Create Folder In GitHub Repository

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Published: 2/1/2024
By default, Git is designed to track the content of only files. If a directory has no files in it, Git presumes there is nothing to be tracked. This means that directories exist in Git only implicitly through their contents.
The short answer
Since Git only tracks content, a common way for developers to push an (almost) empty directory to an initialized Git repository is to create an empty .placeholder file within that directory.
For example, if you want to push an empty directory named config, you can start by creating it using the mkdir command:
$ mkdir config
Then you can create an empty .placeholder file within it using the touch command:
$ touch config/.placeholder
Finally, you can commit this new file to the repository using the following git commands:
$ git add config/.placeholder
$ git commit -m "Create empty config directory"
And finally push it out using git push origin
$ git push origin main
This will, by extension, also commit the config directory to preserve the file structure of your repository.
Note that although the result is the same, it is also possible to use an empty README.md file instead of a .placeholder file, or any other empty file for that matter as long as it is tracked by Git.
Easily retrieve this command using Warp’s AI Command Search
If you’re using Warp as your terminal, you can easily retrieve this command using the Warp AI Command Search feature:
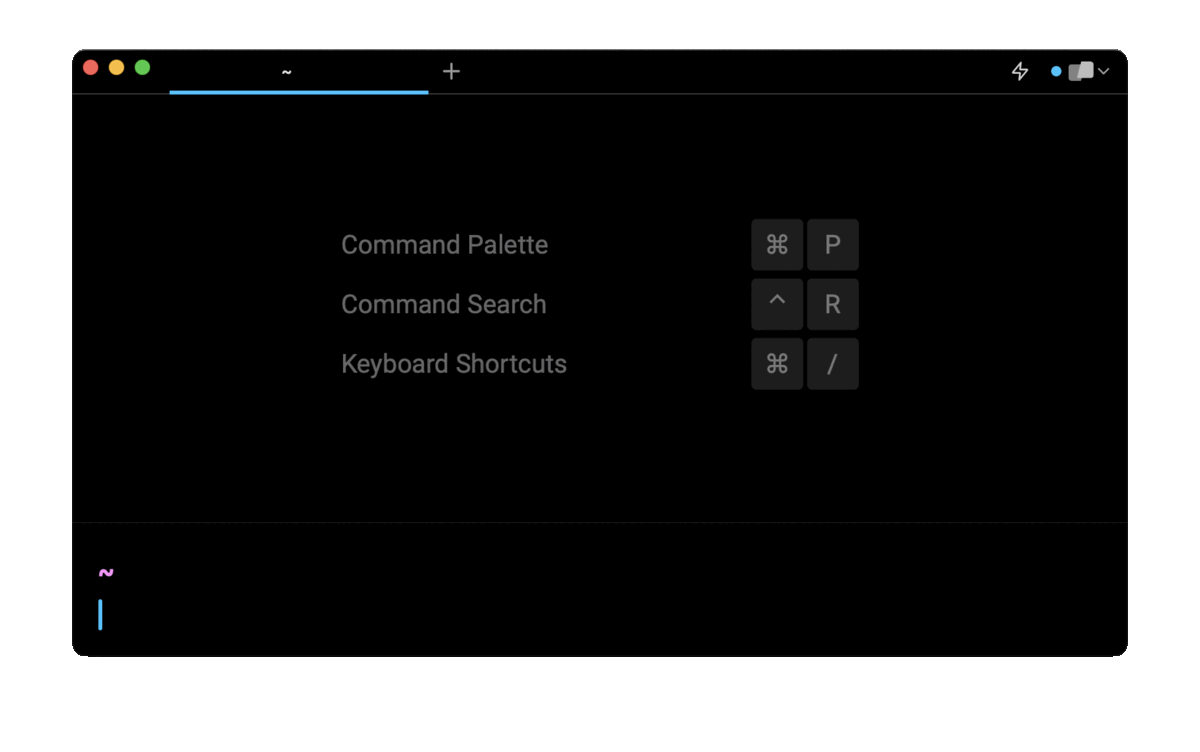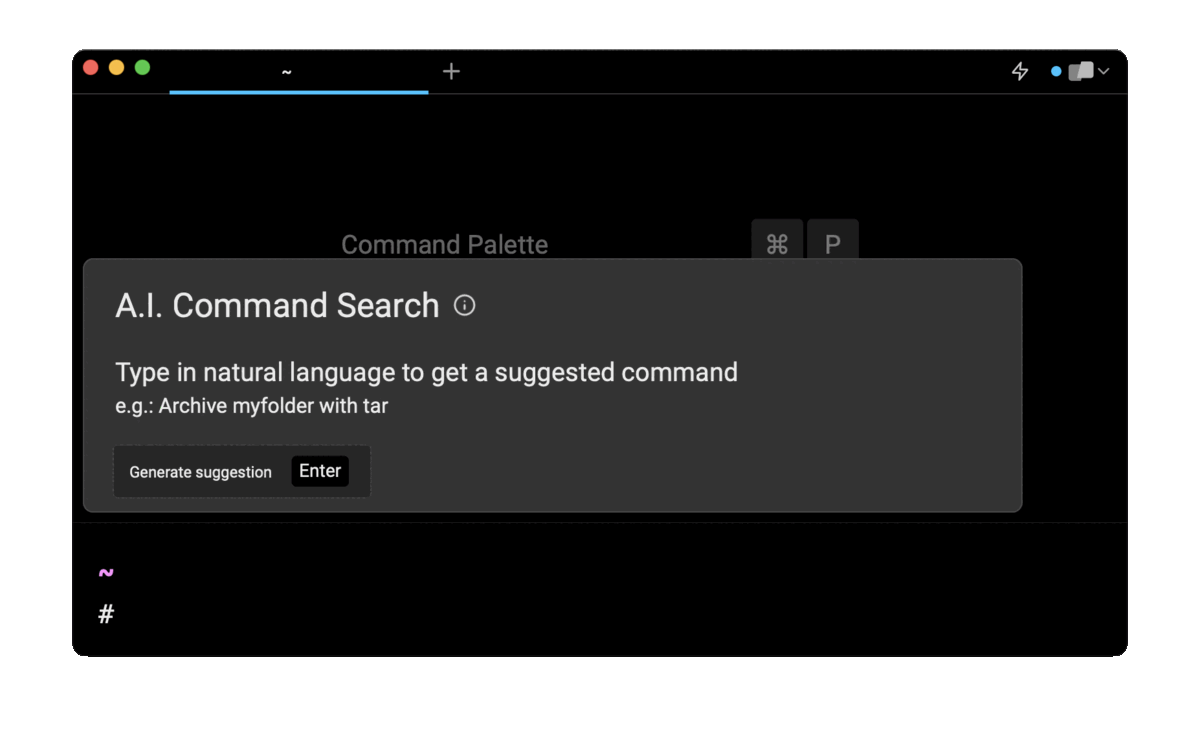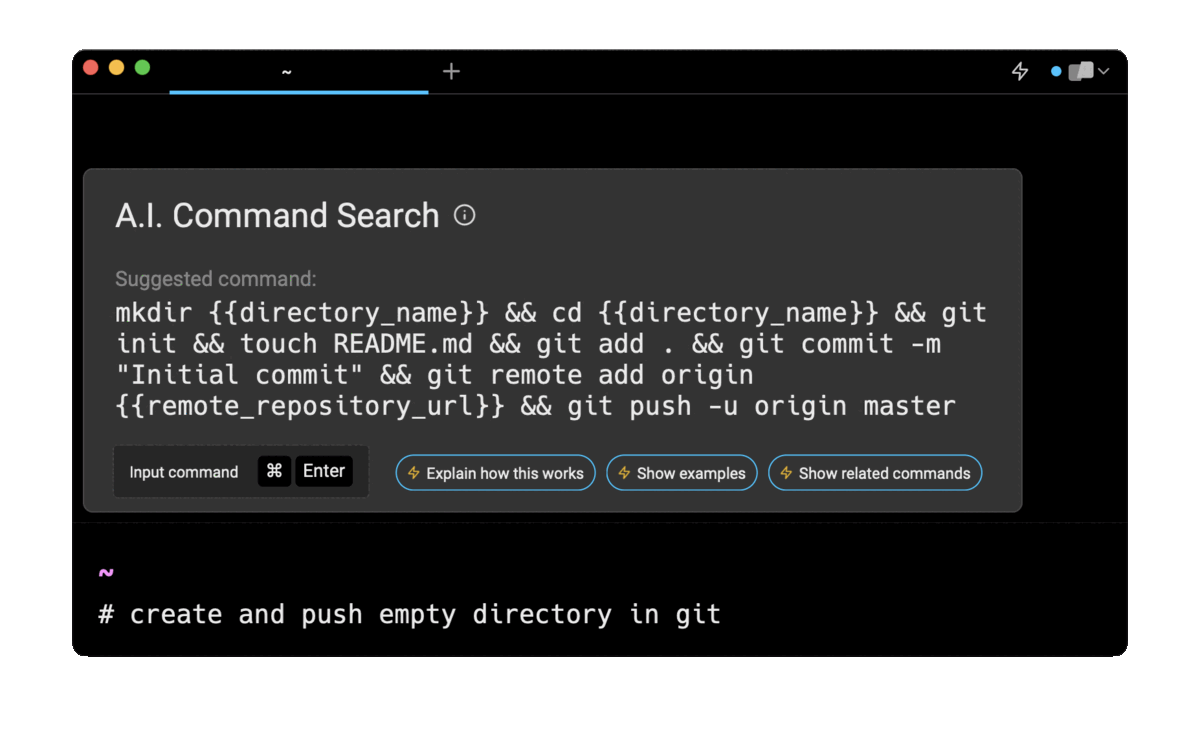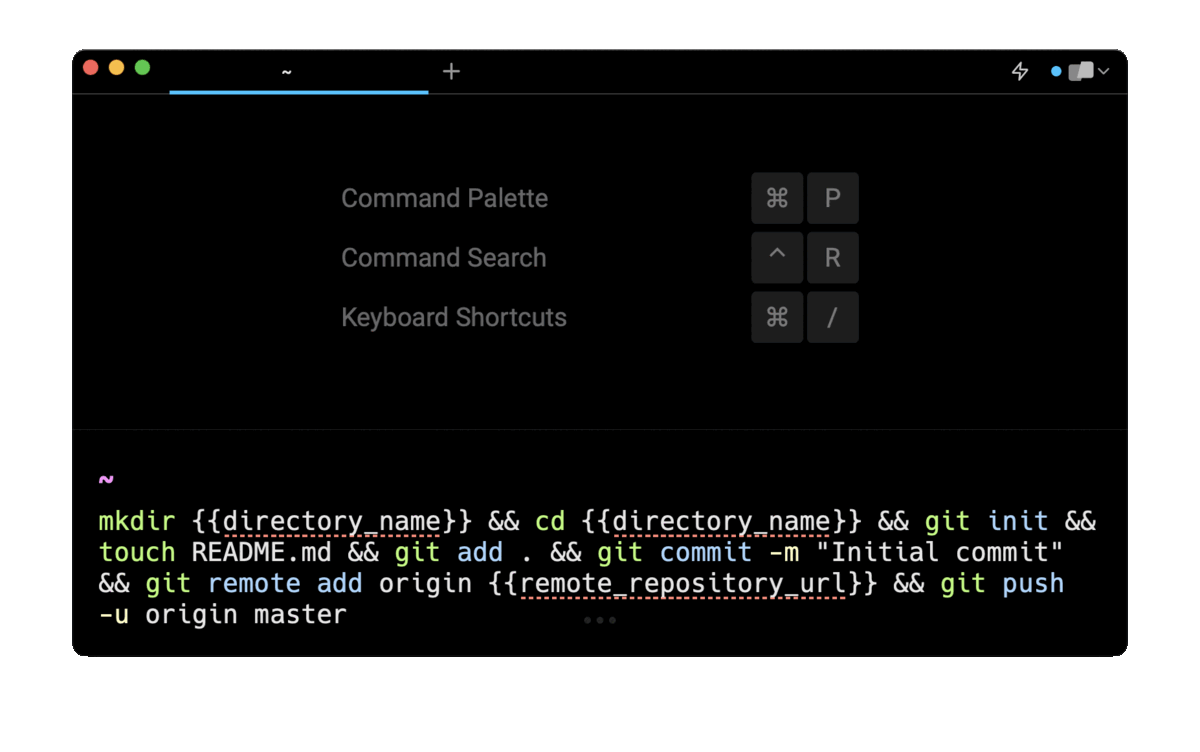
Entering create and push empty directory in git in the AI Command Search will prompt a one-line command that can then quickly be inserted into your shell by doing CMD+ENTER.
Note that if your repository is already initialized, you can remove the git init instruction from the suggested command.
A word on the .gitkeep file
In some cases, you might see developers using a .gitkeep file instead of a .placeholder or README.md file.
Since this file has not explicitly been prescribed by Git (it has no actual meaning, unlike the .gitignore file, for instance), I strongly discourage you from using it as it often leads to confusion, making people second guess its utility.
As a rule of thumb, the .git prefix should be reserved for files that Git itself officially uses.
Pushing multiple empty folders at once
To push multiple empty folders at once on a Git repository, you can either create a .placeholder file in the very last directory of the directory tree:
$ touch dir_1/dir_2/.placeholder
Or you can create a .placeholder file in each directory using a brace expansion
$ touch {dir_1,dir_2}/.placeholder
Then use the aforementioned git-add, git-commit and git-push commands.
How to add a folder via the GitHub UI
If you are using nvm as your Node.js version manager, you can update npm to the latest version supported by your current Node.js distribution in use with the following nvm command:
$ nvm install-latest-npm
To create a new folder in Github, you can navigate to the desired repository, then:
- Click on the "Add file" button followed by the "Create new file" link in the dropdown menu.
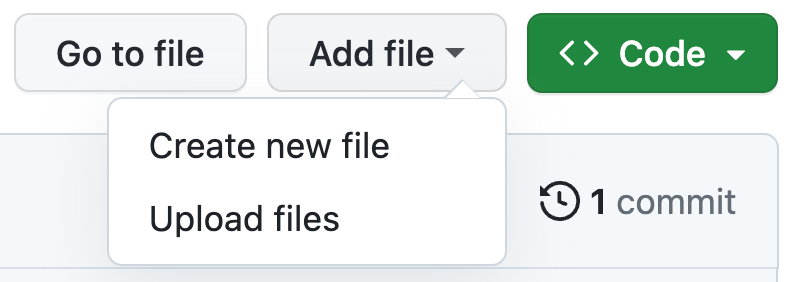
- Type the directory name followed by a slash character (e.g. empty_folder/).

- Type the file name.

-
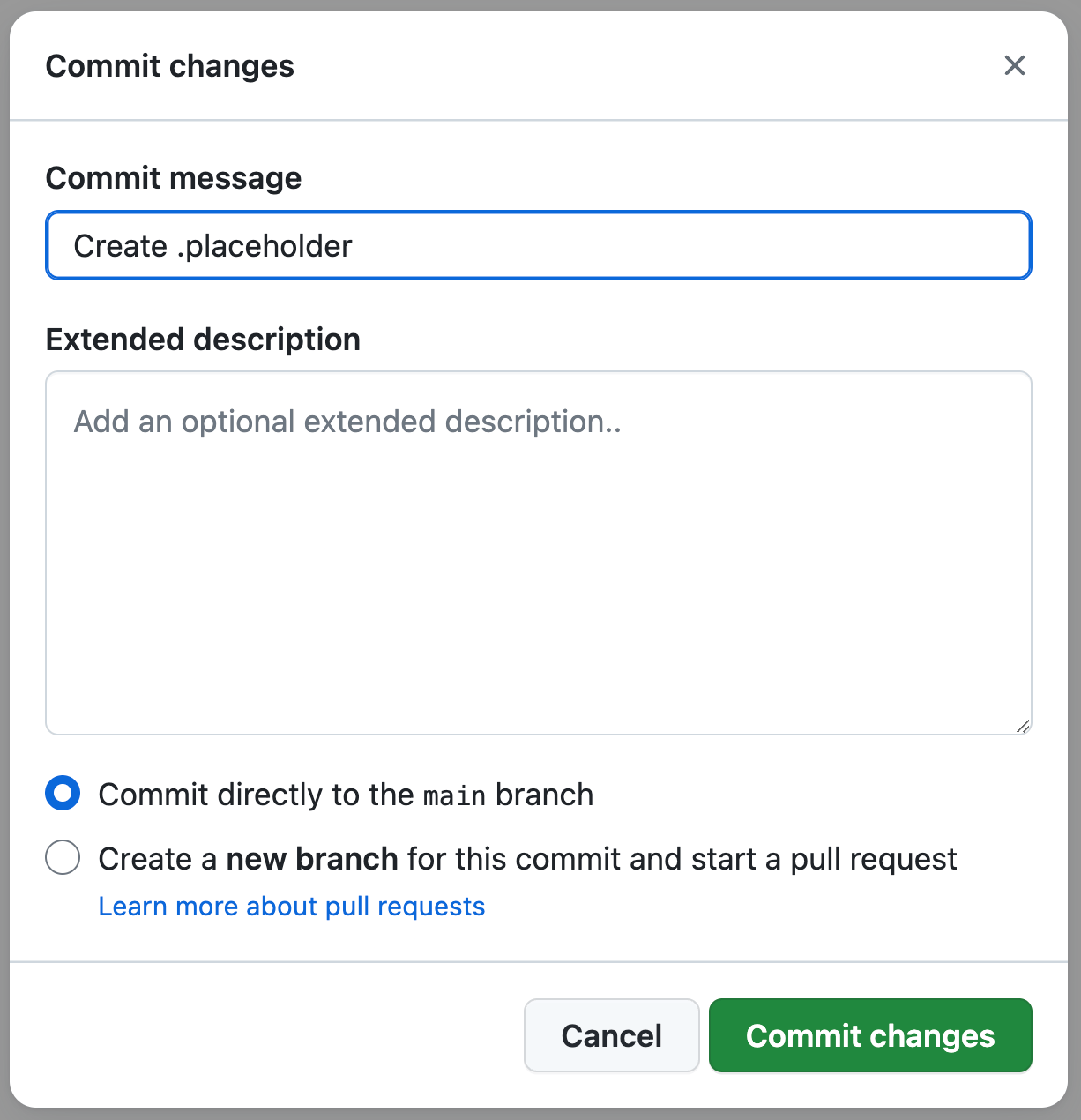
Click on the "Commit changes" button.
-
Write a commit message, select the branch to commit the files to, and click on the "Commit changes" button to save the changes.
How to upload a folder via the GitHub UI
To create a new folder in Github, you can navigate to the desired repository, then:
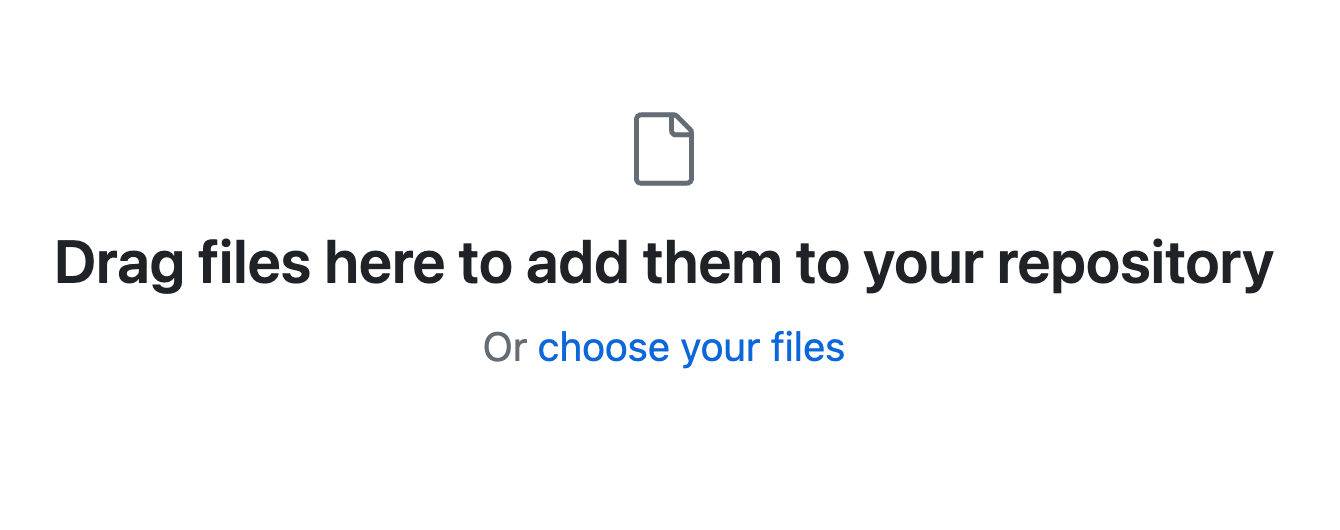
- Click on the "Add file" button followed by the "Upload files" link in the dropdown menu.

- Drag the folder you want to upload in that area.
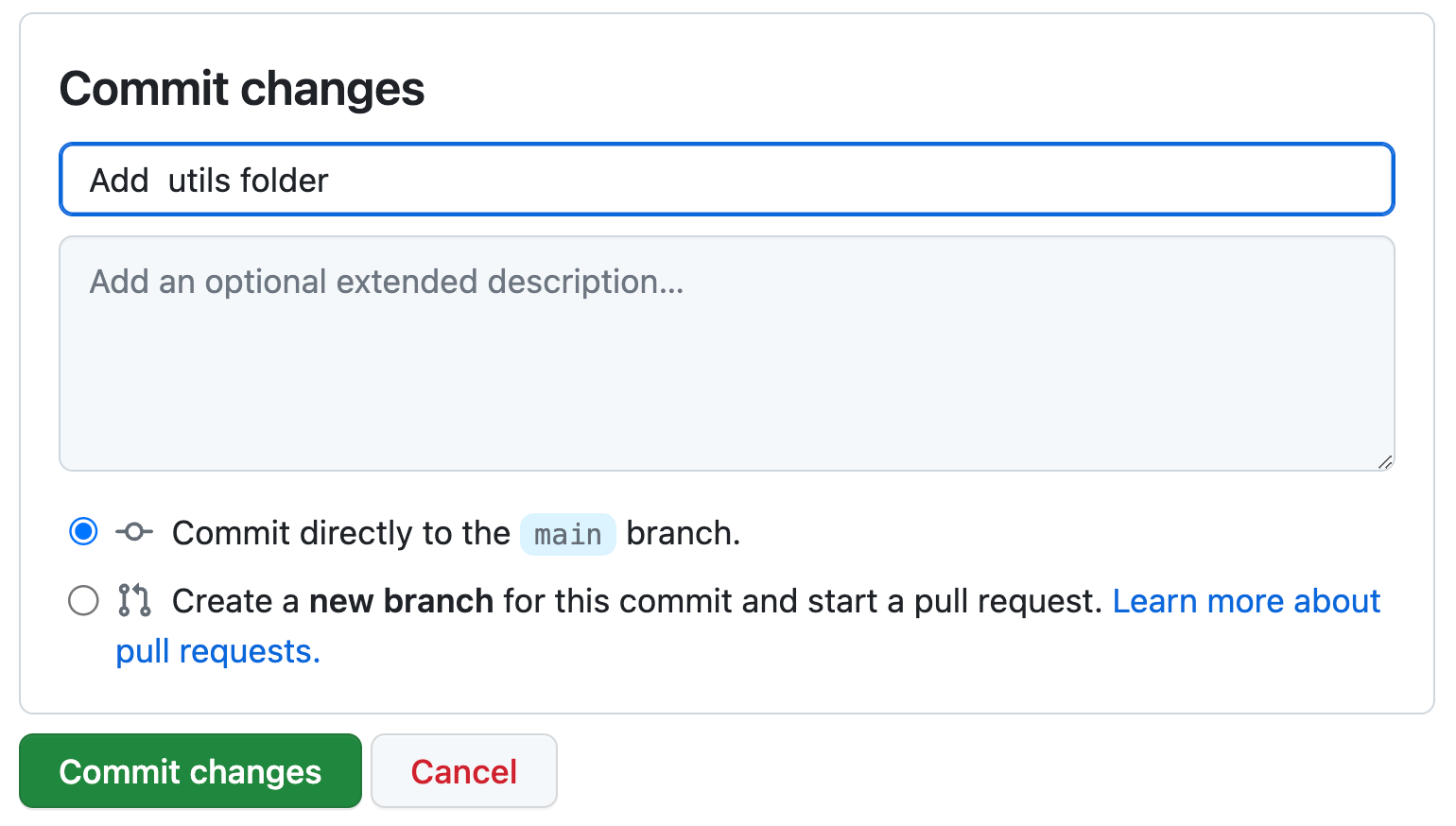
- Write a commit message, select the branch to commit the files to, and click on the "Commit changes" button to save the changes.
Written by

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Filed Under
Related Articles
Undo A Git Pull
How to effectively remove the commits introduced by a pull in Git using git-reset and preserve your local changes using git-stash. Also, how to cancel an unmerged pull request on GitHub.

Undo a Git Merge
How to rollback the changes introduced by a merge in Git by adding new opposite commits using git-revert and effectively removing commits using git-reset.

Prompt Show Git Branch In Prompt
Enhance your terminal with a custom Git prompt. Learn different ways to integrate this contextual info, from custom shell functions to Warp context chips and toolkits like Starship and P10K.

How To Remove Secrets From The Git History Remove Secrets From The Git History
Learn how to remove secrets from the Git history using the BFG and git-filter-repo command-line tools.

Adding a Submodule in Git
This post will show you how to simply add a submodule to a local repository, clone a repository with a submodule, and work within a repository that has a submodule.

Undo a git push
This post will show you had to simply undo a git push three different ways.

Undo Git Add
Learn how to effectively use 'git add' to stage files in Git for committing, and discover two powerful methods to undo accidental stagings.

Undo a Git Rebase
This post will show you how to undo a rebase using git reset, git rebase and git revert

Git Push Origin
A breakdown of git push origin

Git Push Tags
This post will show you how to push a single tag, multiple tags, all tags, and tags with commits.

Undoing Git Commits
Explore ways to undo a commit, including git reset, git checkout, and git revert with git while preserving commit history.

Delete Local Git Branch
Learn how to delete local branches from your git repository, including ones with unmerged changes, as well as local remote-tracking branches.

