The short answer
To remove a package with Homebrew, you can start by listing all the packages currently installed on your system and managed by Homebrew using the brew list command, then run the following brew uninstall command:
$ brew uninstall [package …]
Where:
- package … is the name of the package(s) you want to remove.
When executing this command, you will be prompted to confirm whether you want to remove that package, to which you can type y and press ENTER to confirm.
Alternatively, you can use the --formula flag to remove CLI packages only:
$ brew uninstall --formula [package …]
Or the --cask flag to remove GUI packages only:
$ brew uninstall --cask [package …]
Note that brew remove and brew rm are both aliases of the brew uninstall command and will have the exact same effect. If you want to learn more about the brew list command, you can read our post on how to list installed packages with Homebrew.
brew uninstall specific packages like node, python, etc.
If you’re using Warp as your terminal, you can easily retrieve commands to remove common packages such as mysql, postgres, go, or docker using the Warp AI Command Search feature:
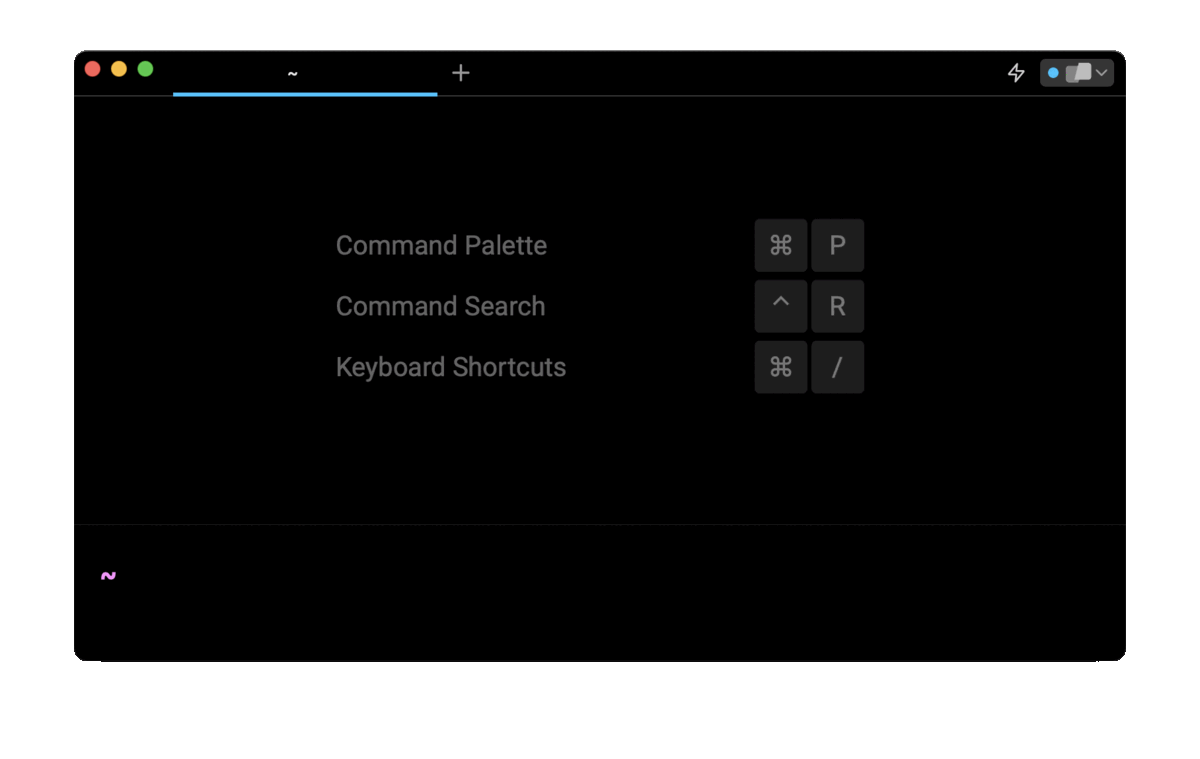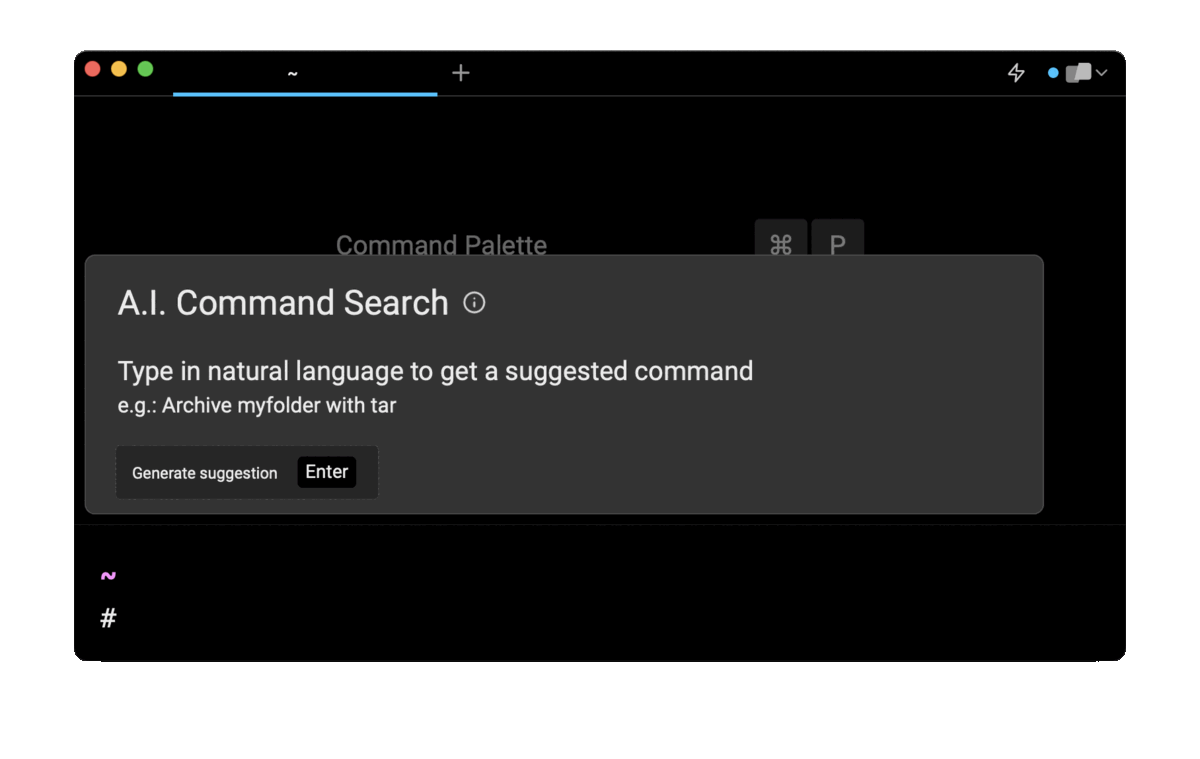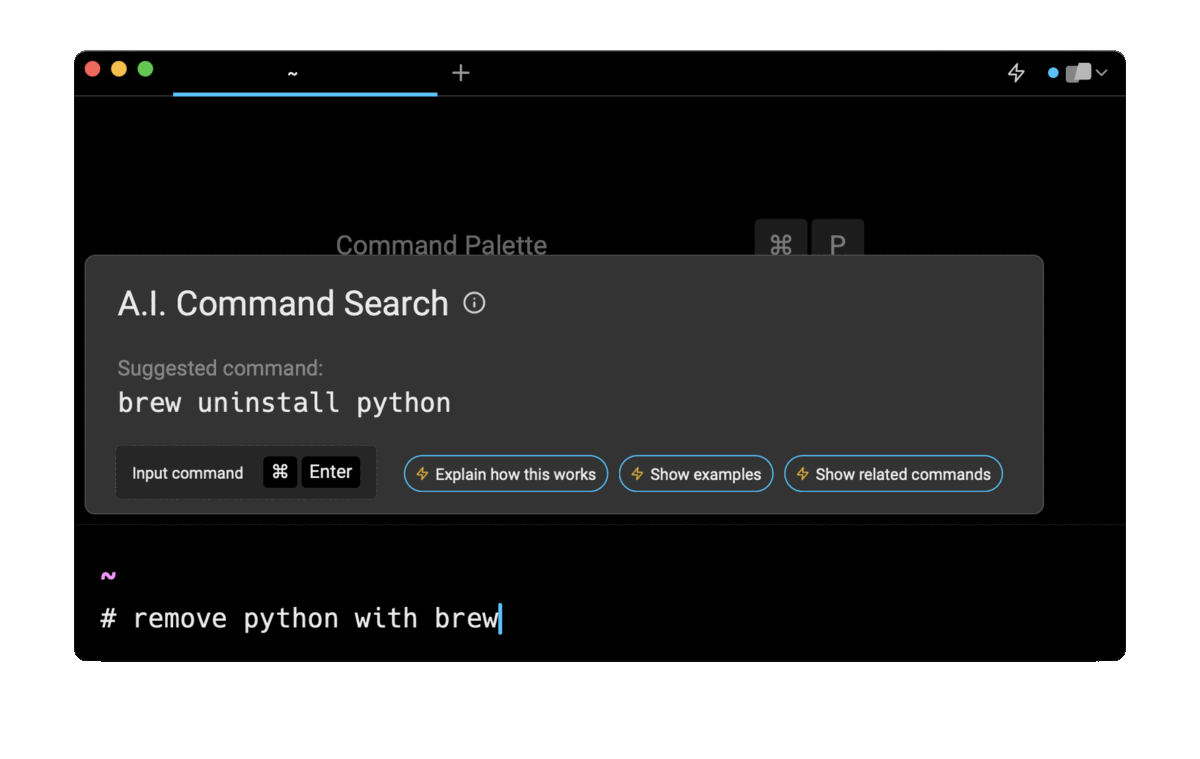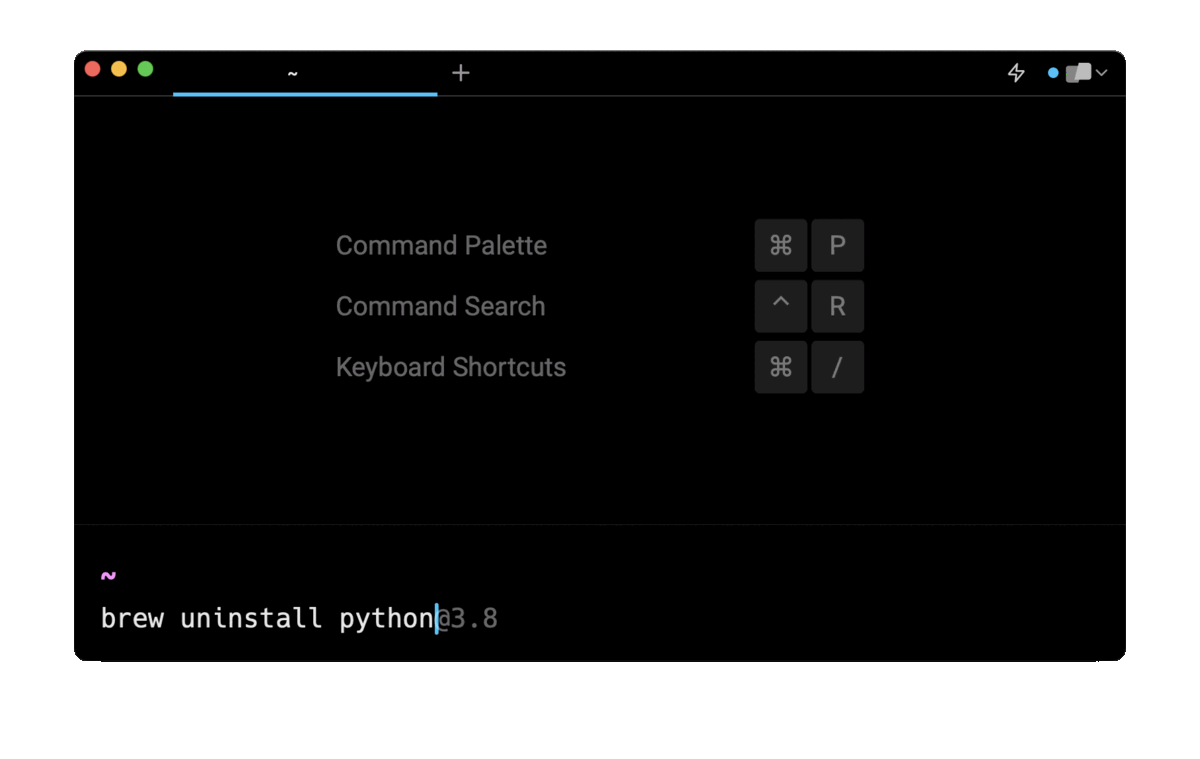
Entering remove python with brew in the AI Command Search prompt results in brew uninstall python, which you can then quickly insert into your shell by doing CMD+ENTER.
Remove unused dependencies
Packages often require one or more other packages (i.e. dependencies) to function properly. When installing a package with Homebrew, its dependencies are automatically installed with it. However, when removing a package, only the specified package is removed but not its dependencies, as they may also be used by other locally installed packages.
To free up disk space and remove the dependencies that are no longer required by any package, you can use the following command:
$ brew autoremove [--dry-run]
Note that to list the dependencies that would be removed without actually removing them, you can use the --dry-run flag.
Remove outdated versions and residual files
To free up even more space, you can remove stale lock files, symbolic links, and outdated package versions using the following command:
$ brew cleanup [--dry-run]
Note that, by default, this command will remove all downloads that are older than 120 days, which can be changed using the HOMEBREW_CLEANUP_MAX_AGE environment variable.
brew uninstall all packages at once
To remove all the packages previously installed with Homebrew at once, you can use a combination of the brew uninstall and the brew list commands as follows:
$ brew uninstall --force $(brew list)
Where:
- The --force flag is used to remove packages without prompting for confirmation.
- The $(brew list) expression will be replaced by the list of currently installed packages.
Note that this command will also remove any dependencies that were installed alongside the packages you are removing, which means that anything previously installed with Homebrew will be completely removed from your system.
Beware that you can’t brew uninstall packages that weren’t installed with Homebrew
The packages installed with Homebrew are added to the Homebrew database and are kept in separate directories from the ones used by the operating system.
When using the brew uninstall command, Homebrew checks its own database to locate the package you want to uninstall, and removes it along with any files associated with it.
If you try to remove a package that is not managed by Homebrew, it won't be able to find the package information in its database, and therefore won't be able to uninstall it.
To remove a package that was not installed with Homebrew, you'll need to use a different method, such as manual removal.
Written by

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Filed Under
