Scale Deployments in Kubernetes

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Updated: 7/12/2024
Published: 7/12/2024
The short answer
In Kubernetes, to scale a Deployment, you can use the kubectl scale command as follows:
$ kubectl scale deployment <deployment> --replicas=<replicas>
Where:
- deployment is the name of the Deployment you want to scale.
- replicas is the number of replicas you want to define for the specified Deployment.
For example:
$ kubectl scale deployment node-worker --replicas=3
$ kubectl get deployment node-worker
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
node-worker 3/3 3 3 1m
Auto-scaling Deployments
To automatically scale your Deployment and distribute the load by increasing the number of Pods, you can use the kubectl autoscale command as follows:
$ kubectl autoscale deployment <deployment> --cpu-percent=<percent> --min=<min> --max=<max>
Where:
- percent is the average CPU usage percentage.
- min is the minimum number of Pod replicas.
- max is the maximum number of Pod replicas.
When executing this command, Kubernetes will automatically increase the number of Pods if the average CPU utilization per Pod is higher than the specified percentage.
For example:
$ kubectl autoscale deployment node-worker --cpu-percent=80 --min=1 --max=3
Easily retrieve these commands using Warp's AI Command Suggestions feature
If you’re using Warp as your terminal, you can easily retrieve this command using the Warp AI Command Suggestions feature:
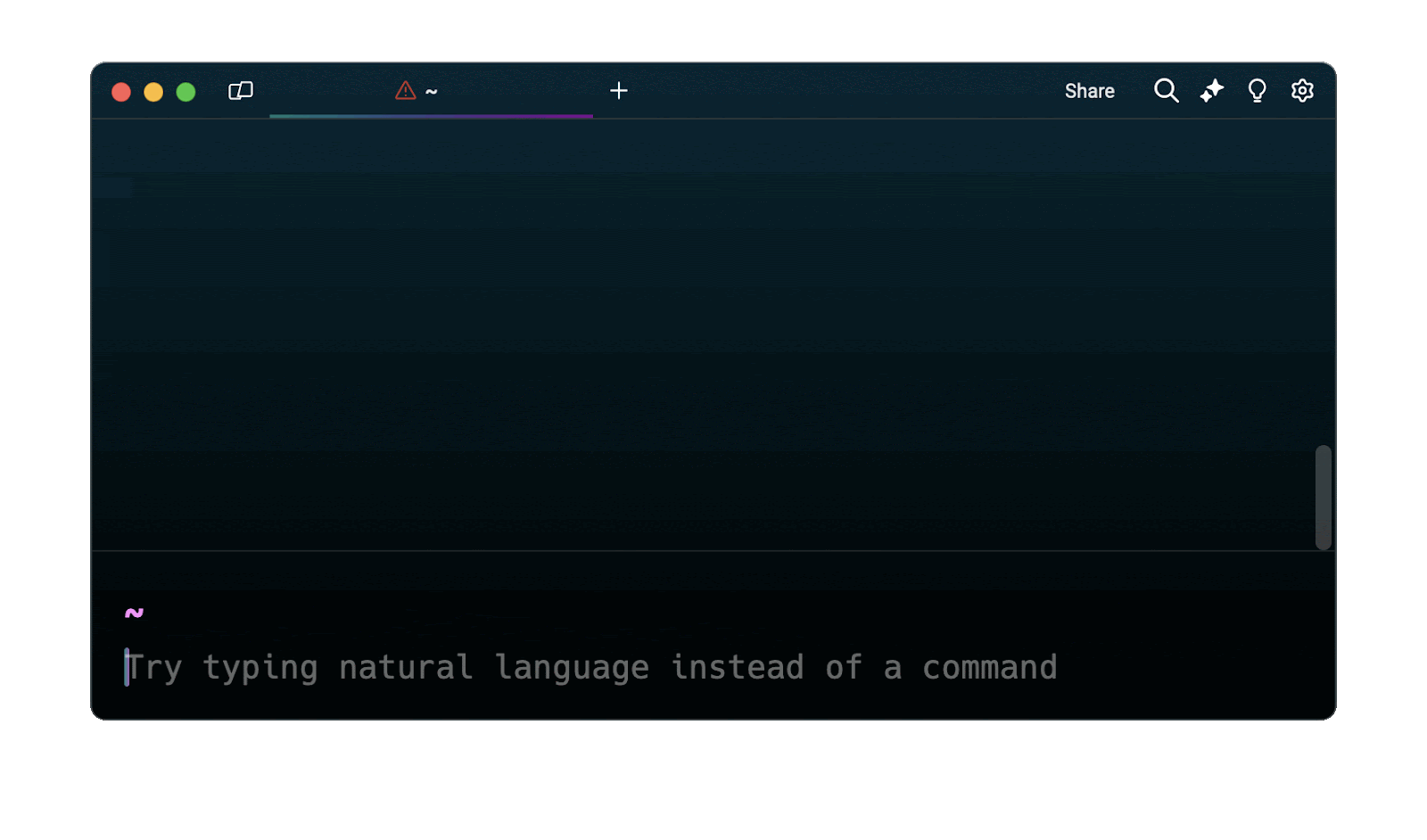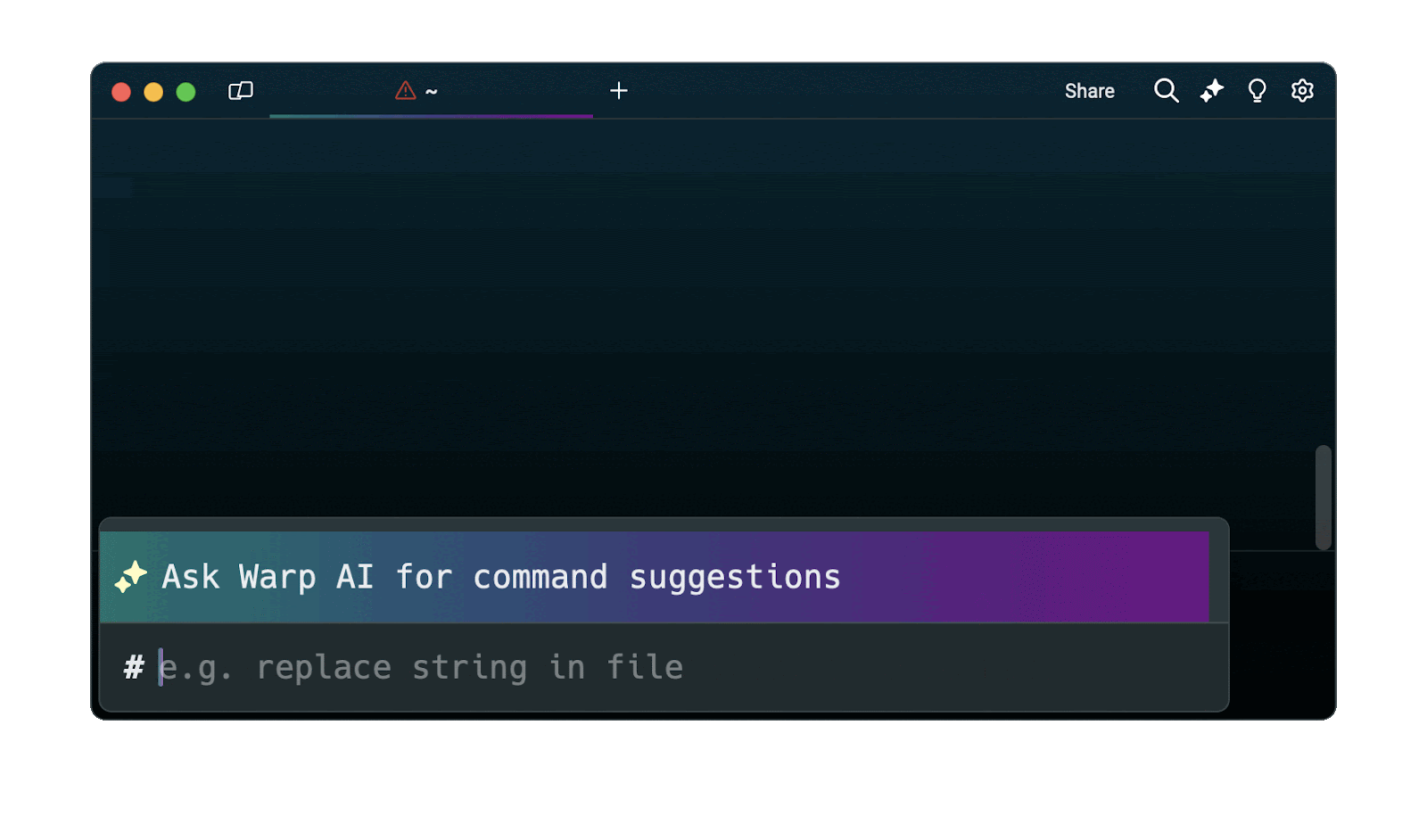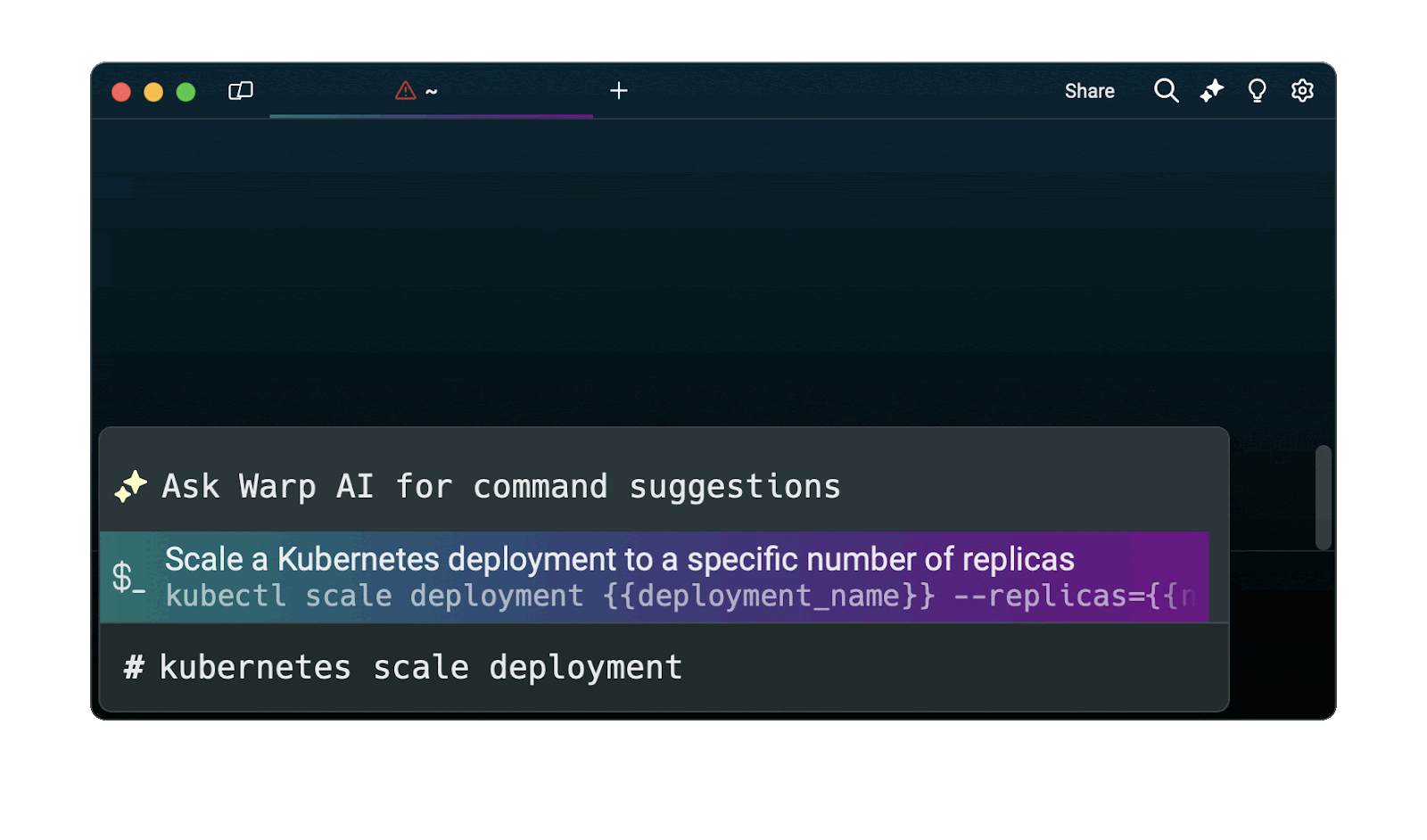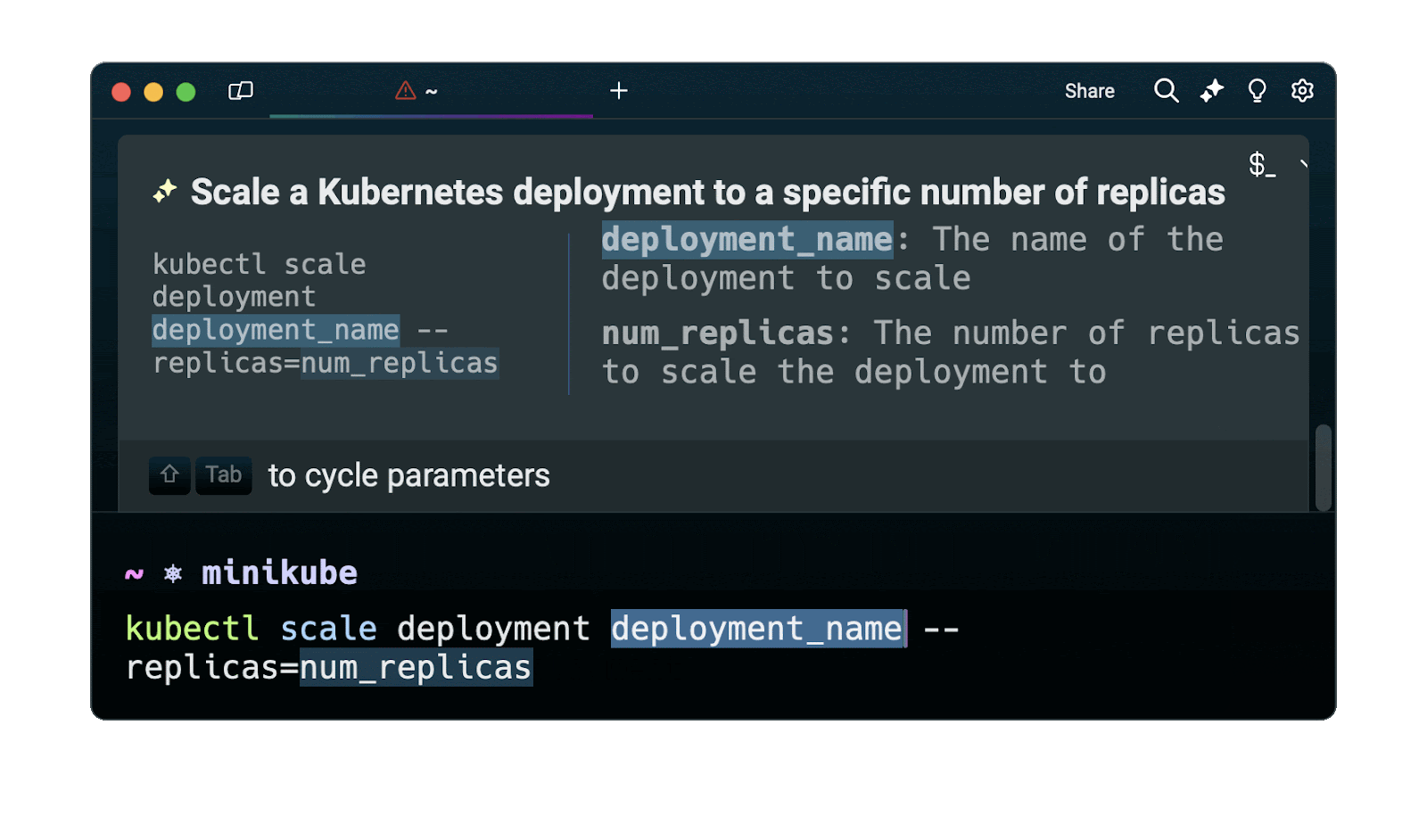
Entering kubernetes scale deployment in the AI Command Suggestions will prompt a kubectl command that can then quickly be inserted into your shell by doing CMD+ENTER.
Written by

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Filed Under
Related Articles
Copy Files From Pod in Kubernetes
Learn how to copy files and directories from within a Kubernetes Pod into the local filesystem using the kubectl command.

Get Kubernetes Logs With kubectl
Learn how to get the logs of pods, containers, deployments, and services in Kubernetes using the kubectl command. Troubleshoot a cluster stuck in CrashloopBackoff, ImagePullBackoff, or Pending error states.

Forward Ports In Kubernetes
Learn how to forward the ports of Kubernetes resources such as Pods and Services using the kubectl port-forward command.
Tail Logs In Kubernetes
Learn how to tail and monitor Kubernetes logs efficiently to debug, trace, and troubleshoot errors more easily using the kubectl command.
Get Context In Kubernetes
Learn how to get information about one or more contexts in Kubernetes using the kubectl command.
Delete Kubernetes Namespaces With kubectl
Learn how to delete one or more namespaces and their related resources in a Kubernetes cluster using the kubectl command.
Get Kubernetes Secrets With kubectl
Learn how to list, describe, customize, sort and filter secrets in a Kubernetes cluster by name, type, namespace, label and more using the kubectl command.

List Kubernetes Namespaces With kubectl
Learn how to list, describe, customize, sort and filter namespaces in a Kubernetes cluster by name, label, and more using the kubectl command.

How To List Events With kubectl
Learn how to list and filter events in Kubernetes cluster by namespace, pod name and more using the kubectl command.

Kubernetes vs Docker: The Backbone of Modern Backend Technologies
Lean the fundamentals of the Kubernetes and Docker technologies and how they interplay with each other.

Set Context With kubectl
Learn how to create, modify, switch, and delete a context in Kubernetes using the kubectl config command.

List Pods With kubectl
Learn how to list and filter Kubernetes Pods by name, namespaces, labels, manifests, and more using the kubectl command.

