Grep Multiple Strings

Spencer Evans
Senior Full-Stack Engineer, Silo
Updated: 7/16/2024
Published: 1/2/2023
The short answer
To match multiple strings or patterns at once with grep, you can either repeat the -e flag multiple times:
$ grep -e 'pattern' [-e 'pattern'] <file>
Or you can use the | separator:
$ grep 'pattern[\|pattern]' <file>
For example, both of these commands will search for the strings ERROR and WARNING in the logs.txt file and output the matching lines:
$ grep -e 'ERROR' -e 'WARNING' logs.txt
$ grep 'ERROR\|WARNING' logs.txt
Note that, by default, grep is case sensitive. You can learn more about that by reading our other article on how to make grep case insensitive.
Using extended regular expressions
To enable grep to use the extended regular expression syntax (like egrep would) , you can use the -E flag instead of the -e flag as follows:
$ grep -E 'pattern[|pattern]' <file>
Note that when using this flag, you don't need to escape the | pattern separator.
For example, considering the following logs file:
$ cat logs
2024-05-01 | ERROR 401 | Login failure
2024-05-06 | INFO 200 | Login success
2024-06-22 | INFO 201 | Account created
2024-06-01 | ERROR 404 | Page not found
2024-06-01 | WARN 429 | Request limit reached
2024-06-03 | ERROR 404 | Page not found
This command will output all the lines containing the string ERROR followed by a space character and 3-digit numbers:
$ grep -E 'ERROR [0-9]{3}' logs
2024-05-01 | ERROR 401 | Login failure
2024-06-01 | ERROR 404 | Page not found
2024-06-03 | ERROR 404 | Page not found
And this command will output all the lines starting with 2024-06, followed by two digit numbers, followed by the ERROR or WARN string:
$ grep -E '^2024-06-[0-9]{2} \| (ERROR|WARN)' logs
2024-06-01 | ERROR 404 | Page not found
2024-06-01 | WARN 429 | Request limit reached
2024-06-03 | ERROR 404 | Page not found
Easily retrieve this command using Warp’s AI Command Suggestions
If you’re using Warp as your terminal, you can easily retrieve this command using the Warp AI Command Suggestions feature:
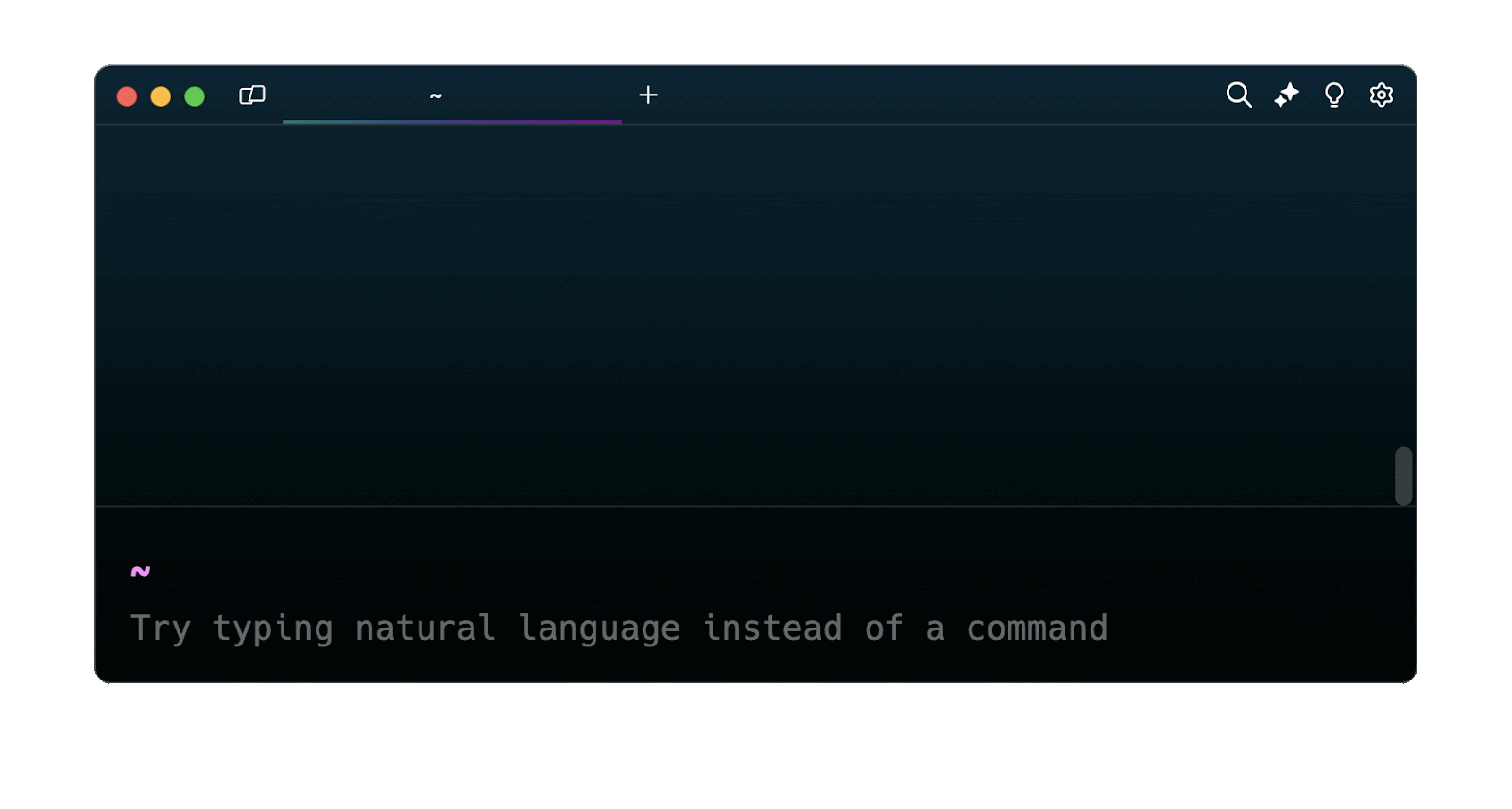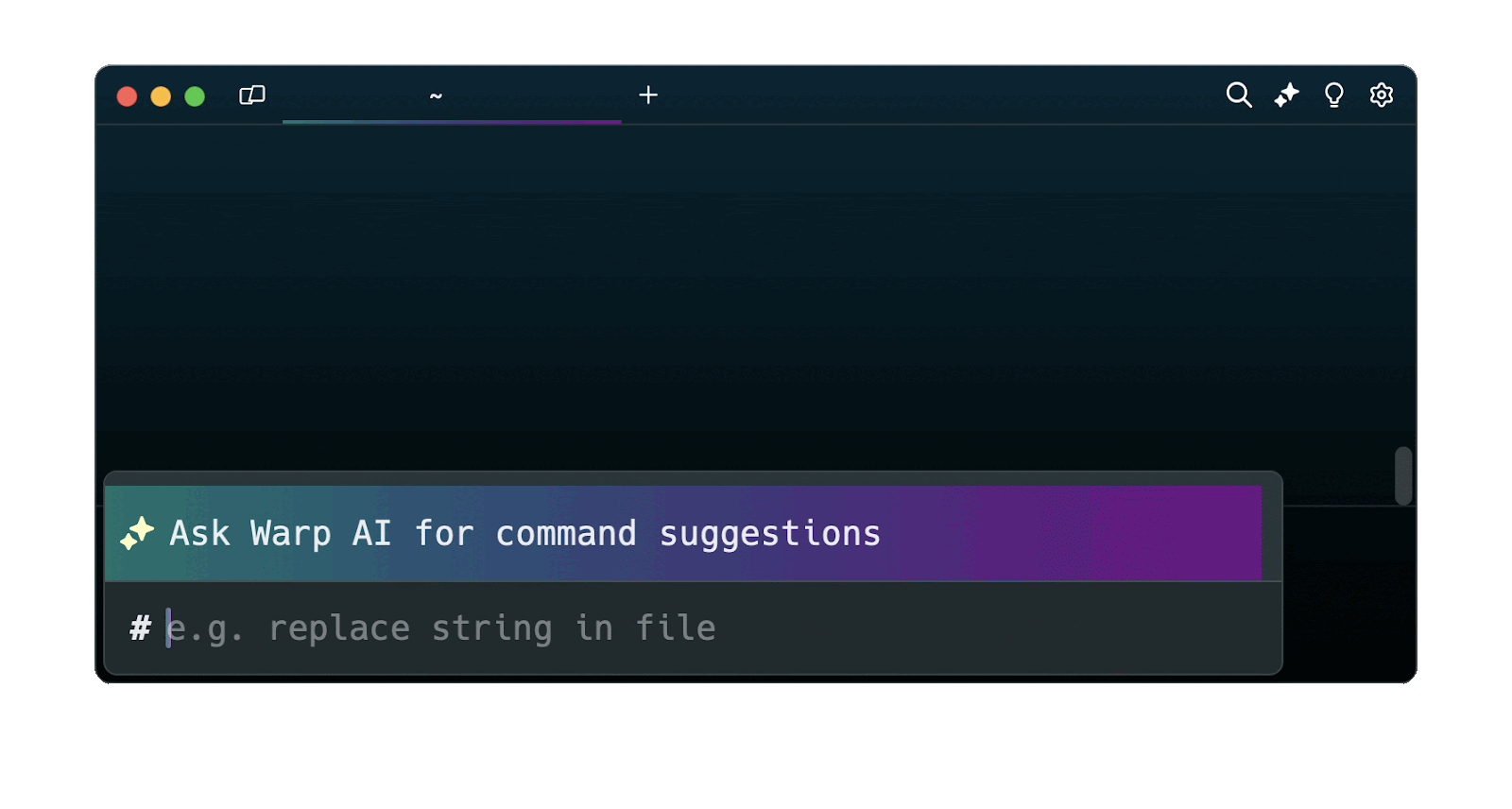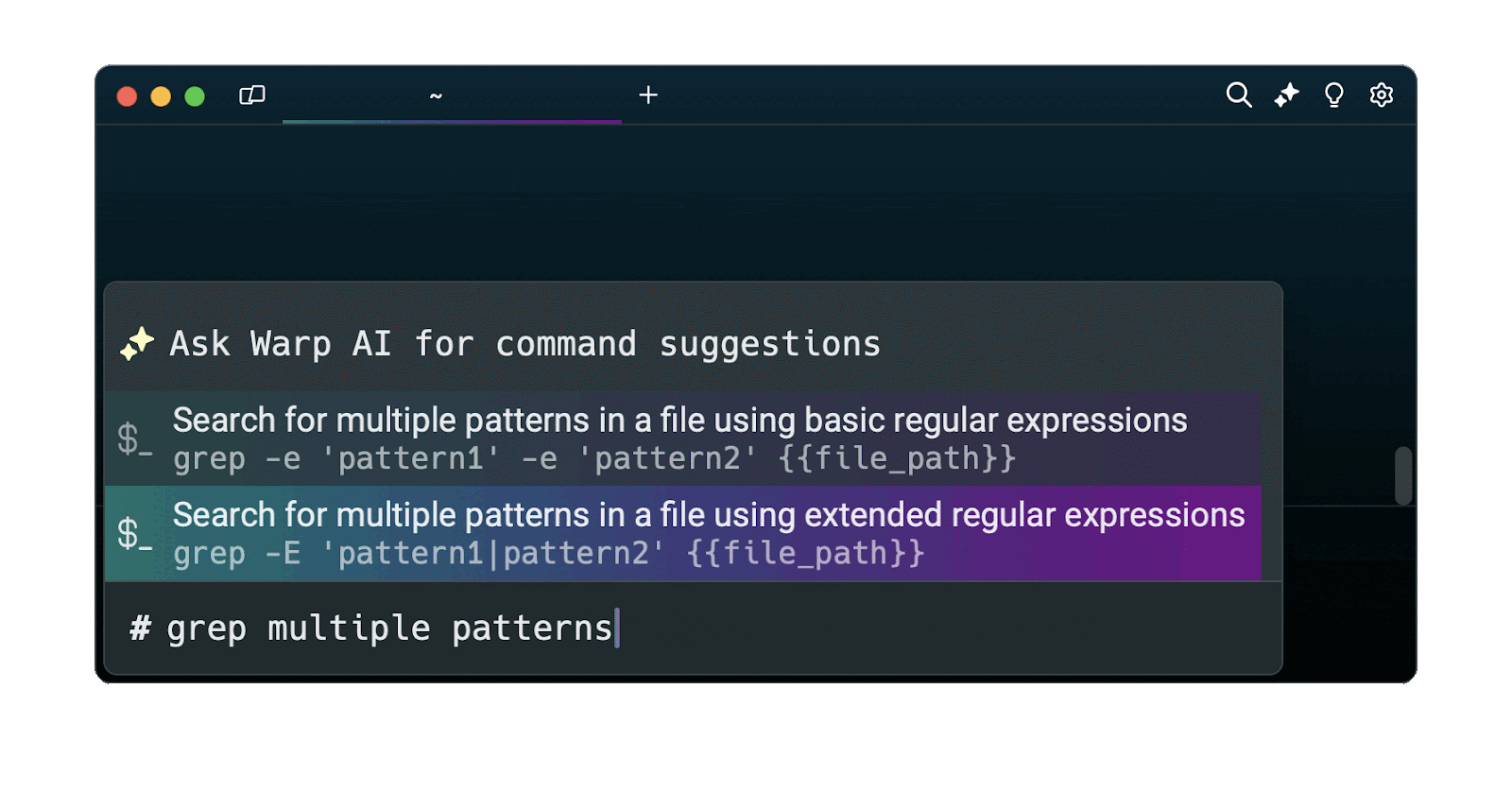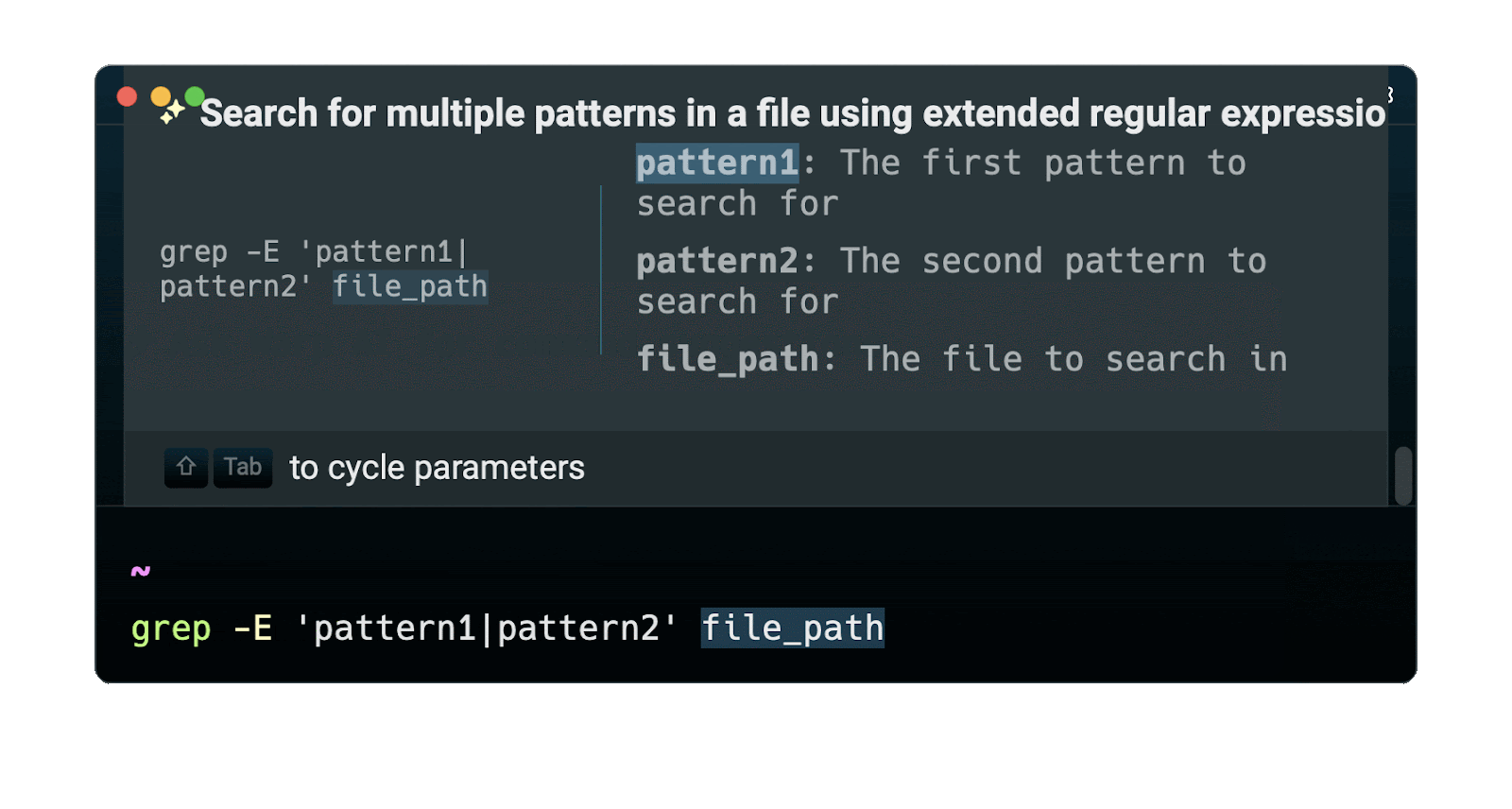
Entering grep multiple patterns in the AI Command Suggestions will prompt a grep command that can then be quickly inserted in your shell by doing CMD+ENTER .
Searching for patterns stored in a text file
To search for a list of patterns stored in the file, you can use the -f flag as follows:
$ grep -f <patterns> <file>
For example, this command will load a list of patterns contained in the patterns.txt file and match them against the lines of the logs.txt file:
$ grep -f patterns.txt logs.txt
Extracting text before, after, and between patterns
Extracting text before a pattern
To extract the text before a specified pattern, you can use the grep command with the -oP flags and the ?=expression as follows:
$ grep -oP 'value(?=pattern)' <file>
For example, considering the following logs file:
$ cat logs
2024-06-18 12:34:56 INFO UserID=12345 Action=Login
2024-06-18 12:35:00 ERROR UserID=67890 Action=Timeout
2024-06-18 12:35:05 WARN UserID=54321 Action=Retry
This command will extract the text before the ERROR or WARN strings:
$ grep -oP '.*(?= ERROR|WARN)' logs
2024-06-18 12:35:00
2024-06-18 12:35:05
Extracting text after a pattern
On the other hand, to extract the text after a specified pattern, you can use the ?<= expression instead:
$ grep -oP '(?<=pattern)value' <file>
For example, considering the following logs file:
$ cat logs
2024-06-18 12:34:56 INFO UserID=12345 Action=Login
2024-06-18 12:35:00 ERROR UserID=67890 Action=Timeout
2024-06-18 12:35:05 WARN UserID=54321 Action=Retry
This command will extract the text after the Action= string:
$ grep -oP '(?<=Action=).*' logs
Login
Timeout
Retry
Extracting text between two patterns
To extract the text between two patterns, you can combine the two previous expressions as follows:
$ grep -oP '(?<=pattern)value(?=pattern)' <file>
For example, considering the following logs file:
$ cat logs
2024-06-18 12:34:56 INFO UserID=12345 Action=Login
2024-06-18 12:35:00 ERROR UserID=67890 Action=Timeout
2024-06-18 12:35:05 WARN UserID=54321 Action=Retry
This command will extract the text located between the UserID= and Action strings:
$ grep -oP '(?<=UserID=).*(?= Action)' logs
12345
67890
54321
Written by

Spencer Evans
Senior Full-Stack Engineer, Silo
Filed Under
Related Articles
How To Filter The Output of Commands
Learn how to filter and format the output of commands and logs using the grep, awk, uniq, head, and tail commands.

How to Make Grep Case Insensitive
By default, grep is case sensitive

Grep Across Multiple Lines
Guide on several cases of using grep across multiple lines

Grep In a Directory
Learn how to use grep to search for words and phrases within a directory and all its subdirectories, a specific directory, all files, and other variations.

Exclude With Grep
Excluding unwanted key terms or directories when using grep

Grep Count
Efficiently count lines or occurrences in a file.

