The short answer
In Git, to discard all the changes made to your local repository by a pull, including the working directory and the staging area, you need to first identify the last commit hash before the pull using the git reflog command:
$ git reflog
Then reset the current branch to that commit using the git reset command as follows:
$ git reset --hard <commit>
Where:
- commit is a commit hash.
Alternatively, you can specify the commit number using the following syntax instead:
$ git reset --hard HEAD@{<number>}
Where:
- number is a commit number.
For example, the following command will reset the current branch to the commit identified by the hash b4173b7:
$ git reflog
3a5ccb8 HEAD@{1}: pull: Fast-forward
b4173b7 HEAD@{2}: commit: update home page content
d38d82f HEAD@{3}: commit: add login feature
$ git reset --hard b4173b7
Note that the following command is equivalent to the previous one:
$ git reset --hard HEAD@{2}
You can learn more about identifying local commits by reading our other article on how to navigate the commit history in Git.
Easily retrieve this command using Warp’s AI Command Suggestions
If you’re using Warp as your terminal, you can easily retrieve this command using the Warp AI Command Suggestions feature:
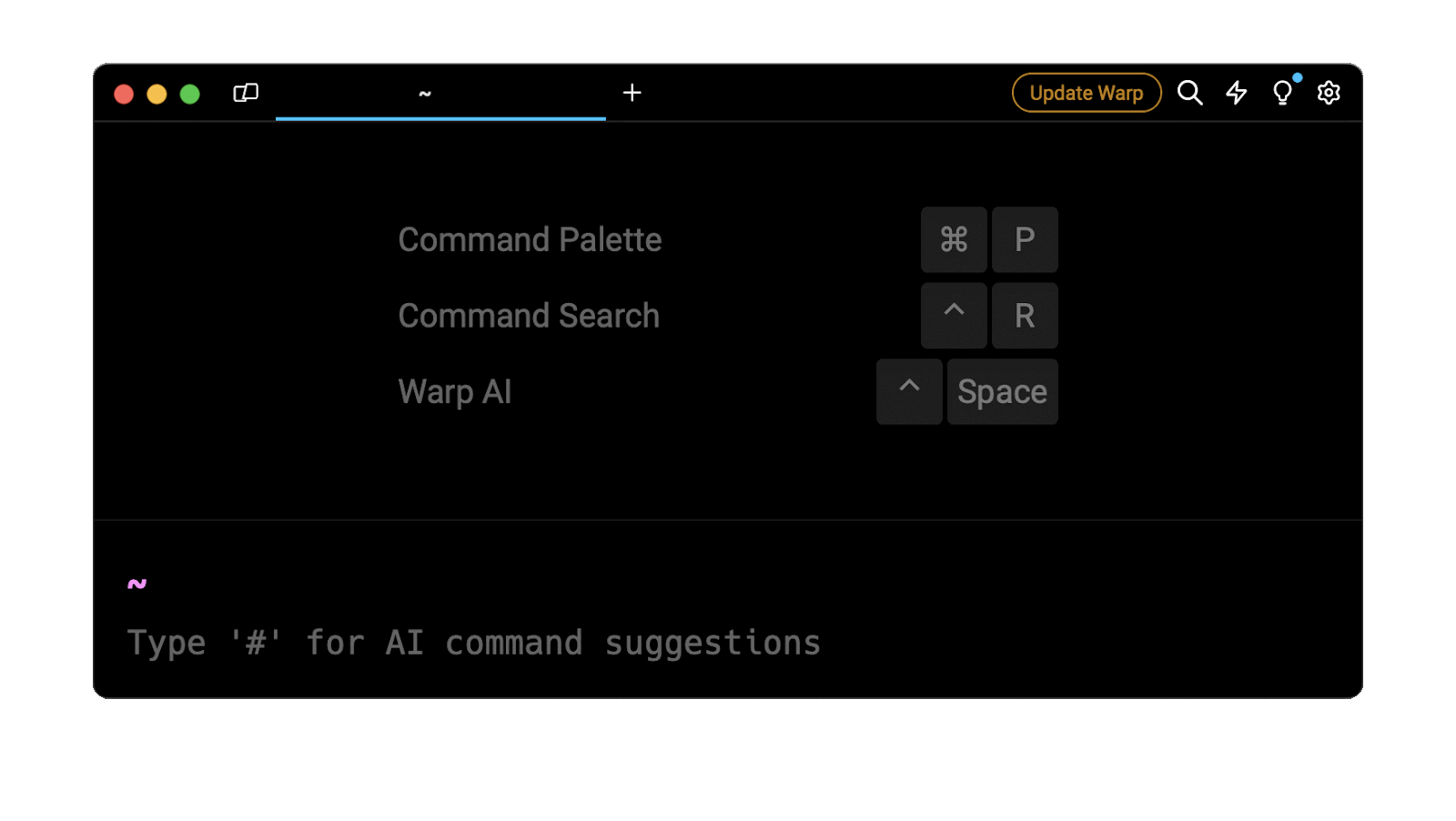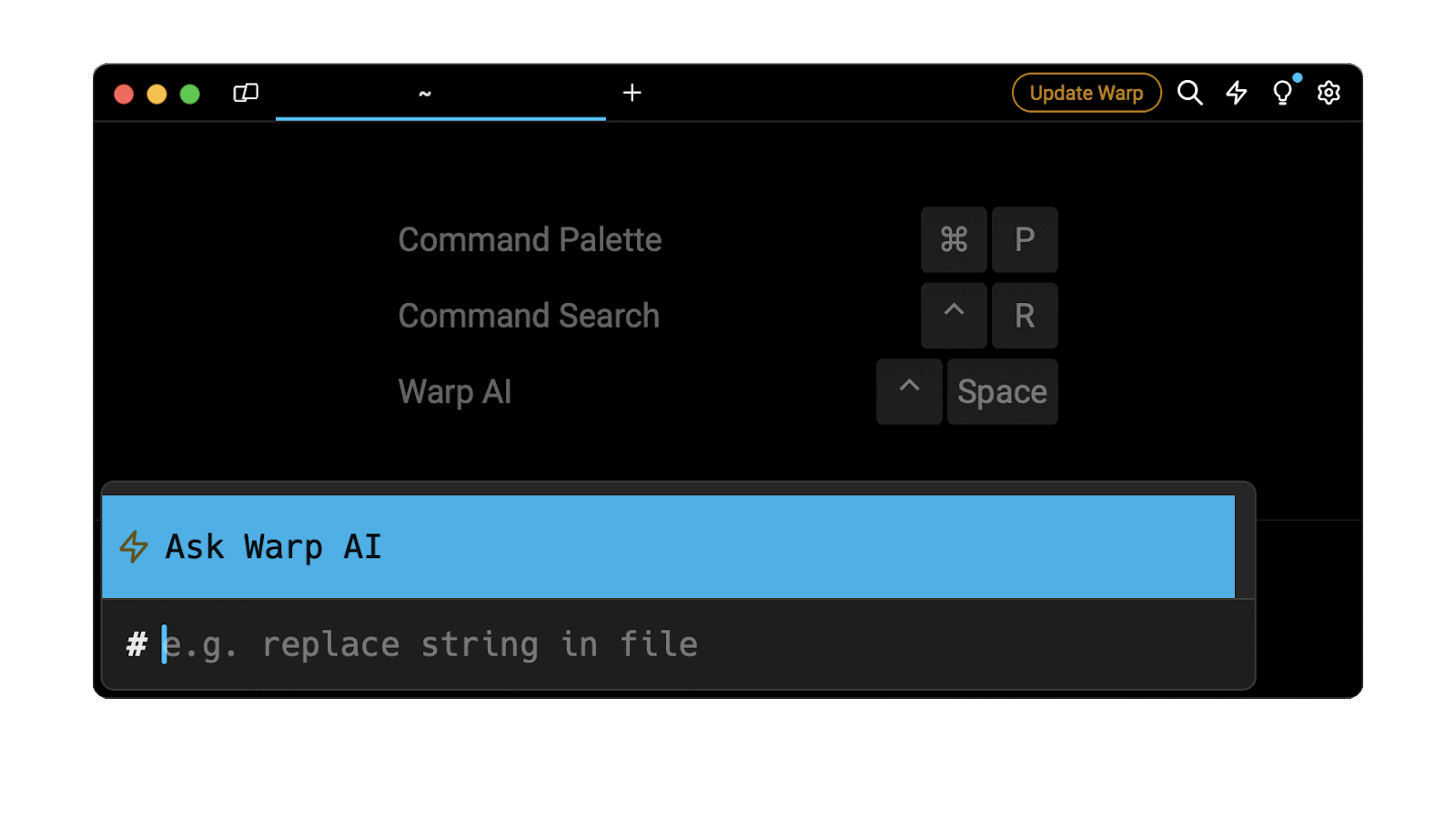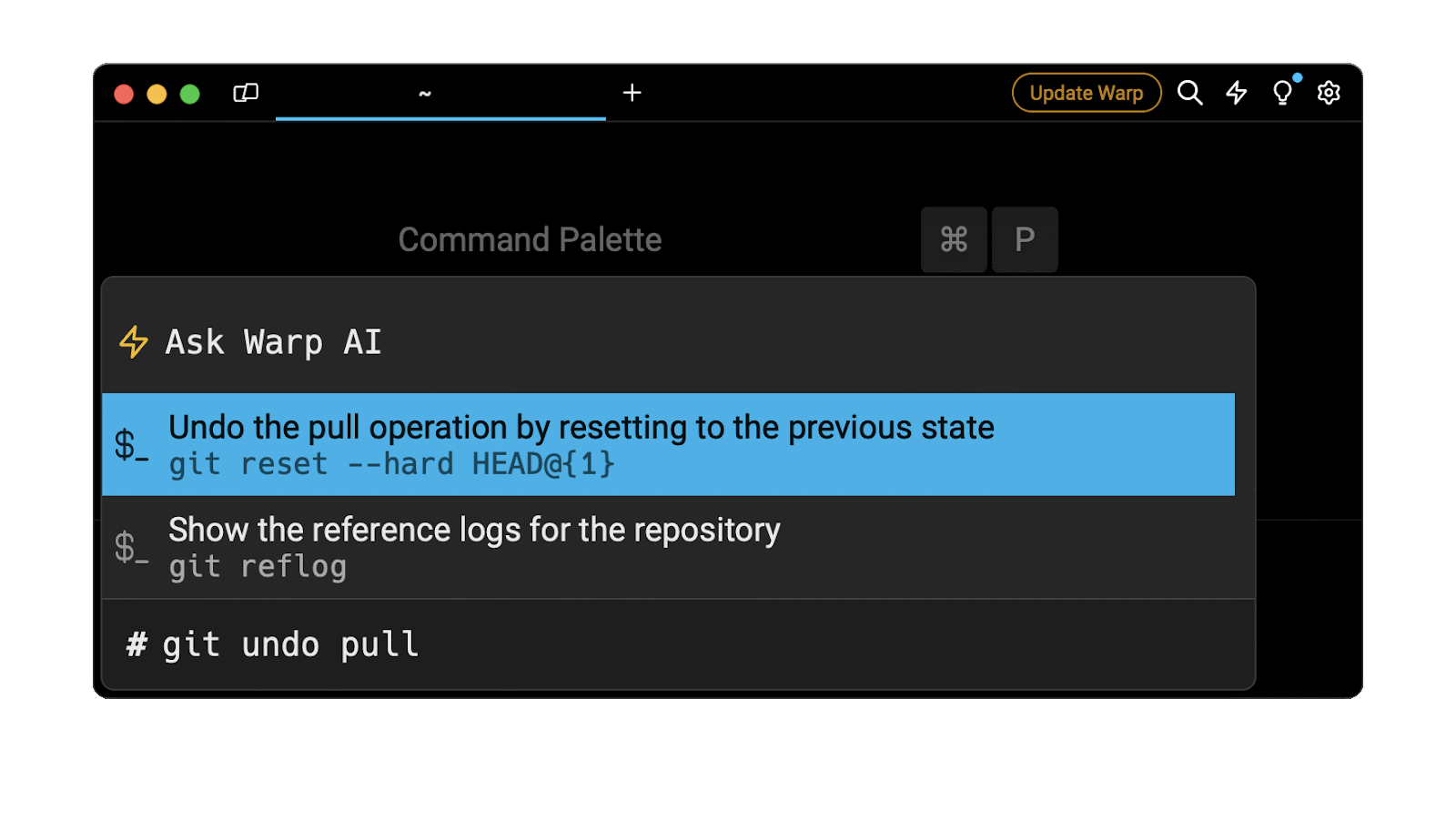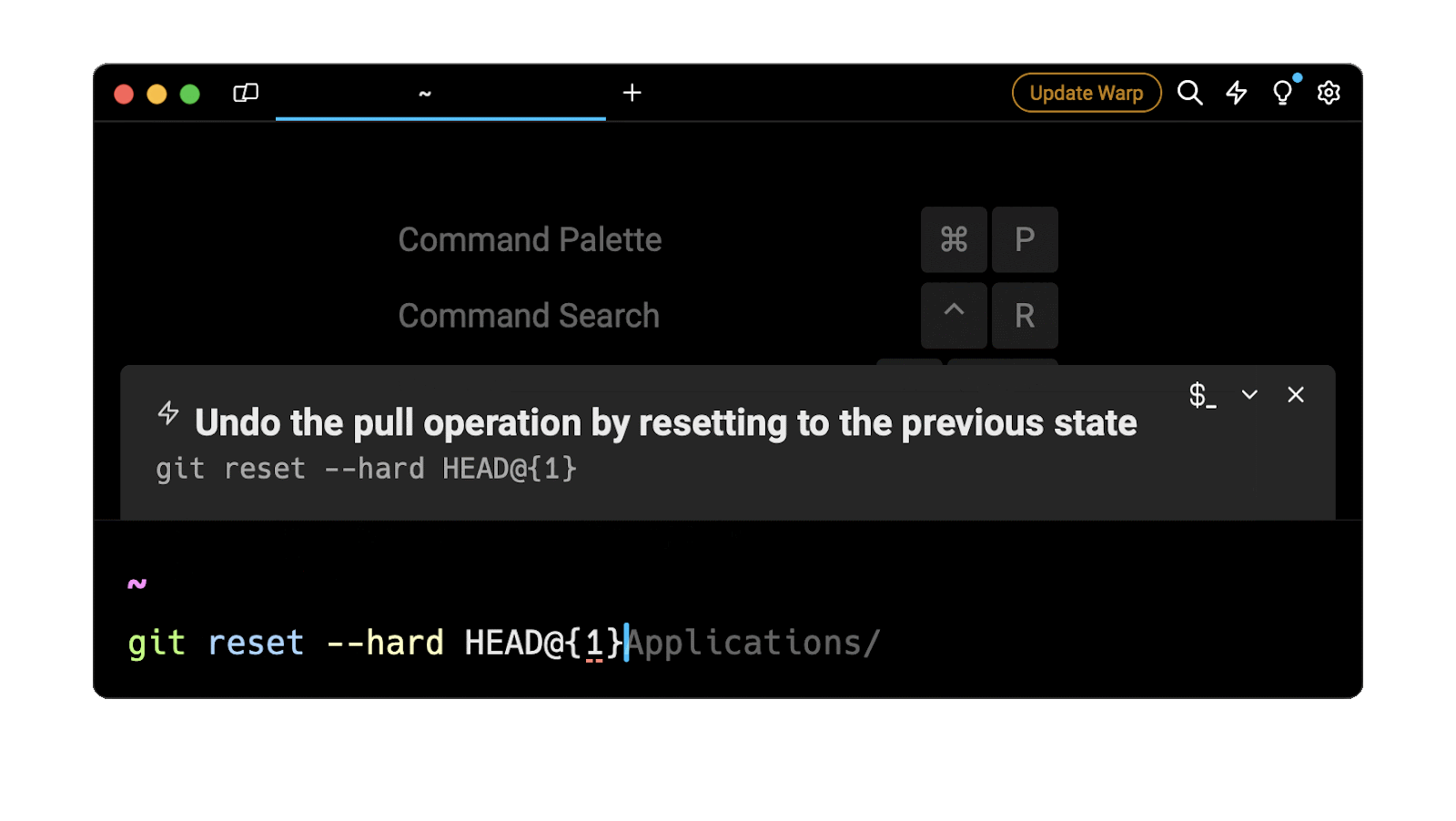
Entering git undo pull in the AI Command Suggestions will prompt a git command that can then be quickly inserted in your shell by doing CMD+ENTER .
Partially undoing a pull
Discarding a specific number of commits
To only discard a specific amount of commits introduced by a pull rather than all of them, you can use the git reset command as follows:
$ git reset --hard HEAD~N
Where:
- N represents the number of commits before the HEAD pointer.
For example, this command will discard the last 3 commits:
$ git reset --hard HEAD~3
Discarding commits based on a time reference
To discard all the commits prior to a relative time reference, you can use the git reset command as follows:
$ git reset --hard HEAD@{<time>}
Where:
- time is a dot-separated time reference.
For example, the following command will reset the branch to the state is was in 5 minutes ago:
$ git reset --hard HEAD@{5.minutes.ago}
Preserving local changes
To preserve the changes made to the working directory and the staging area before performing a reset, you can first temporarily stash them using the git stash command:
$ git stash
Then reset your branch using the git reset command:
$ git reset --hard <commit>
And finally, reapply these changes on top of the current branch using the git stash apply command:
$ git stash apply
Aborting an ongoing pull
It may sometimes happen that a pull creates multiple merge conflicts.
Rather than trying to manually fix these conflicts, you can abort the pull and reset your branch to its previous state using the following git merge command:
$ git merge --abort
Alternatively, to abort an in-flight pull, you can use the CTRL + C key combination.
Undoing a pull request on GitHub
Undoing an unmerged pull request
To undo or close a pull request that has not been merged:
- 1. Go to the pull request page and click on the button that says "Close pull request"
- 2. Go to the repository and select the "Branches".
- 3. Once you've located your branch, click on the "Delete branch" button next to your branch name.
Undoing a merged pull request
To undo a merged pull request and revert your changes:
- 1. Go to the pull request page and scroll to the bottom of the page
- 2. Click on the "Revert" button
You can learn more about pull requests by reviewing GitHub’s official documentation pages on closing a pull request and reverting a merged pull request.
Written by

Glory Kim
Software Engineer, Loom
Filed Under
Related Articles
Undo a Git Merge
How to rollback the changes introduced by a merge in Git by adding new opposite commits using git-revert and effectively removing commits using git-reset.

Prompt Show Git Branch In Prompt
Enhance your terminal with a custom Git prompt. Learn different ways to integrate this contextual info, from custom shell functions to Warp context chips and toolkits like Starship and P10K.

How To Remove Secrets From The Git History Remove Secrets From The Git History
Learn how to remove secrets from the Git history using the BFG and git-filter-repo command-line tools.

Adding a Submodule in Git
This post will show you how to simply add a submodule to a local repository, clone a repository with a submodule, and work within a repository that has a submodule.

Undo a git push
This post will show you had to simply undo a git push three different ways.

Undo Git Add
Learn how to effectively use 'git add' to stage files in Git for committing, and discover two powerful methods to undo accidental stagings.

Undo a Git Rebase
This post will show you how to undo a rebase using git reset, git rebase and git revert

Git Push Origin
A breakdown of git push origin

Create Folder In GitHub Repository
Learn how to create and push one or more empty directories in a Git repository using `.placeholder` and `README.md` files using both the CLI and the GitHub interface.

Git Push Tags
This post will show you how to push a single tag, multiple tags, all tags, and tags with commits.

Undoing Git Commits
Explore ways to undo a commit, including git reset, git checkout, and git revert with git while preserving commit history.

Delete Local Git Branch
Learn how to delete local branches from your git repository, including ones with unmerged changes, as well as local remote-tracking branches.

