’re using Warp as your terminal and you need to quickly retrieve this command, you can use Warp's Workflows feature by pressing CTRL-SHIFT-R and typing copy files:
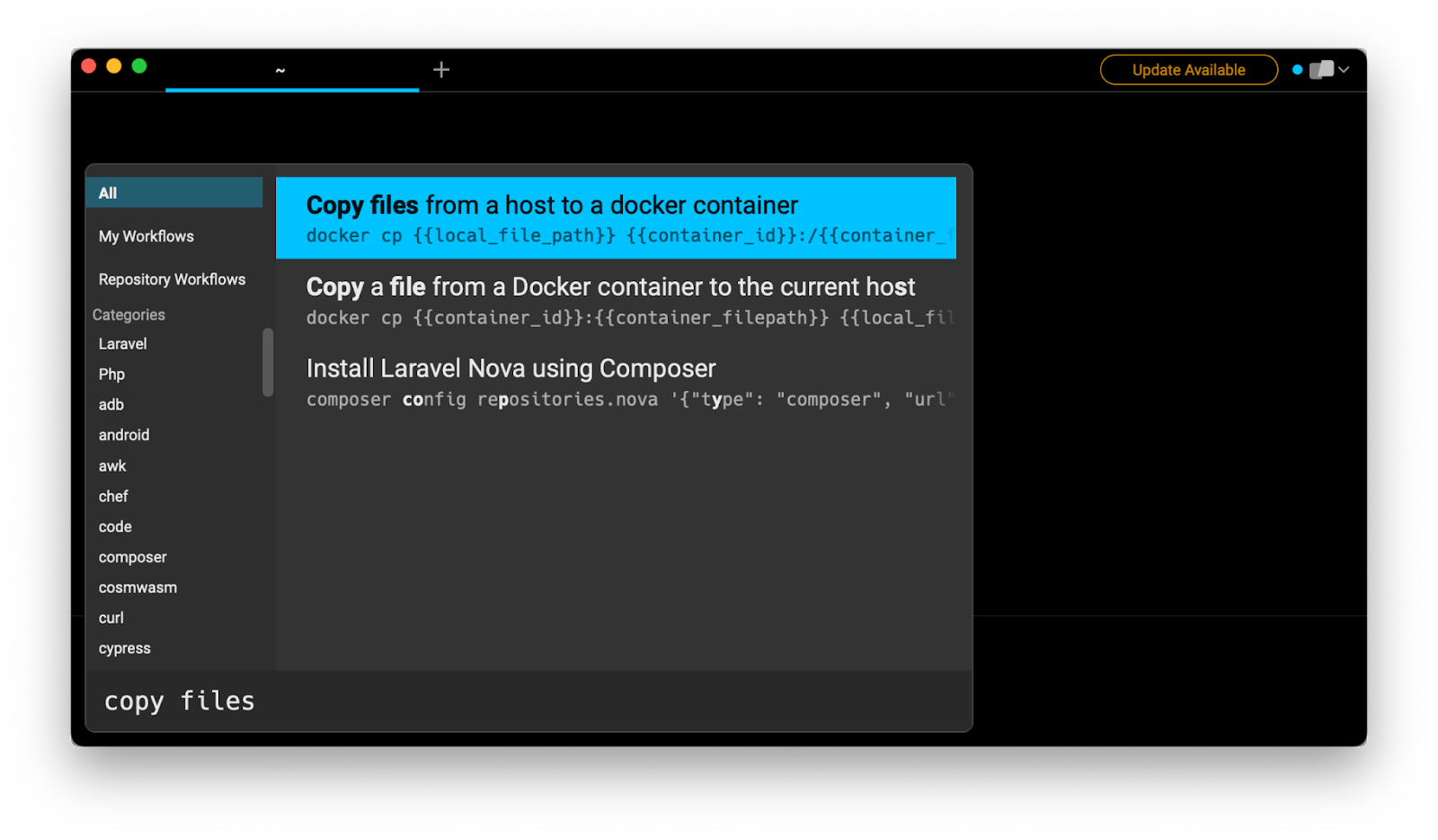
Then pressing ENTER to use the suggested command:
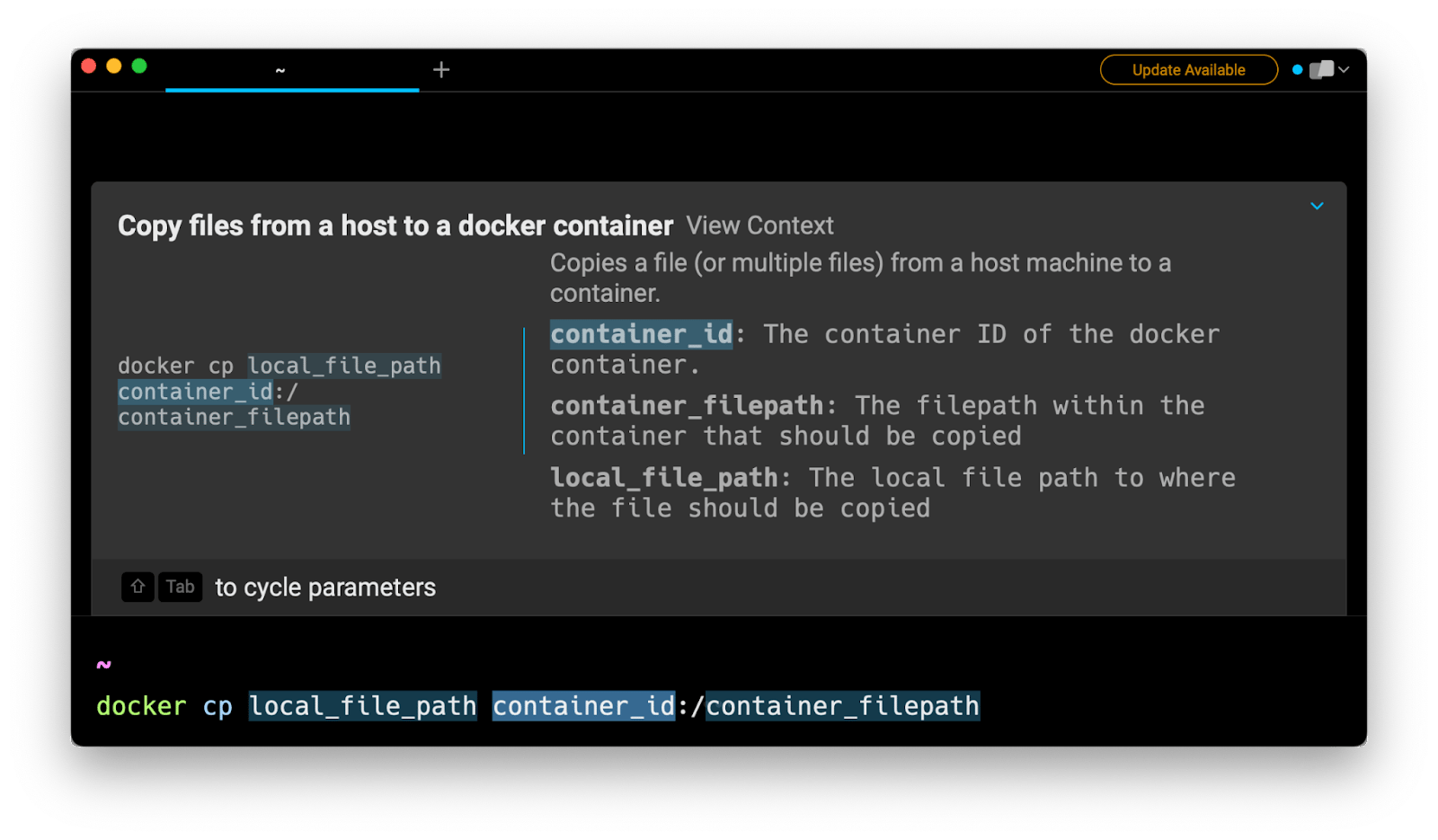
Using docker cp to copy files to docker containers
Copying individual files
To copy a file to a container, you can either use its relative or absolute path, and specify the destination directory as follows:
$ docker cp ./file.txt container:/app/
Alternatively, you can copy and rename at the same time, by providing the full destination path:
$ docker cp ./file.txt container:/app/script.txt
Note that it is not possible to copy multiple files at once using the docker cp command, unless you either use a for loop:
for file in *.txt; do docker cp $file container:/app; done
Or copy the entire directory that contains them (if located in the same directory).
Copying entire directories recursively
When copying a directory, the docker cp command will behave like the Unix cp -a command, which means that the directory will be copied recursively with permission preserved if possible.
$ docker cp ./dir container:/app/
Copying absolute and relative paths, such as a parent directory
The docker cp assumes container paths are relative to the container's root directory (i.e. /). A destination path can therefore be written with or without the initial forward slash, as docker cp will see these two commands as identical:
$ docker cp ./file.txt container:tmp
$ docker cp ./file.txt container:/tmp
Source paths on the other hand, can be written either in their relative form:
$ docker cp ./file.txt container:/tmp
Or in their absolute form:
$ docker cp /home/johndoe/Documents/file.txt container:/tmp
You can learn more about the docker cp command in the official Docker documentation.
Copying files at build-time using a Dockerfile
A Dockerfile is a text file that contains all the necessary instructions for building a Docker image. These instructions can be used for installing and configuring command line tools, declaring environment variables, exposing ports, copying files from the local environment, and so on.
To copy files and directory at build-time, you can use the COPY instruction:
Where:
- src is the path on your local machine of the file(s) you want to copy.
- dest is the path on the container you want to copy the file to.
COPY source path options
Unlike with the docker cp command, the COPY instruction allows you to copy multiple sources at once–which can be files, directories, or both–by separating them with a whitespace character:
COPY file.txt dir /app
These source paths may also contain wildcards:
COPY *.txt /app
It is important to note that the paths of the source files and directories will be interpreted as relative to the source of the context of the build, which means that only the files contained in the directory where the Dockerfile is located will be copied.
You can therefore copy the entire directory of the build context using the dot notation:
COPY . /app
But you cannot copy files that are outside of the build context of the Dockerfile:
# This command will not work
COPY ../file.txt /app
Also note that when copying a directory, only the content of the directory will be copied, but not the directory itself.
For example, the following command will copy the content of the dir directory into the /app directory:
COPY dir /app
COPY destination path options
The destination path may either be an absolute path:
COPY file /app
Or a path relative to the one specified in the WORKDIR instruction:
WORKDIR /app
COPY file .
The WORKDIR instruction is used to set the working directory for instructions such as COPY, ADD, RUN, etc. If the specified directory doesn't exist, it will be automatically created. In Unix, this is the equivalent of the following command:
$ mkdir dir && cd dir
Written by

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Filed Under
Related Articles
Override the Container Entrypoint With docker run
Learn how to override and customize the entrypoint of a Docker container using the docker run command.
The Dockerfile ARG Instruction
Learn how to define and set build-time variables for Docker images using the ARG instruction and the --build-arg flag.

Start a Docker Container
Learn how to start a new Docker container from an image in both the foreground and the background using the docker-run command.

Stop All Docker Containers
How to gracefully shutdown running containers and forcefully kill unresponsive containers with signals in Docker using the docker-stop and docker-kill commands.

Use An .env File In Docker
Learn how to write and use .env files in Docker to populate the environment of containers on startup.
Run SSH In Docker
Learn how to launch and connect to a containerized SSH server in Docker using password-based authentication and SSH keys.

Launch MySQL Using Docker Compose
Learn how to launch a MySQL container in Docker Compose.
Execute in a Docker Container
Learn how to execute one or multiple commands in a Docker container using the docker exec command.

Expose Docker Container Ports
Learn how to publish and expose Docker container ports using the docker run command and Dockerfiles.
Restart Containers In Docker Compose
Learn how to restart and rebuild one or more containers in Docker Compose.

Output Logs in Docker Compose
Learn how to output, monitor, customize and filter the logs of the containers related to one or more services in Docker Compose

Rename A Docker Image
Learn how to rename Docker images locally and remotely using the docker tag command.
