In Kubernetes, a context is a combination of a cluster, a user and a namespace, which defines the operational environment for interacting with a Kubernetes cluster.
The short answer
In Kubernetes, to get concise information about all the existing contexts defined in the kubeconfig file, such as their cluster name, user name and namespace, you can use the kubectl config command with the get-contexts subcommand as follows:
$ kubectl config get-contexts
Once executed, this command will produce an output similar to the following one, where the current context is identified by an asterisk ( * ):
CURRENT NAME CLUSTER AUTHINFO NAMESPACE
* dev-context dev-cluster dev-user development
staging-context staging-cluster staging-user staging
prod-context prod-cluster prod-user production
Easily retrieve this command using Warp’s AI Command Suggestions
If you’re using Warp as your terminal, you can easily retrieve this command using the Warp AI Command Suggestions feature:
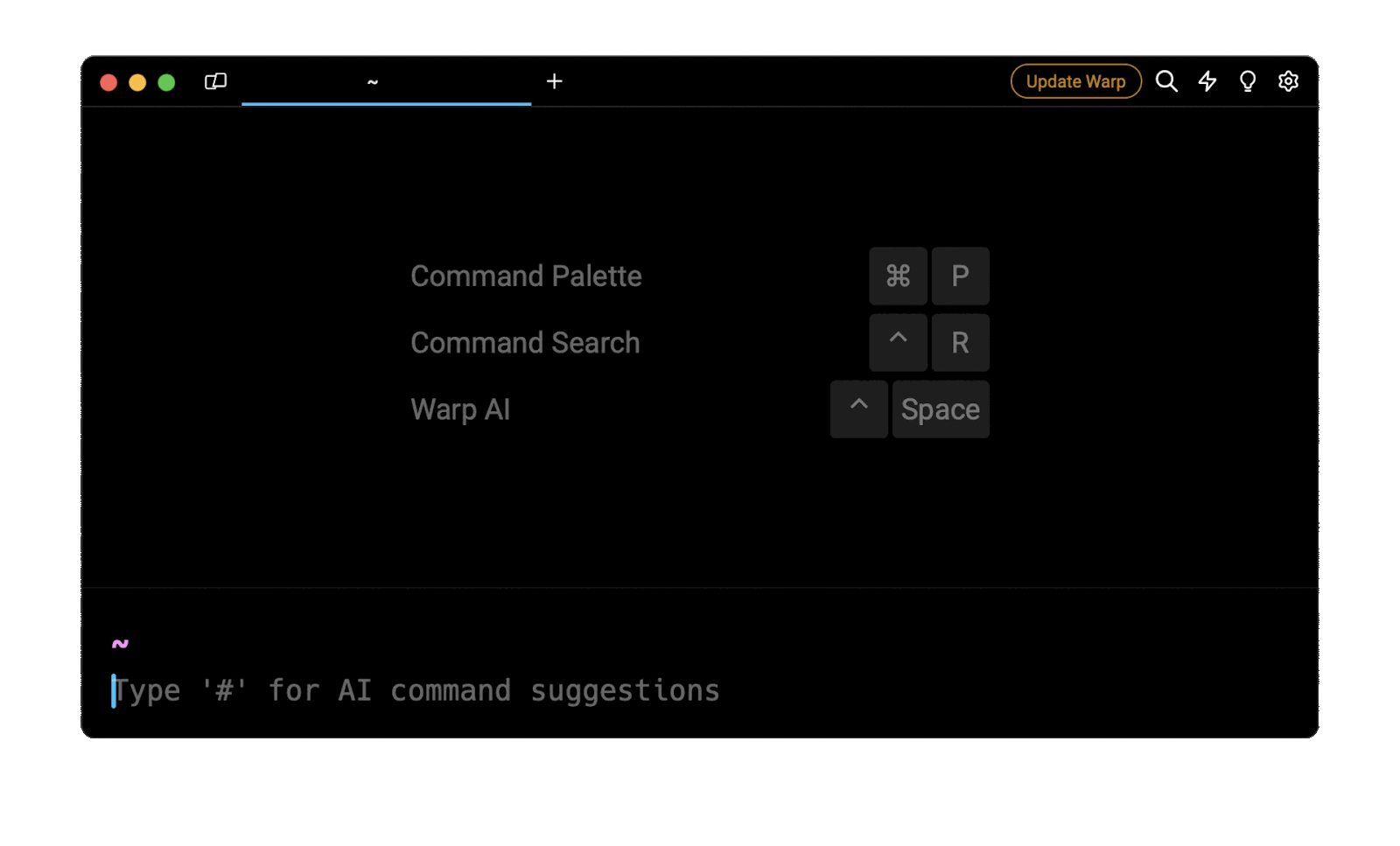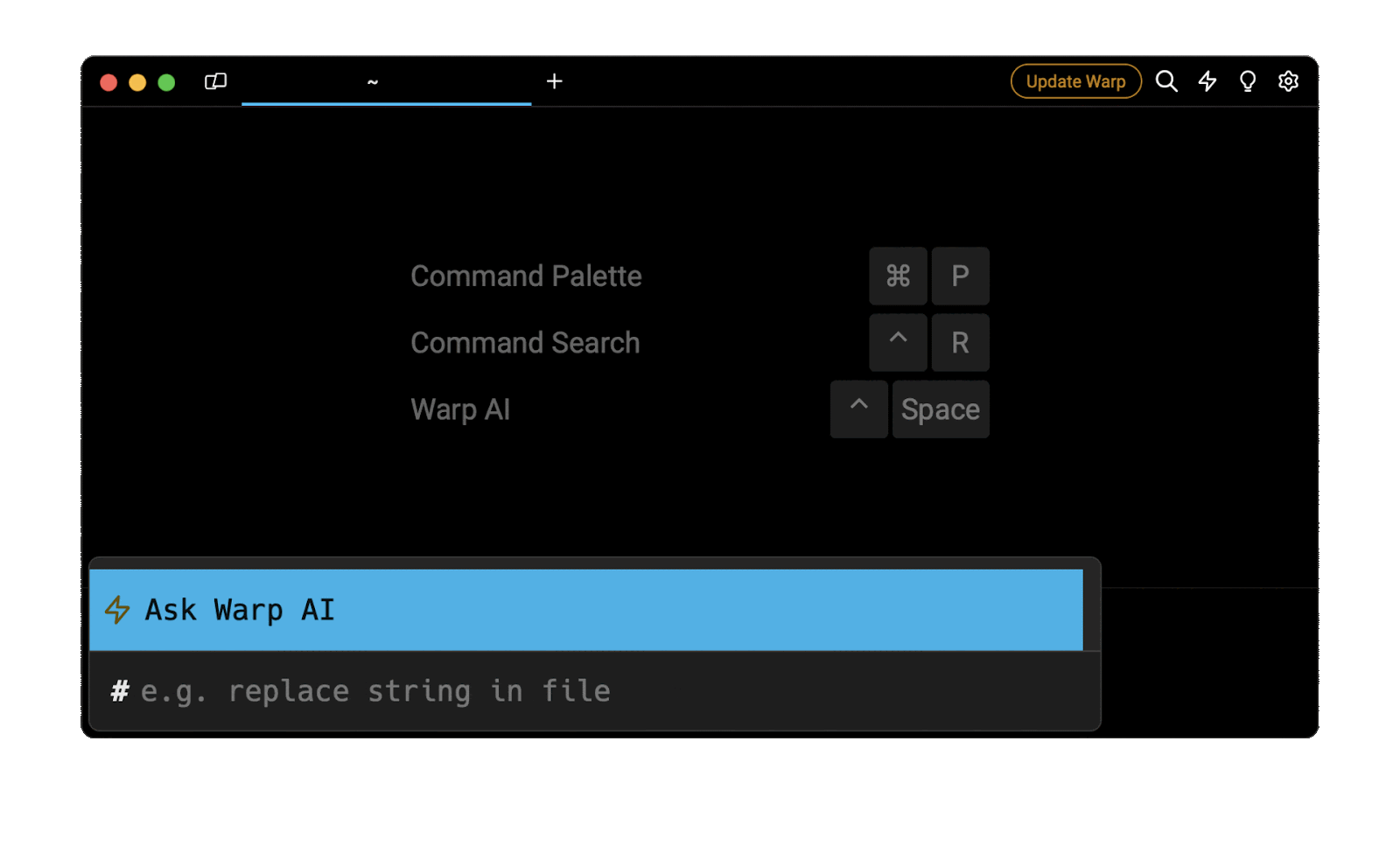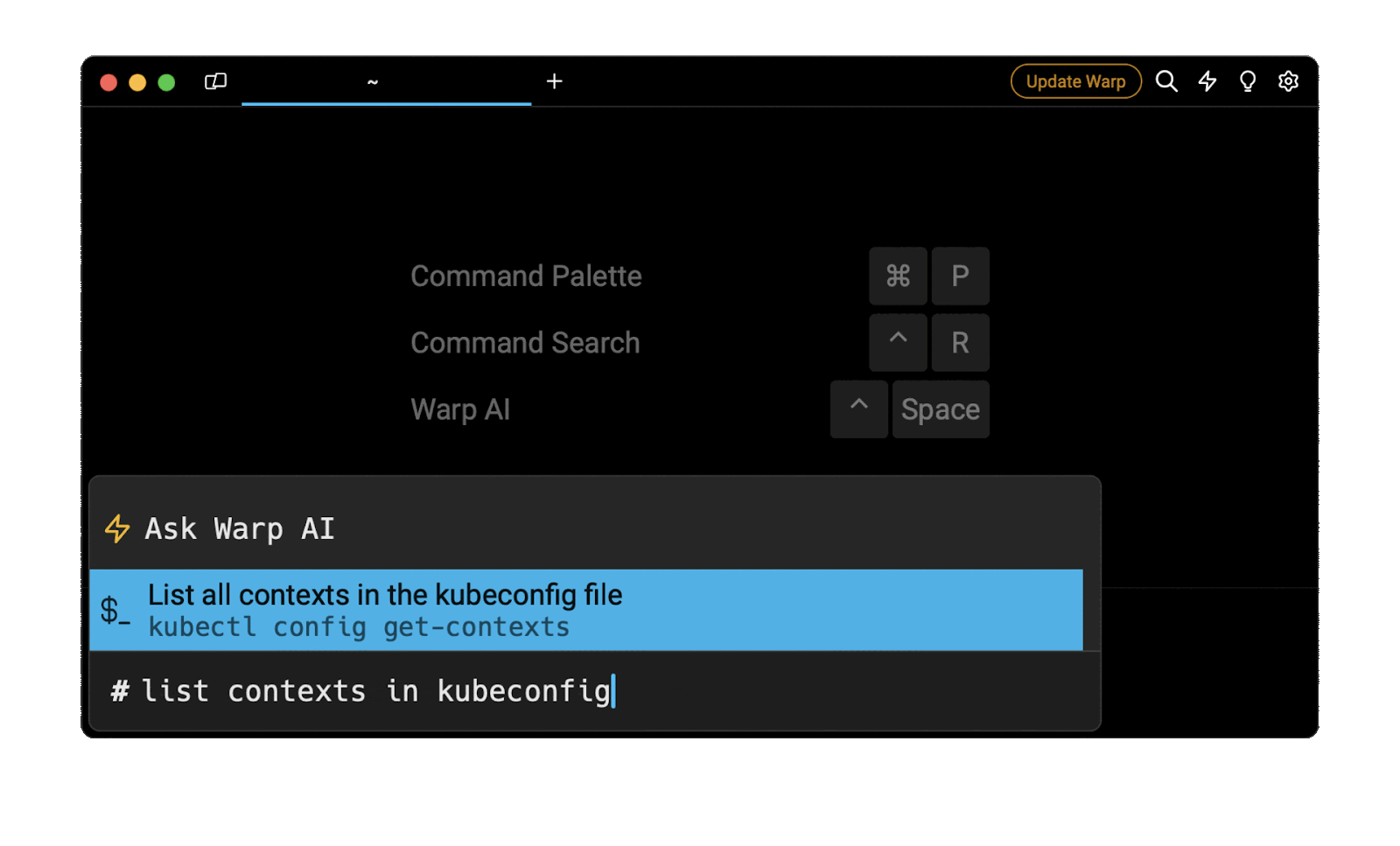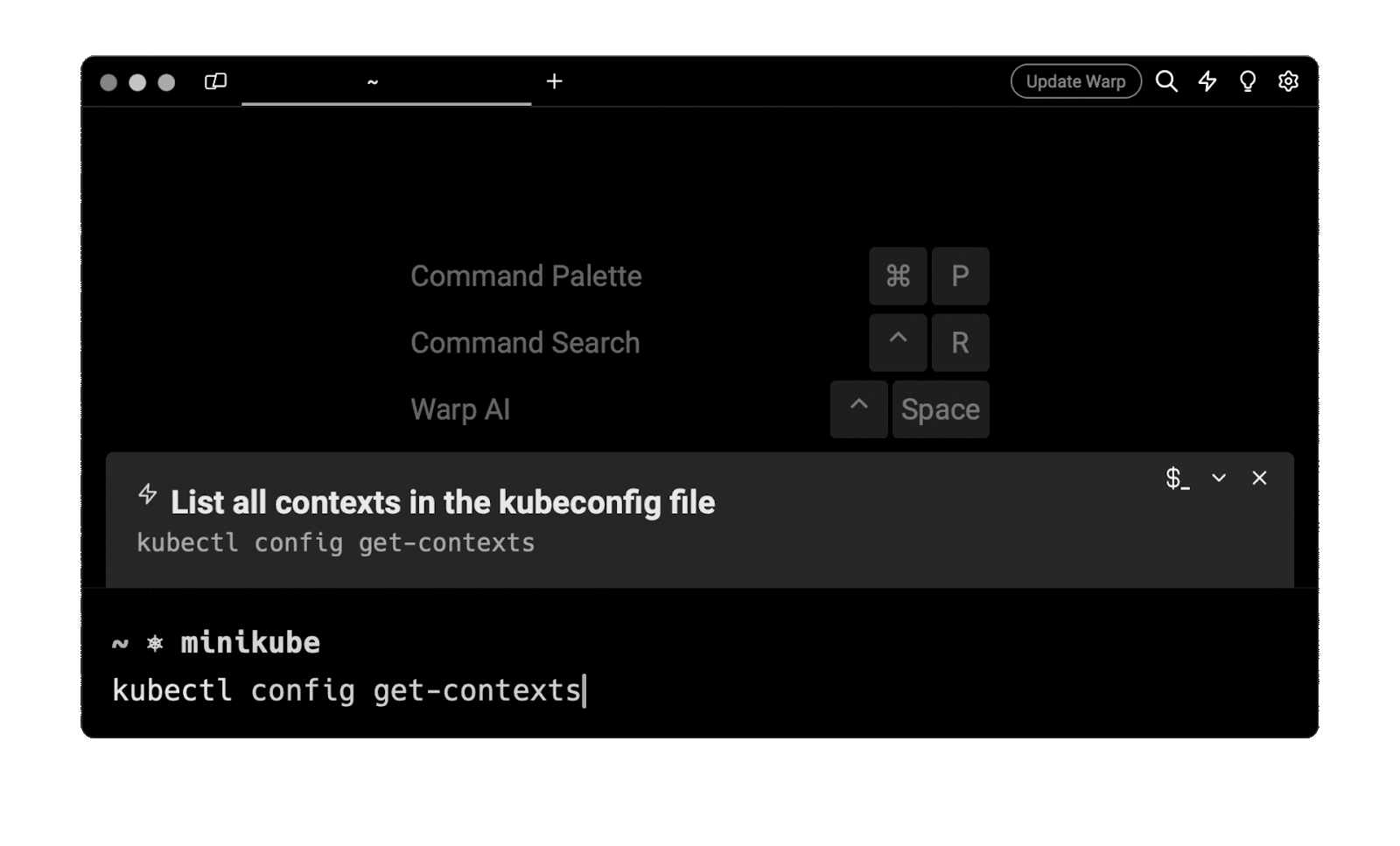
Entering list contexts in kubeconfig in the AI Command Suggestions will prompt a kubectl command that can then quickly be inserted into your shell by doing CMD+ENTER .
Getting information about the current context
To get information about the current context, you can use the current-context subcommand as follows:
$ kubectl config current-context
Getting information about a specific context
To get information about a specific context, you can use the get-contexts subcommand as follows:
$ kubectl config get-contexts <context_name>
Where:
- context_name is the name of the context.
For example, the following command will display the information related to the context named staging-context :
$ kubectl config get-contexts staging-context
If you want to learn more about modifying existing contexts in Kubernetes, you can read our other article on how to set a context with kubectl.
Getting comprehensive context overview
To output a comprehensive overview of the kubeconfig file settings, including information about clusters, users, API servers and more, you can use the view subcommand as follows:
$ kubectl config view
Note that, by default, this command will output information in the YAML format.
To output it in the JSON format instead, you can use the -o flag (short for --output ) as follows:
$ kubectl config view -o json
Viewing the details of the current context
To only output the detailed overview of the current context, you can use the --minify flag as follows:
$ kubectl config view --minify
Viewing the details of a specific context
To only output the detailed overview of a specific context, you can combine the --minify flag with the --context flag as follows:
$ kubectl config view --minify --context=<context_name>
Retrieving context properties
To retrieve a particular property from a specific context, you can use the -o jsonpath flag combined with a JSONPath expression as follows:
$ kubectl config view --minify -o jsonpath='{..<property>}'
Where:
- property is the name of the property you want to retrieve (e.g., cluster , user , namespace , etc).
Retrieving the namespace of the current context
To retrieve the namespace of the current context, you can use the aforementioned command with the following JSONPath expression:
$ kubectl config view --minify -o jsonpath='{..namespace}'
Retrieving the namespaces of all contexts
To retrieve the namespaces of all the contexts defined in kubeconfig file in the form of a list, you can use the aforementioned command with the following JSONPath expression:
$ kubectl config view --minify -o jsonpath='{.contexts[*].context.namespace}'
Alternatively, to also retrieve the name of the context each namespace is associated to, you can use the following for loop instead:
$ for context in $(kubectl config get-contexts -o name); do
namespace=$(kubectl config view -o jsonpath="{.contexts[?(@.name == \"${context}\")].context.namespace}")
echo "Context: $context, Namespace: ${namespace:-default}"
done
Where:
-
The for loop iterates over the list of context names returned by the kubectl config get-contexts -o name command.
-
Retrieves the namespace related to that context using the kubectl config view -o jsonpath="{.contexts[?(@.name == "${context}")].context.namespace}" command.
-
Outputs the context name and namespace using the echo command.
Getting information about the resources of a specific context
To get information on a resource type related to a specific context, you can use the kubectl get command with the --context flag as follows:
$ kubectl get <resource_type> --context <context_name>
Where:
-
resource_type is the name of the resource type (e.g., pods , nodes , services , etc).
-
context_name is the name of the context.
For example, the following command will output information about the Services related to the context named staging-context :
$ kubectl get services --context staging-context
Written by
Muhammad Khabbab
Filed Under
Related Articles
Copy Files From Pod in Kubernetes
Learn how to copy files and directories from within a Kubernetes Pod into the local filesystem using the kubectl command.

Scale Deployments in Kubernetes
Learn how to manually and automatically scale a Deployment based on CPU usage in Kubernetes using the kubectl-scale and kubectl-autoscale commands.

Get Kubernetes Logs With kubectl
Learn how to get the logs of pods, containers, deployments, and services in Kubernetes using the kubectl command. Troubleshoot a cluster stuck in CrashloopBackoff, ImagePullBackoff, or Pending error states.

Forward Ports In Kubernetes
Learn how to forward the ports of Kubernetes resources such as Pods and Services using the kubectl port-forward command.
Tail Logs In Kubernetes
Learn how to tail and monitor Kubernetes logs efficiently to debug, trace, and troubleshoot errors more easily using the kubectl command.
Delete Kubernetes Namespaces With kubectl
Learn how to delete one or more namespaces and their related resources in a Kubernetes cluster using the kubectl command.
Get Kubernetes Secrets With kubectl
Learn how to list, describe, customize, sort and filter secrets in a Kubernetes cluster by name, type, namespace, label and more using the kubectl command.

List Kubernetes Namespaces With kubectl
Learn how to list, describe, customize, sort and filter namespaces in a Kubernetes cluster by name, label, and more using the kubectl command.

How To List Events With kubectl
Learn how to list and filter events in Kubernetes cluster by namespace, pod name and more using the kubectl command.

Kubernetes vs Docker: The Backbone of Modern Backend Technologies
Lean the fundamentals of the Kubernetes and Docker technologies and how they interplay with each other.

Set Context With kubectl
Learn how to create, modify, switch, and delete a context in Kubernetes using the kubectl config command.

List Pods With kubectl
Learn how to list and filter Kubernetes Pods by name, namespaces, labels, manifests, and more using the kubectl command.

