Importing Data into an Existing Table from a CSV file
Using the psql command-line tool to copy data from a CSV
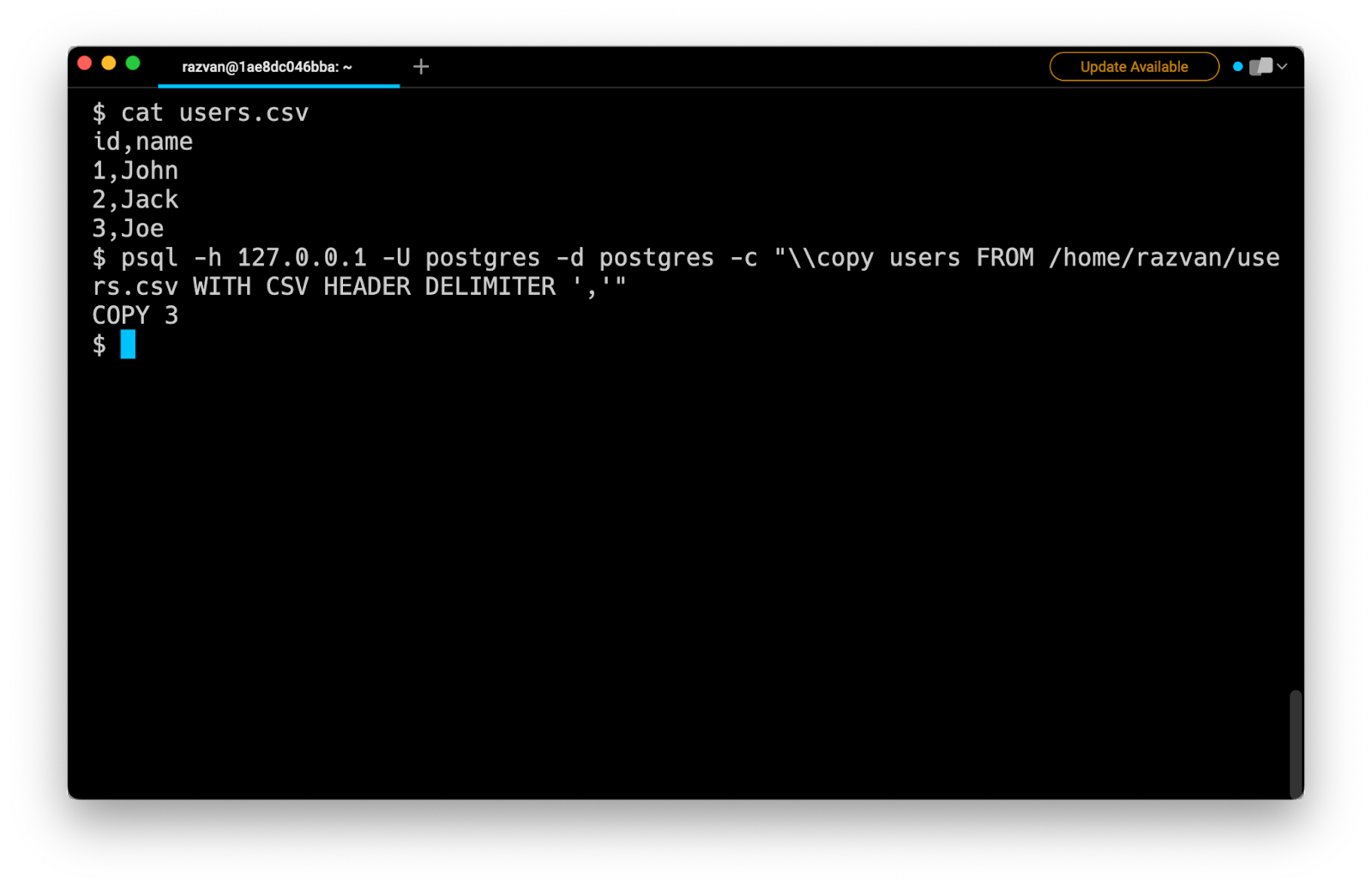
One option for importing a CSV file in PostgreSQL is to use the psql command-line tool combined with the -c option flag, which allows you to execute a given command string in line:
$ psql -h host_name -U user_name -d database_name -c
"\\copy table_name FROM 'file_path' WITH CSV HEADER DELIMITER ','"
Where:
- host_name is the address of the server the database runs on
- user_name is the name of the PostgreSQL user you want to execute the command as.
- database_name is the name of the database you want to connect to.
- table_name is the name of the table you want to import the data into.
- file_path is the path to the CSV file you want to load.
For example:
Note that if you want to import a file on a remote database server, you will need to upload the file on the target machine using the scp command first:
$ scp file.csv username@host:/path/to/directory/.
If you want to use this same approach starting from a SQL file instead of a CSV, you can read our post on how to import a SQL file in PostgreSQL.
Importing a CSV file using the Postgres interface
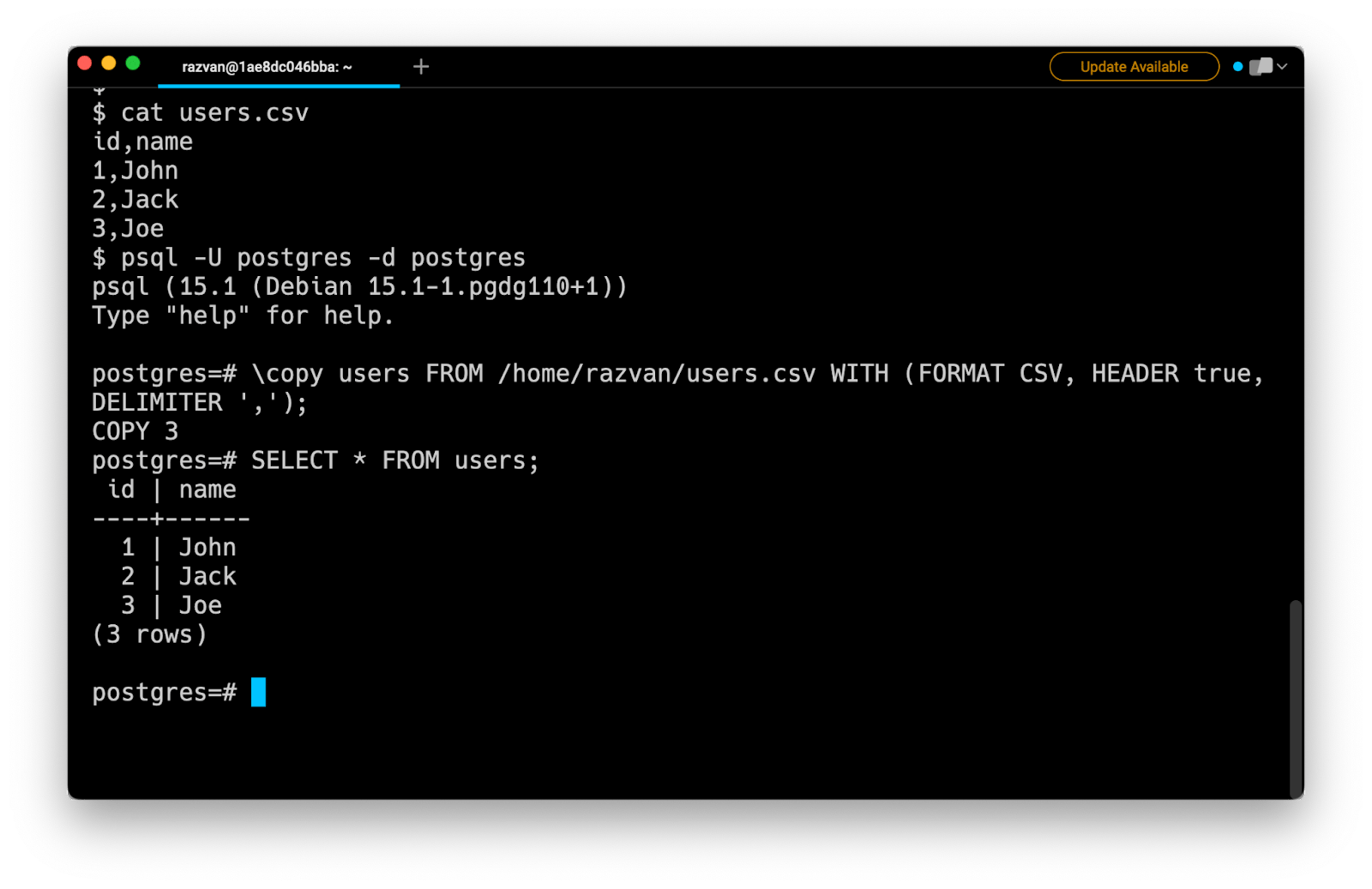
Another option for importing a CSV file in PostgreSQL is to connect to the database using the psql command:
$ psql -U user_name -d database_name
Then use the \copy meta-command:
postgres=# \copy table_name FROM 'file_path' WITH (FORMAT CSV,
HEADER true, DELIMITER ',')
Where:
- table_name is the name of the table you want to import the data into.
- file_path is the path to the CSV file you want to import.
For example:
Note that the WITH clause is optional, but it allows you to specify the format of the file (CSV), whether the first row contains header information (HEADER true), and the delimiter used in the file (DELIMITER ',').
Importing a CSV file using pgAdmin
It is also possible to import a CSV file in PostgreSQL using GUI tools such as pgAdmin, a popular open-source management tool for PostgreSQL. It allows you to import data into a table by going to the "Import/Export" option, selecting the file to import, specifying the format, delimiter, encoding, and the column names.
Common errors
Importing a CSV file might fail for various reasons. Here is a list of the most common errors you might encounter, and that you will need to resolve before the file can successfully be imported.
undefined_file: File not found
The undefined_file error indicates that the file you are trying to import doesn’t exist. Make sure that the file actually exists, and that the provided file path is valid.
syntax_error: Incorrect format or delimiter
The syntax_error indicates that the format of the CSV file or the delimiter used in the file does not match the specifications provided in the import command, which may result in the import failing or the data being corrupted.
datatype_mismatch: Incorrect data types
The datatype_mismatch error indicates that the data types of the columns in the CSV file do not match the data types of the columns in the target table.
invalid_parameter_value: Incorrect encoding
The invalid_parameter_value error could indicate that the CSV file is not encoded in UTF-8, which may result in the import failing or the data being corrupted.
null_value_not_allowed: Not null violation
The null_value_not_allowed error indicates that the CSV file contains null values and the import is trying to insert that into the table which has a not null constraint.
Creating a Postgres Table from a CSV file
Unfortunately, PostgreSQL doesn't provide a native way to create a new table from a CSV file. However, you can use the csvsql command-line tool instead, which can be downloaded using the pip command:
$ pip install csvkit psycopg2-binary
To create a table from a CSV file and import the data it contains all at once, you can run the following command:
$ csvsql --db "postgresql://user_name:user_password@host_name:port_number/database_name"
--insert --create-if-not-exists --db-schema "public" file.csv
Where:
- user_name is the database user you want to execute the command as.
- user_password is the password of the user you want to connect as.
- host_name is the name of the host the PostgreSQL server runs on.
- port_number is the port the PostgreSQL server listens to.
- database_name is the name of the database you want to create a table in.
Note that the csvsql command will automatically create the table based on the provided file name (e.g. users.csv will create the table users) and assume the column types based on the values contained in the CSV file.
Written by

Razvan Ludosanu
Founder, learnbackend.dev
Filed Under
Related Articles
How To Run A PSQL File With psql
How to execute multiple SQL statements stored in a file on a specified PostgreSQL database using the psql command. Also, how to handle and fix common errors.

How To Run a SQL File With psql
Importing a SQL file into a PostgreSQL database with psql

